Requirements Traceability Matrix: A Complete Guide for Project Success
Managing project requirements effectively can make the difference between project success and failure.
A Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) serves as the backbone of requirement management, helping teams track and validate project deliverables from start to finish.
Key Highlights
- Clear tracking of project requirements
- Efficient validation of project deliverables
- Smart management of requirement changes
- Seamless integration with testing phases
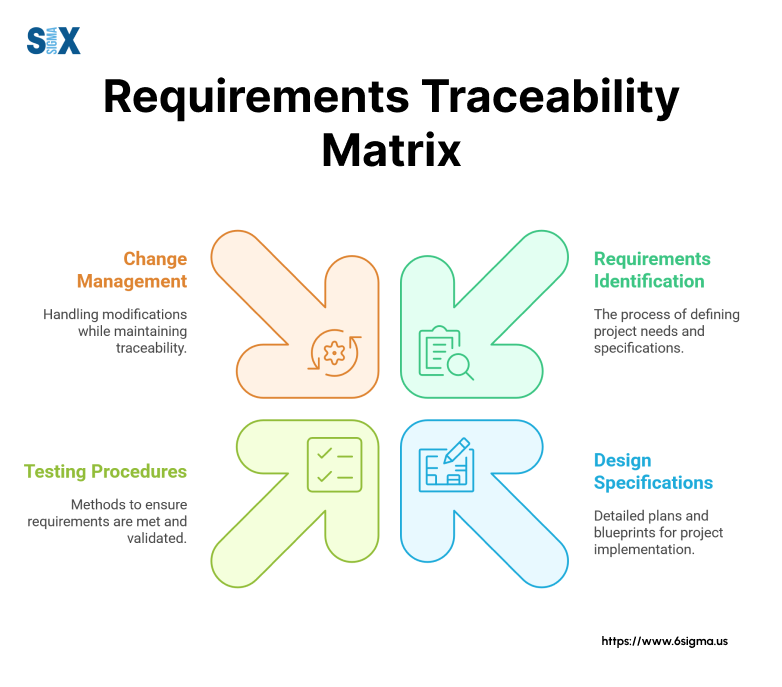
What Is a Requirements Traceability Matrix?
A Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) functions as a structured document that maps and monitors project requirements from their initial definition through to final delivery.
This essential project management tool creates clear links between business needs, technical specifications, and testing outcomes.
The matrix serves multiple critical functions in project execution. It verifies that each requirement adds value to the project goals and helps teams spot missing or unnecessary requirements early.
Project managers use RTM to maintain control over scope changes while ensuring every feature or deliverable ties back to specific business objectives.
Key Functions of Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) in Project Delivery
RTM plays a vital role in requirement validation by establishing clear connections between different project elements.
When stakeholders request changes, the matrix shows how these modifications might affect other project components. This visibility helps teams make informed decisions about resource allocation and priority setting.
For testing teams, RTM ensures complete coverage of all requirements through dedicated test cases.
Quality assurance professionals rely on this documentation to confirm that every requirement undergoes proper testing and validation.
The matrix also supports regulatory compliance by maintaining detailed records of requirement implementation and verification.
Business Impact of RTM Implementation
Organizations that properly implement RTM often see improved project outcomes. The matrix reduces rework by catching requirement gaps early and ensures teams build features that align with business goals.
It also streamlines communication between stakeholders by providing a single source of truth for project requirements.
In agile environments, RTM adapts to support iterative development while maintaining traceability across sprints.
Modern project management tools often include RTM capabilities, making it easier for teams to maintain this crucial documentation throughout the project lifecycle.
