Quality Policy: Definition, Examples, and Best Practices
Quality policy is foundation of every organization’s commitment to deliver excellence in their particular field.
Learn how an organization approaches quality management and sets standards for its products, services and operations.
Key Highlights
- Quality Policy Basics Explained
- Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
- Real Industry Examples Included
- ISO 9001 Requirements Detailed

What is Quality Policy and Its Business Impact
A quality policy defines an organization’s vision and commitment to quality standards.
This formal document guides employees, satisfies stakeholders, and ensures consistent delivery of products and services.
Quality policies help organizations meet ISO 9001 requirements while building customer trust through standardized quality practices.
The ISO 9001 Connection
ISO 9001 standards require organizations to maintain documented quality policies. These policies must align with organizational goals and provide a framework for setting quality objectives.
The policy serves as evidence of management’s commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
Organizations seeking ISO certification need quality policies that:
- State clear quality commitments
- Support strategic business direction
- Match organizational context
- Follow regulatory requirements
- Enable measurement of success
Business Benefits of Quality Policies
Quality policies drive success through multiple channels. They reduce operational costs by preventing errors and minimizing waste.
Strong policies improve customer satisfaction by ensuring consistent product quality. They also boost employee engagement by clarifying quality expectations and responsibilities.
When Organizations Need a Quality Policy
Every organization benefits from implementing quality policies, regardless of size or industry. Manufacturing companies use them to maintain product standards.
Service providers rely on them to ensure consistent customer experiences. Technology firms implement quality policies to manage data integrity and software reliability.
Total Quality Management Integration
Quality policies form the foundation of total quality management systems. They guide:
- Quality objective setting
- Process standardization
- Performance measurement
- Continuous improvement efforts
- Employee training programs
Modern Quality Policy Evolution
Today’s quality policies address emerging business needs. Environmental sustainability requirements influence policy development.
Remote work environments demand new quality control approaches. Digital transformation introduces additional quality considerations for data management and cyber security.
Measuring Quality Policy Success
Organizations track policy effectiveness through:
- Customer satisfaction scores
- Product defect rates
- Process efficiency metrics
- Compliance audit results
- Employee feedback data

Quality policies continue evolving with changing business requirements.
Regular reviews and updates ensure these policies remain relevant and effective in supporting organizational goals.
Key Components of an Effective Quality Policy
A well-structured quality policy statement contains five essential elements that work together to drive organizational excellence.
These components ensure the policy serves both internal operations and external stakeholders effectively.
Management’s Quality Commitment
The quality policy must reflect top management’s dedication to quality standards. This commitment shows through:
- Clear quality objectives
- Resource allocation
- Regular policy reviews
- Active participation in quality initiatives
- Support for quality-focused training
Customer-Centric Approach with a Quality Policy
Customer focus forms the backbone of any company quality policy. Organizations demonstrate this by establishing methods to:
- Identify customer requirements
- Meet customer expectations
- Handle customer feedback
- Improve customer satisfaction
- Track customer experience metrics
Drive for Continuous Improvement
Quality policies need built-in mechanisms for ongoing enhancement. This includes regular evaluation of:
- Process effectiveness
- Product quality metrics
- Service delivery standards
- Employee performance
- Quality management systems
Organizations should document specific improvement methods and set measurable targets for advancement.
