Quality Risk Management (QRM): A Comprehensive Guide for Excellence
Proactively detecting, gauging, and lessening risks endangering quality, safety, and obedience is crucial for organizations. Quality risk management presents a systematic, risk-focused framework structuring evaluations and controls for manufacturing, design, and business undertakings linked concerns.
QRM bases itself on scientifically-led, customer-protecting assessment logic steered in careful balance with formalized efforts matching identified priorities.
This evidence-guided calibration empowers focused coordination, and attentiveness where importance demands while optimizing coordinated strides.
For continual progress-pursuers committed to performance and relations uplift through shared challenges overcome, quality risk management emerges as a prudent partner.
Key Highlights
- Definition and importance of quality risk management in ensuring product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance
- QRM principles: science and risk-based decision-making, level of effort proportional to risk
- The QRM process: risk assessment (identification, analysis, evaluation), risk control (reduction, acceptance), risk review, and communication
- Essential QRM tools and techniques: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), Hazard Operability Analysis (HAZOP)
- Role of QRM in the pharmaceutical industry and regulatory requirements (GMP, GDP)
- Benefits of implementing QRM: cost reduction, improved operational efficiency, strengthened customer confidence, and brand reputation
- Challenges and considerations: cultural change, resource allocation, integration with existing systems, continuous improvement
- Importance of building a robust QRM culture through cross-functional collaboration, employee training, and leveraging technology
What is Quality Risk Management (QRM)?
Quality Risk Management (QRM) is a systematic, risk-based approach that provides a structured framework for evaluating and controlling risks associated with manufacturing processes, product design, and business operations.
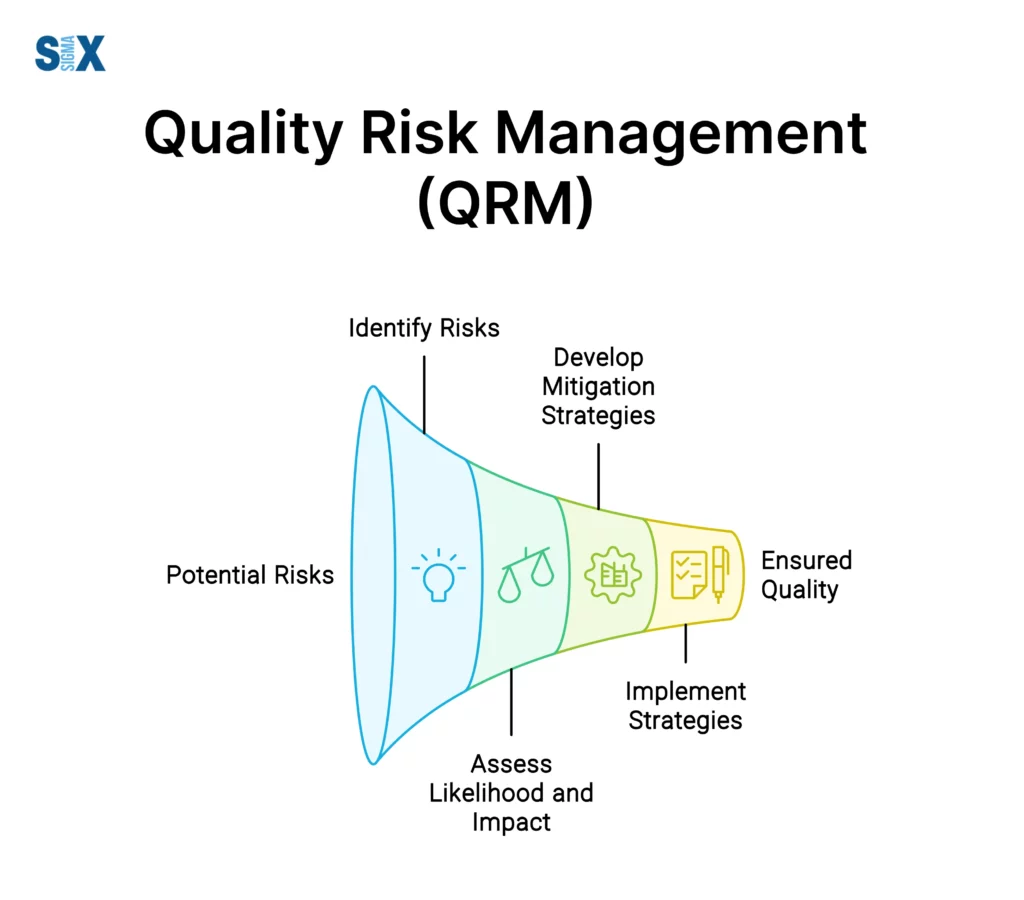
Quality risk management is the process of assessing, controlling, communicating, and reviewing risks related to product quality and patient safety.