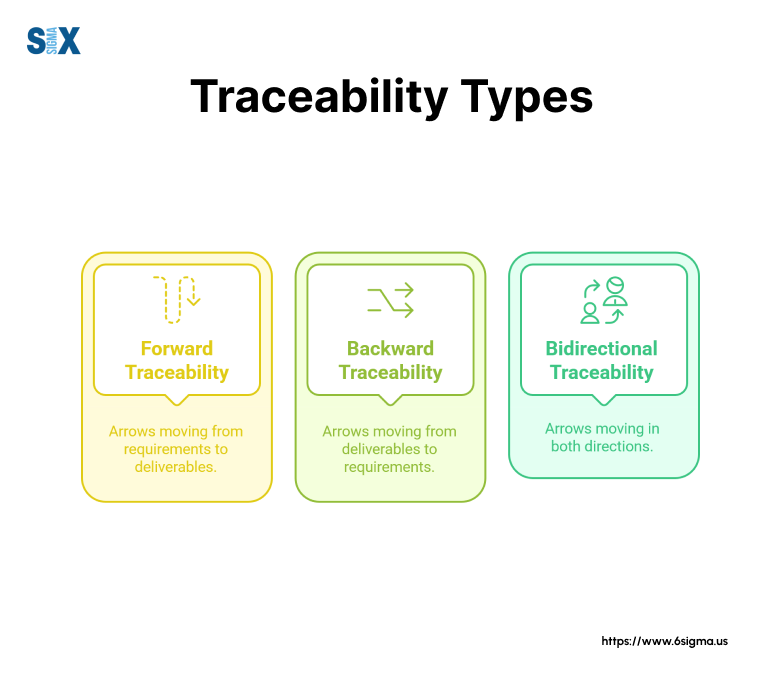
The Three Types of Requirements Traceability Matrices
Project teams select specific types of requirements traceability matrices based on their project needs and objectives.
Each type offers distinct advantages for tracking and managing requirements throughout the project lifecycle.
Forward Traceability
Forward traceability maps requirements to their future implementation stages and test cases. This approach helps teams plan development work and ensure proper test coverage.
Project managers use forward traceability to schedule resources and track progress toward deliverables.
When stakeholders request new features, forward traceability shows how these additions will impact the project timeline and resources.
Testing teams rely on this method to create test cases that verify each requirement meets its intended purpose.
Backward Traceability
Backward traceability links project deliverables back to their original requirements and business objectives.
This method proves particularly valuable when teams need to validate that every feature serves a specific business need.
Quality assurance teams use backward traceability to ensure no unnecessary features slip into the final product.
During audits or compliance reviews, backward traceability provides clear documentation of why specific features were implemented.
It helps prevent scope creep by identifying elements that don’t trace back to approved requirements.
Bidirectional Traceability
Bidirectional traceability combines both forward and backward approaches, offering the most complete requirements tracking solution.
This method creates a full circle of accountability from initial business needs through implementation and back again.
Teams working on complex projects often choose bidirectional traceability to maintain tight control over requirement changes and their impacts.
This approach proves especially valuable in regulated industries where teams must demonstrate full requirement coverage and justification.
Each type of requirements traceability matrix serves specific project needs, and many organizations use different types at various project stages.
The choice depends on project complexity, regulatory requirements, and team preferences.
Unlock Advanced Requirement Traceability Techniques
Key Components of a Requirements Traceability Matrix
A well-structured requirements traceability matrix contains several essential components that work together to track project requirements effectively.
Understanding these elements helps teams build and maintain an RTM that serves their project needs.