Regulatory Compliance Framework
The policy must address relevant industry regulations and standards. This section typically covers:
- ISO 9001 requirements
- Industry-specific regulations
- Local legal requirements
- International standards
- Environmental regulations
Employee Engagement Strategy with a Quality Policy
Successful quality policies actively involve employees at all levels. The policy should outline:
- Staff responsibilities
- Training requirements
- Communication channels
- Recognition programs
- Feedback mechanisms
Integrating Policy Components
These five elements must work together seamlessly. The quality policy links them through:
- Clear documentation
- Regular communication
- Performance measurement
- Management reviews
- Continuous updates
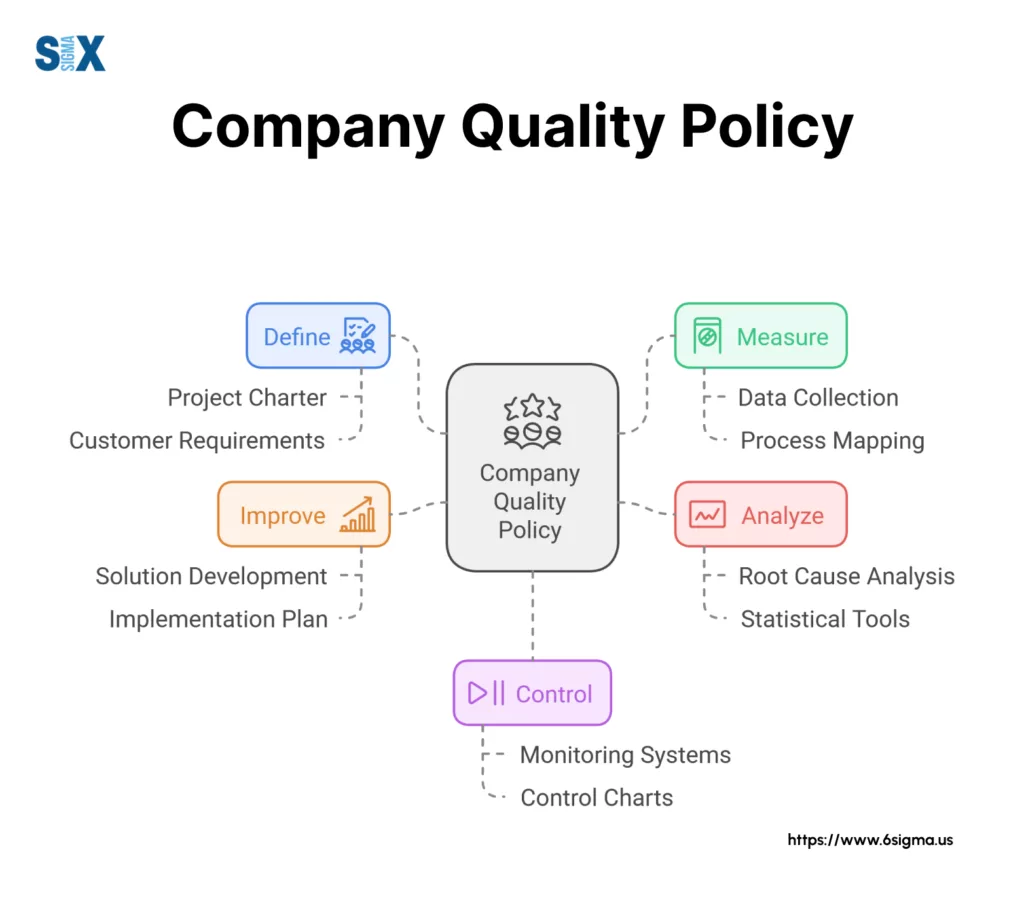
Measuring Component Effectiveness with a Quality Policy
Organizations should establish specific metrics for each component:
- Management Commitment: Leadership participation rates
- Customer Focus: Satisfaction scores
- Continuous Improvement: Process efficiency gains
- Regulatory Compliance: Audit results
- Employee Engagement: Staff feedback ratings
Regular monitoring of these metrics ensures the quality policy remains effective and relevant to business needs.
Creating an Effective Quality Policy: A Step-by-Step Guide
The first step in designing a quality policy involves evaluating your organization’s current quality management practices and future goals.
Start by examining existing processes, customer feedback, and industry requirements. Review past quality issues and identify areas needing improvement.
This assessment provides the foundation for a policy that addresses specific organizational challenges while supporting business objectives.
Engaging Key Stakeholders
Successful quality policies require input from various organizational levels. Department heads provide operational insights, while front-line employees offer practical perspectives on implementation challenges.
Quality teams ensure alignment with ISO standards and regulatory requirements. Customer feedback helps shape policy priorities.
Most importantly, top management must actively participate to demonstrate leadership commitment.