This proactive approach enables organizations to identify potential hazards, analyze their likelihood and severity, and implement effective measures to mitigate or eliminate those risks before they manifest into larger issues.
The value of QRM lies in its ability to ensure consistent product quality, protect patient safety, and support regulatory compliance. Six Sigma certification offers structured training in risk management and process improvement for those looking to build expertise in these areas.
In industries such as pharmaceuticals and medical devices, where product quality directly impacts consumer health, Quality Risk Management (QRM) is an absolute necessity.
Regulatory bodies, including the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH), have established guidelines and expectations for implementing robust QRM practices.
Two fundamental principles govern the effective implementation of Quality Risk Management (QRM). First, quality risk evaluation must be based on scientific knowledge, data, and research, ensuring that decisions are grounded in factual evidence rather than subjective assumptions.
Second, the level of effort, formality, and documentation involved in the QRM process should be proportional to the identified risks.
Explore how QRM fits into the quality improvement framework. Lean Six Sigma Overview course introduces you to a comprehensive toolkit for managing quality and risk.
This risk-based approach allows organizations to allocate resources efficiently, focusing their efforts on the most critical areas while maintaining a balanced approach for lower-risk activities.
The Quality Risk Management (QRM) Process
The Quality Risk Management (QRM) process is a structured, systematic approach that involves several key steps, each designed to identify, analyze, and mitigate potential risks effectively.
Risk identification
The first step in the risk assessment process is to identify potential failure modes or hazards that could compromise product quality or patient safety.
This involves a thorough analysis of the manufacturing process, product design, and related systems, leveraging techniques such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP).
Effective application of these tools often requires root cause analysis training to systematically identify underlying issues.
Risk analysis
Once potential risks have been identified, the next step is to analyze their likelihood of occurrence and the severity of their potential consequences.
This analysis involves assessing factors such as the frequency of occurrence, the detectability of the risk, and the potential impact on product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance.
Risk evaluation with Quality Risk Management (QRM)
Based on the risk analysis, organizations can evaluate and prioritize risks using various tools and techniques, such as risk matrices and quantification methods.
Risk matrices provide a visual representation of risks, allowing organizations to categorize them based on their likelihood and severity.
Quantification methods assign numerical values to risks, enabling a more objective and data-driven approach to risk evaluation.
Risk reduction
After evaluating the risks, organizations can implement risk reduction strategies, which involve taking preventive and corrective actions to minimize the likelihood of occurrence and mitigate the potential impact of identified risks.
These actions may include process improvements, enhanced controls, additional training, or design modifications.
Risk acceptance with Quality Risk Management (QRM)
In some cases, organizations may decide to accept certain risks, particularly when the cost or effort required to mitigate them outweighs the potential benefits.
This decision should be based on clearly defined acceptance criteria and supported by a thorough cost-benefit analysis.
Continuous monitoring and improvement
QRM is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement.
Organizations should regularly review and reassess their risk management strategies, taking into account new data, changes in processes or products, and evolving regulatory requirements.
Stakeholder communication and documentation
Effective communication and documentation are essential components of the QRM process.
Organizations should maintain transparent communication with all stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, and document their risk management activities, decisions, and rationales to ensure traceability and accountability.
Quality Risk Management (QRM) Tools and Techniques
To support the implementation of the QRM process, organizations can leverage various tools and techniques that have proven effective in identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks:
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
FMEA is a systematic method for identifying potential failure modes, their causes, and their effects on product quality or process performance.
By analyzing the Risk Priority Number (RPN), which considers the likelihood, severity, and detectability of failures, organizations can prioritize and address the most critical risks.