Primary Matrix Elements
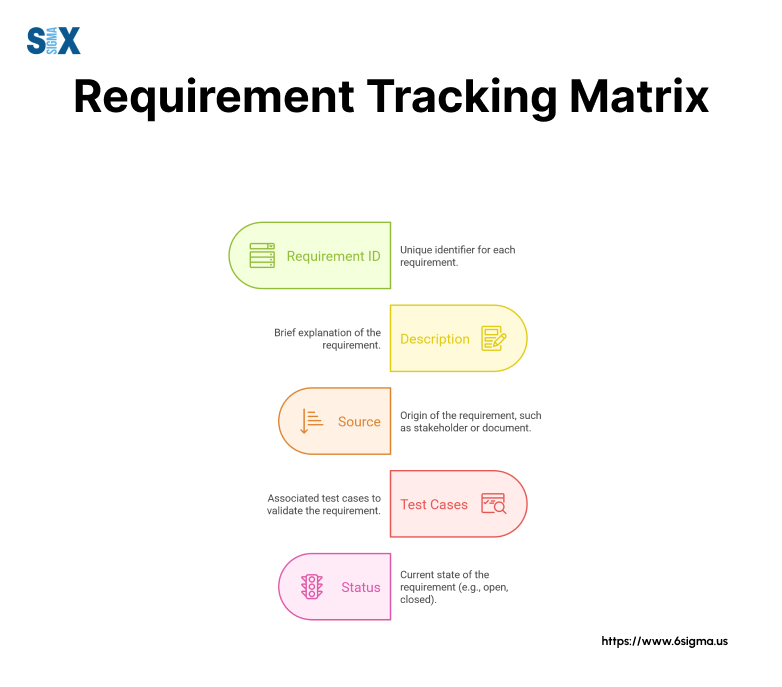
The foundation of every RTM starts with a unique requirement identifier. This ID number or code ensures each requirement can be tracked individually throughout the project lifecycle.
Next to the ID, teams include a clear, specific description of the requirement that leaves no room for misinterpretation.
Source information documents where each requirement originated, whether from stakeholder interviews, business documents, or regulatory requirements.
Priority levels help teams focus on the most critical requirements first, while status indicators show the current stage of implementation.
Testing and Verification Components
Test case references link requirements to specific testing procedures. This connection ensures every requirement undergoes proper verification.
Teams also include test results and validation status to maintain a clear record of requirement fulfillment.
Dependencies between requirements appear in dedicated columns, showing how changes to one requirement might affect others.
This visibility helps project managers assess the impact of proposed changes and maintain project stability.
Documentation Elements of Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
Version control information tracks requirement changes over time. Teams record modification dates, change authors, and reasons for updates.
These details create an audit trail that proves valuable during project reviews and compliance checks.
The matrix also includes fields for stakeholder sign-off and implementation notes. These components help teams maintain accountability and document important decisions throughout the project lifecycle.
Develop advanced skills in requirement measurement and validation
Creating an Effective Requirements Traceability Matrix
Building a requirements traceability matrix requires careful planning and systematic execution.
The process starts with gathering project requirements and ends with a dynamic tool that guides project success.
Initial Setup and Planning
First, gather all project documentation, including business requirements, technical specifications, and stakeholder input. Review these materials to identify and list every requirement.
Each requirement needs a unique identifier and clear description that project team members can easily understand.
Next, establish the matrix structure based on project needs. While spreadsheets work for smaller projects, larger initiatives might need specialized RTM software.
The chosen format should allow easy updates and accessibility for all team members.
Building the Matrix Structure
Start populating the requirements traceability matrix by entering basic requirement information. Create columns for requirement IDs, descriptions, and sources.
Add priority levels based on business impact and implementation complexity. Include fields for test cases and validation criteria that will verify each requirement.
Set up dependency tracking to show relationships between requirements. This step proves crucial when assessing change impacts later in the project.
Add columns for status tracking and implementation notes to monitor progress throughout the development cycle.