Drafting Your Quality Policy
When writing the policy, focus on clear, actionable statements that reflect your organization’s quality commitments.
The policy should include specific quality objectives, measurement criteria, and implementation strategies.
Keep the language simple and avoid technical jargon unless necessary. Structure the document logically, moving from broad quality principles to specific implementation guidelines.
Key Elements to Include
- Quality mission statement
- Specific quality objectives
- Implementation methods
- Measurement criteria
- Review procedures
Review and Refinement Process with a Quality Policy
The draft policy requires thorough review from multiple perspectives. Legal teams ensure compliance with regulations. Operations managers verify practicality.
Quality teams confirm alignment with ISO standards. Gather feedback from all stakeholders and make necessary adjustments.
This iterative process ensures the policy meets all requirements while remaining practical and effective.
Implementation and Communication Strategy
Rolling out the quality policy demands careful planning. Create a structured implementation timeline with clear milestones.
Develop training programs to help employees understand their roles in policy execution.
Establish communication channels for ongoing feedback and questions. Regular updates keep all stakeholders informed about progress and changes.
Policy Authorization and Signatures
The CEO or highest-ranking executive typically signs the final quality policy, demonstrating top-level commitment. Additional signatures might include:
- Quality Management Representative
- Department Heads
- Board Members
- ISO Management Representative
Monitoring and Adjustment with a Quality Policy
Policy effectiveness requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. Track key performance indicators related to quality objectives.
Regular audits ensure compliance and identify improvement opportunities. Update the policy as needed to address changing business conditions and emerging quality challenges.
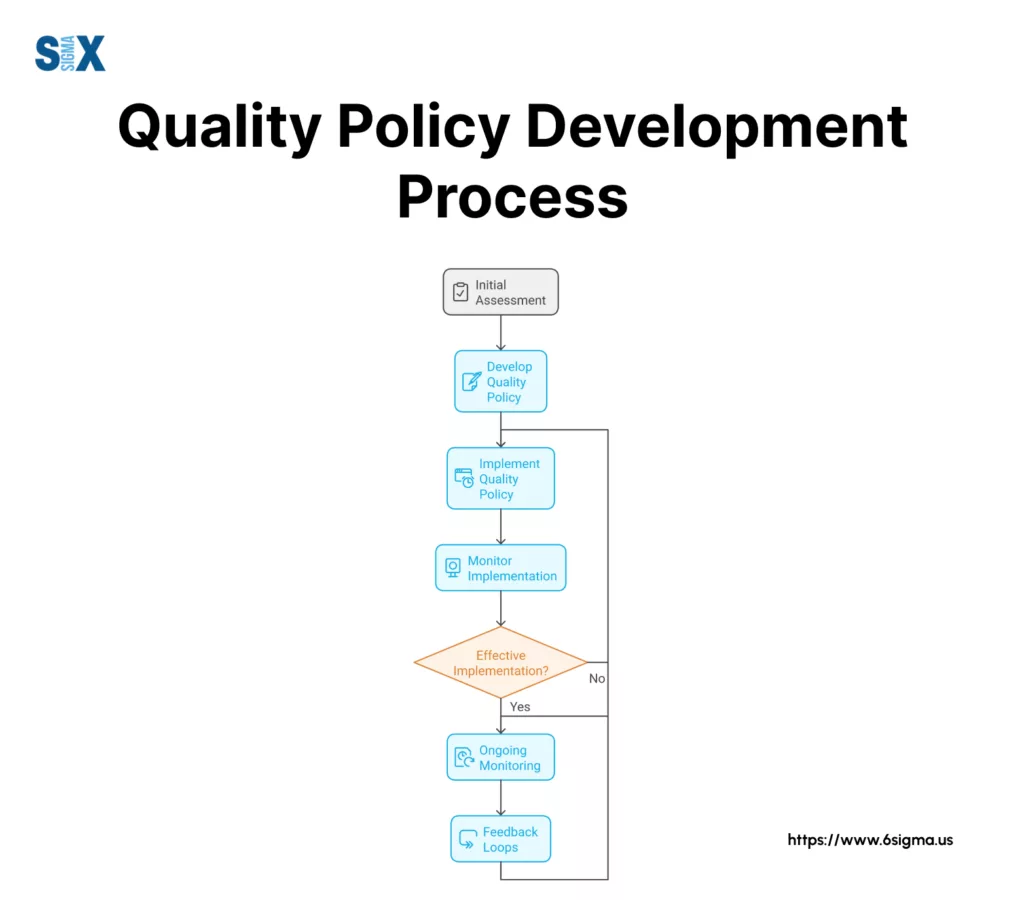
Documentation Requirements
Maintain detailed records of the policy development process. Document stakeholder input, review comments, and revision history.