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)
HACCP is a preventive approach widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries to identify and control hazards that could compromise product safety.
It involves identifying critical control points in the manufacturing process and implementing effective control measures to mitigate identified hazards.
Hazard Operability Analysis (HAZOP)
HAZOP is a structured technique used to identify potential hazards and operability issues in manufacturing processes or systems.
It involves a systematic examination of deviations from normal operating conditions and their potential consequences, enabling organizations to implement appropriate safeguards and controls.
Master one of the most powerful QRM tools. Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) course offers in-depth training on this essential risk assessment technique.
Quality Risk Management (QRM) in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry is subject to stringent regulatory requirements and global guidelines that emphasize the importance of quality risk management.
Two key regulatory frameworks that govern QRM practices in this industry are:
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
GMP regulations, established by regulatory bodies like the FDA, provide guidelines for ensuring that pharmaceutical products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards.
QRM is an integral part of GMP compliance, enabling manufacturers to identify and mitigate risks throughout the product lifecycle, from raw material sourcing to distribution.
Good Distribution Practices (GDP)
GDP guidelines focus on maintaining the quality and integrity of medicinal products during the distribution phase.
Quality Risk Management (QRM) plays a crucial role in ensuring that temperature controls, equipment calibration, and supply chain integrity are effectively managed to mitigate risks associated with product distribution.
Examples of QRM applications in the pharmaceutical industry include temperature and environment control, equipment qualification and validation, and supply chain integrity measures.
By implementing robust Quality Risk Management practices, pharmaceutical companies can demonstrate their commitment to product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance.
Benefits of Quality Risk Management (QRM) Implementation
Implementing a comprehensive quality risk management program can yield numerous benefits for organizations across various industries:
Cost reduction
By proactively identifying and mitigating risks, organizations can prevent product failures, minimize customer complaints, and reduce the associated costs of recalls, rework, and customer dissatisfaction.
Improved Operational Efficiency with Quality Risk Management (QRM)
QRM enables organizations to streamline their processes, eliminate waste, with Lean Fundamentals and optimize resource allocation, leading to improved operational efficiency and productivity.
Strengthened customer confidence and brand reputation
Consistently delivering high-quality products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations can enhance customer confidence and strengthen brand reputation, leading to increased customer loyalty and market share.
Challenges and Considerations of Quality Risk Management (QRM)
While the benefits of implementing QRM are significant, organizations must also be aware of potential challenges and considerations:
Cultural change and employee training
Adopting a risk-based mindset and integrating QRM principles into daily operations may require a cultural shift within the organization.
Effective employee training uch as pursuing a Six Sigma Green Belt certification and change management strategies are crucial for successful implementation.
Resource allocation and time management
Implementing Quality Risk Management can be resource-intensive, requiring dedicated personnel, specialized training, and time for risk assessments and mitigation strategies.
Organizations must allocate appropriate resources and manage time effectively to ensure successful implementation.
Integration with existing systems
Quality Risk Management (QRM) should be seamlessly integrated with an organization’s existing Quality Management System (QMS) and other processes.
This integration may require modifications to existing systems and procedures, as well as cross-functional collaboration and alignment.
Lead quality improvement and risk management initiatives in your organization. Our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt course prepares you to implement and manage comprehensive quality programs.
Conclusion
Quality risk management proves indispensable for thriving organizations.
Adopting a systematic, risk-focused quality approach empowers proactive risk detection, assessment, and lessening – shielding quality, safety, and regulatory obedience.
Benefits range greatly from spending cuts, efficiency gains, and customer/reputation strengthening.
Successful execution demands cultural evolution, dedicated resources, and principled integration within existing systems and workflows.
By following QRM’s guidance, tools, and techniques, organizations make understanding, evidence-based choices prioritizing quality and mitigation for long-term success amid complex, regulated landscapes.
I encourage all industries to adopt such practices as quality and risk cornerstones with Six Sigma certification serving as a proven framework for developing these competencies. Sound navigation protects products and clients, positioning leadership wherever quality matters deeply.
May share insights sustain all journeying together for enduring service, cooperation, and relationships uplifted through challenges overcome as one.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