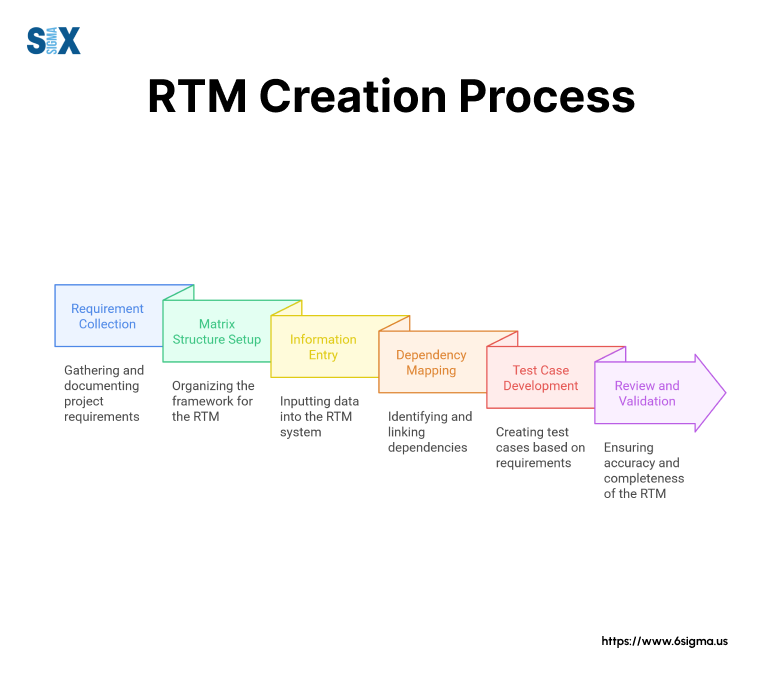
Review and Validation Process
Once the initial matrix is complete, conduct a thorough review with stakeholders. Verify that all requirements align with project objectives and business goals.
Check that test cases adequately cover each requirement and that dependency mappings are accurate.
Establish a change control process for updating the matrix as requirements evolve. Define roles and responsibilities for maintaining the RTM throughout the project lifecycle. Regular reviews help ensure the matrix remains current and valuable for project tracking.
The final step involves training team members on using and updating the matrix.
Clear guidelines for matrix maintenance help preserve its value as a project management tool. Regular audits ensure the RTM continues to serve its purpose effectively.
RTM in Different Project Management Methodologies
The requirements traceability matrix adapts to various project management approaches, serving unique purposes in each methodology while maintaining its core tracking function.
Traditional Project Management Implementation
In waterfall projects, the RTM follows a linear progression through project phases. Teams create detailed requirements documentation upfront and use the matrix to track progress through development, testing, and deployment.
This structured approach works well for projects with stable requirements and clear end goals.
Project managers in traditional environments often maintain extensive RTMs that capture every requirement detail.
The matrix serves as a key document for phase-gate reviews and helps ensure nothing slips through the cracks during handoffs between project stages.
Agile Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) Adaptation
Agile teams modify the requirements traceability matrix to support iterative development. Rather than creating a massive upfront document, they maintain a living RTM that evolves with each sprint.
User stories replace traditional requirements, while acceptance criteria serve as validation points.
The matrix in agile projects often links user stories to epics and features, helping teams maintain alignment with product vision.
Sprint planning sessions use RTM data to prioritize backlog items and ensure proper coverage of business needs.
Six Sigma Integration
Six Sigma projects leverage the RTM to support data-driven quality improvements.
The matrix helps teams track critical-to-quality characteristics and ensures each requirement ties directly to measurable performance indicators.
Teams following DMAIC methodology use the matrix to verify that improvements address root causes and meet defined targets.
The RTM supports both process improvement projects and quality control initiatives by maintaining clear links between problems and solutions.
This flexibility across methodologies makes the requirements traceability matrix a valuable tool regardless of project approach.
Teams can adapt the structure and usage patterns while maintaining the essential function of requirement tracking and validation.
Tools and Software for RTM Management
Modern requirements traceability matrix tools offer sophisticated features that streamline requirement management and enhance team collaboration.
These solutions range from basic spreadsheet templates to advanced requirement management platforms.
Popular Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) Software Solutions
Modern Requirements for DevOps integrates seamlessly with Azure DevOps and offers real-time requirement tracking capabilities.
The platform includes automated impact analysis and customizable reporting features that help teams maintain accurate requirement documentation.
Jira‘s requirement management plugins provide robust RTM functionality within the familiar Agile project management environment. Teams can link user stories to requirements and track progress through customizable dashboards.
ReqTest focuses on simplifying requirement management through an intuitive interface. Its built-in traceability features help teams maintain clear connections between requirements, test cases, and results.
Choosing the Right Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) Tool
Project size and complexity guide tool selection. Small projects might work well with spreadsheet-based solutions, while enterprise-level initiatives need dedicated requirement management platforms.