Keep records of training sessions and implementation meetings. This documentation proves valuable during audits and helps track policy evolution over time.
Remember that creating an effective quality policy requires patience and attention to detail.
The investment in thorough planning and stakeholder engagement pays off through improved quality outcomes and organizational performance.
Transform your Quality Management Approach With Structured Process Mapping and Analysis Techniques.
Quality Policy Examples Across Industries
Manufacturing Industry Quality Policy
Manufacturing companies often focus their quality policies on product consistency and safety.
Key elements highlighted:
- Product quality standards
- Process control measures
- Employee development
- Cost management
- Customer satisfaction
Service Industry Quality Policy Example
Service organizations emphasize customer experience and service delivery in their quality policies.
The policy prioritizes:
- Service accuracy
- Customer privacy
- Staff competency
- Performance monitoring
- Security measures
Healthcare Quality Policy Model
Healthcare organizations balance patient care quality with regulatory compliance.
This policy addresses:
- Patient safety protocols
- Clinical excellence
- Regulatory compliance
- Staff development
- Quality monitoring systems
Technology Industry Quality Policy
Technology companies focus on innovation and reliability in their quality policies.
Essential components include:
- Product reliability
- Security measures
- Innovation focus
- Testing procedures
- Continuous updates
Common Elements Across Industries
While industry-specific elements vary, successful quality policies share several fundamental components:
- Clear quality objectives
- Measurement criteria
- Implementation methods
- Employee involvement
- Customer focus
Adapting Policy Examples
Organizations should modify these examples to match their specific needs. Consider factors like:
- Company size and structure
- Regulatory requirements
- Customer expectations
- Market conditions
- Available resources
The most effective quality policies blend industry best practices with organization-specific requirements, creating clear guidelines for quality management while supporting business objectives.
Quality Policy vs. Quality Objectives: Understanding the Differences
Quality objectives transform quality policies into measurable targets. While a quality policy outlines broad organizational commitments, objectives provide specific, measurable goals.
These objectives help organizations track progress and demonstrate policy effectiveness through concrete metrics and timelines.
How Quality Policy Shapes Objectives
The quality policy serves as a foundation for developing meaningful objectives.
For example, if a policy emphasizes customer satisfaction, related objectives might target response times, satisfaction scores, or complaint resolution rates.
This alignment ensures all quality initiatives support overall organizational goals.
Common Quality Objectives Examples
Manufacturing organizations often set objectives like:
- Reduce defect rates by 2% quarterly
- Achieve 98% on-time delivery
- Decrease customer complaints by 15%
- Improve first-pass yield to 95%
Service companies might focus on:
- Customer satisfaction scores above 90%
- Response times under 24 hours
- Training completion rates at 100%
- Service accuracy above 99%
Key Differences Between Policies and Objectives
| Feature | Quality Policy | Quality Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad organizational direction | Specific measurable targets |
| Timeline | Long-term vision | Short to medium-term goals |
| Measurement | Qualitative guidelines | Quantitative metrics |
| Review Frequency | Annual or bi-annual | Monthly or quarterly |
| Implementation | Organization-wide | Department-specific |
| Authority | Top management | Department heads |
Setting Effective Quality Objectives
Quality objectives should follow SMART criteria:
- Specific to quality outcomes
- Measurable through data
- Achievable with resources
- Relevant to policy goals
- Time-bound with deadlines
Common Misconceptions b/w Quality Policy vs Quality Objectives
Many organizations mistakenly search for “7 quality policies” when they actually need quality objectives. A single quality policy typically guides multiple objectives across different operational areas.
This policy-objective relationship creates a structured approach to quality management.
Monitoring and Review Process
Regular monitoring helps organizations:
- Track objective progress
- Adjust targets as needed
- Identify improvement areas
- Document achievements
- Plan future objectives
Integration with Business Strategy
Both quality policies and objectives must align with broader business strategies. The policy provides direction while objectives offer concrete steps toward quality goals.
This alignment ensures quality initiatives support overall organizational success.
Evolving Quality Management
Modern quality management systems increasingly integrate:
- Digital monitoring tools
- Real-time data analysis
- Automated reporting systems
- Predictive quality metrics
- Sustainability measures
Organizations should regularly review and update both policies and objectives to reflect changing business needs and emerging quality management practices.
Implementing and Maintaining Your Quality Policy
Successful quality policies require clear communication across all organizational levels. Department meetings provide opportunities to discuss policy requirements and gather feedback.
Digital platforms help distribute updates and track employee engagement. Visual aids posted in workspaces remind staff of quality commitments and procedures.
Organizations should develop structured communication plans that include:
- Regular policy updates
- Implementation milestones
- Success stories
- Performance metrics
- Improvement initiatives
Employee Training Programs
Training ensures every employee understands their role in maintaining quality standards.
New hire orientation should cover quality policy basics, while ongoing training reinforces key concepts.
Department-specific sessions help teams apply policy requirements to their daily tasks.
Essential training components include:
- Quality policy overview
- Role-specific responsibilities
- Documentation procedures
- Problem-solving methods
- Reporting requirements
Review Cycles and Updates of a Quality Policy
Quality policies require regular reviews to maintain effectiveness. ISO 9001 standards recommend annual reviews, but many organizations conduct semi-annual assessments. These reviews should examine:
- Policy relevance to current operations
- Achievement of quality objectives
- Changes in regulatory requirements
- Customer feedback and complaints
- Employee suggestions for improvement
Measuring Policy Effectiveness
Organizations can track policy effectiveness through various metrics:
Operational Metrics:
- Defect rates
- Process efficiency
- Production costs
- Delivery times
Customer-Related Metrics:
- Satisfaction scores
- Complaint volumes
- Return rates
- Repeat business
Internal Metrics:
- Employee engagement
- Training completion
- Audit results
- Documentation compliance
Continuous Improvement Process
Regular monitoring identifies areas needing enhancement. Create improvement plans based on:
- Performance data analysis