Integration capabilities with existing project management tools often determine the final choice.
Security features matter, especially for teams handling sensitive data. Look for tools that offer role-based access control and audit trails. Cloud-based solutions should provide robust data encryption and backup options.
Cost considerations should include both initial setup and ongoing maintenance. Some tools charge per user, while others offer project-based pricing. Factor in training requirements and support costs when evaluating different options.
The right tool should grow with your team’s needs and adapt to changing project management practices. Regular vendor updates and responsive technical support indicate a sustainable long-term solution.
Requirements Traceability Matrix in Six Sigma Projects
Six Sigma projects utilize the requirements traceability matrix to maintain strict quality controls and ensure measurable improvements.
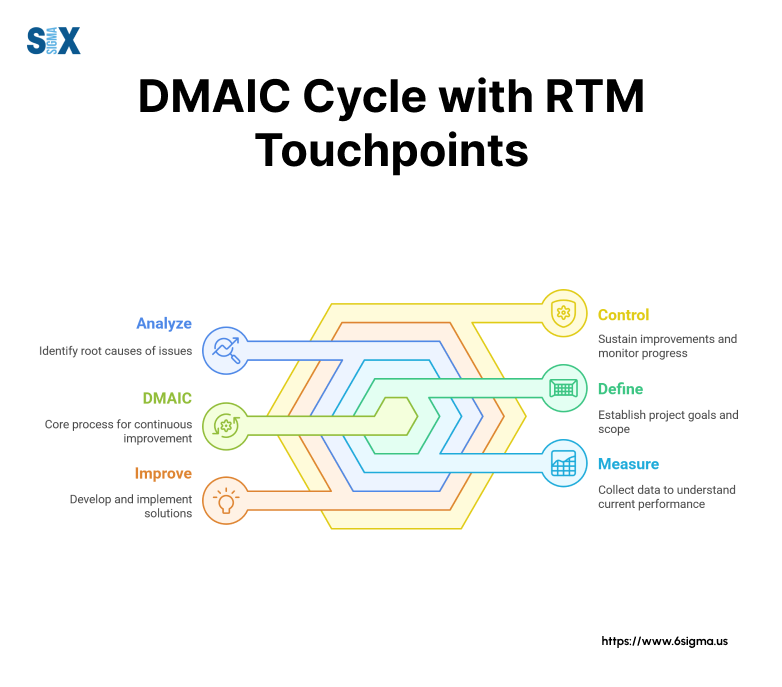
The matrix plays a crucial role in each phase of the DMAIC methodology, supporting data-driven decision-making and process optimization.
RTM Integration with DMAIC Phases
During the Define phase, the matrix captures voice of customer requirements and translates them into measurable specifications. These requirements form the foundation for improvement targets and help teams focus on critical quality factors.
The Measure and Analyze phases use RTM data to track performance metrics and identify root causes. Teams link specific requirements to measurement systems and analytical tools, ensuring all improvement efforts align with project goals.
In the Improve and Control phases, the matrix validates that solutions meet original requirements and maintains long-term process stability. Regular monitoring through RTM helps prevent quality regression and supports continuous improvement efforts.
Quality Management Applications of Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
Quality teams rely on RTM to document compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements. The matrix provides clear evidence that quality specifications are met throughout the improvement process.
Process owners use RTM data to maintain control plans and standard operating procedures.
This documentation ensures sustained performance and helps train new team members on quality requirements.
Create and Implement Powerful Requirements Traceability Matrices
Master Requirements Traceability in Six Sigma with Green Belt Certification

The Road Ahead
The requirements traceability matrix stands as an essential tool for modern project management.
It bridges the gap between business needs and project delivery while supporting various methodologies and quality frameworks.
As projects grow more complex, RTM continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies and adapting to changing business needs.
Teams that master RTM implementation gain a powerful ally in delivering successful projects that meet stakeholder expectations and quality standards.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