- Stakeholder feedback
- Industry benchmarks
- Technology advances
- Market demands
Documentation and Record Keeping of the Quality Policy
Maintain detailed records of policy implementation and updates. This documentation should include:
- Policy revision history
- Training records
- Audit findings
- Corrective actions
- Performance reports
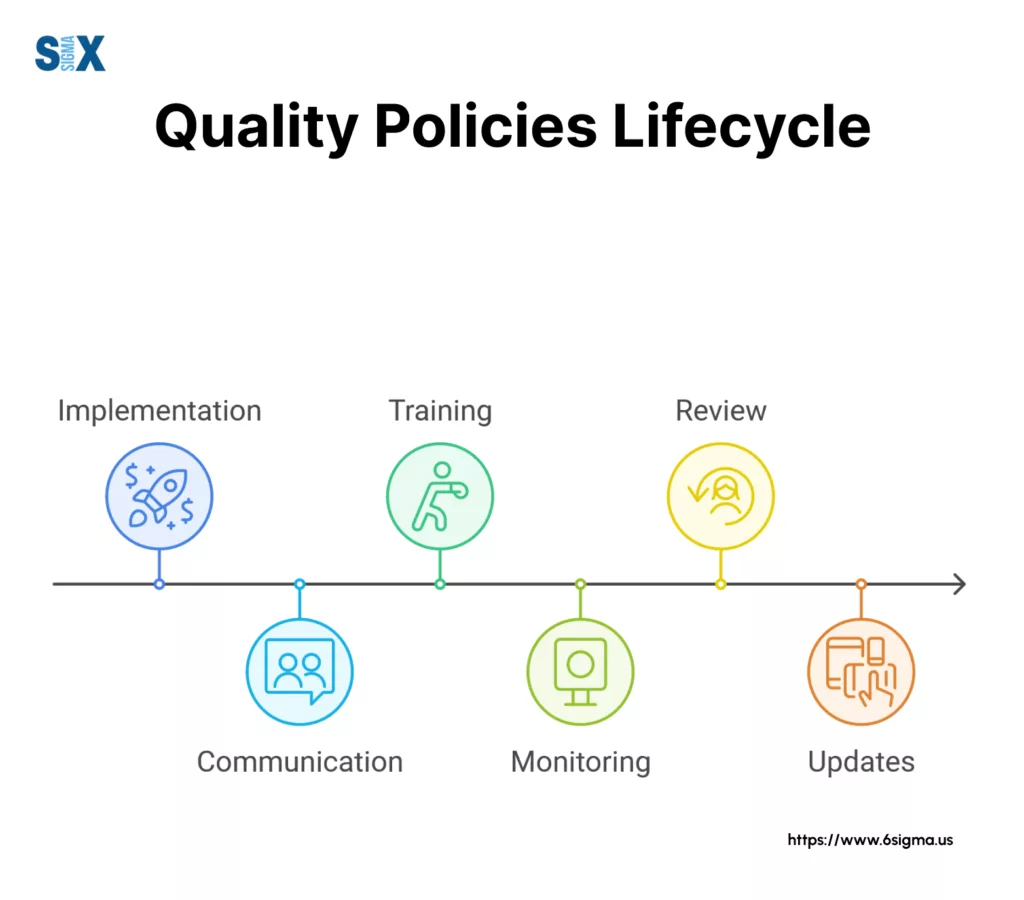
Technology Integration
Modern quality management systems utilize digital tools for:
- Policy distribution and tracking
- Performance monitoring
- Data collection and analysis
- Report generation
- Communication management
Stakeholder Engagement
Regular engagement with stakeholders ensures policy effectiveness. Schedule periodic meetings with:
- Management teams
- Department heads
- Quality specialists
- Employee representatives
- Customer focus groups
These interactions provide valuable insights for policy improvements and help maintain alignment with organizational goals.
Common Mistakes in Quality Policy Creation and How to Avoid Them
Many organizations create quality policies filled with generic statements that lack specific commitments.
Phrases like “committed to quality” or “customer satisfaction” without concrete measures provide little guidance.
Instead, include measurable targets and clear accountability measures that define how quality will be achieved and maintained.
Industry-Specific Requirements
Quality policies often fail when they ignore unique industry demands. Manufacturing companies need different quality measures than service providers.
Healthcare organizations face distinct regulatory requirements compared to technology firms. Successful policies address industry-specific challenges, standards, and customer expectations.
Misalignment of a Quality Policy With Company Values
When quality policies conflict with established company values, implementation becomes difficult.
The policy should reflect and support existing organizational culture while promoting quality improvements.
This alignment helps employees understand and embrace quality initiatives as part of their daily work.
Stakeholder Engagement Gaps
Excluding key stakeholders during policy development leads to implementation challenges. Quality policies affect everyone from front-line workers to top management.
Each group brings valuable perspectives on practical implementation issues and potential improvements. Regular consultation with all stakeholders ensures buy-in and practical policy measures.
Learn How to Prevent Common Quality Policy Mistakes With Proper Measurement System Analysis
Conclusion: The Impact of Quality Policies on Business Success
Well-crafted quality policies drive organizational success through multiple channels. They reduce operational costs, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance employee engagement.
These policies provide clear direction for quality initiatives while supporting continuous improvement efforts.
Future Trends in Quality Management
Quality policies continue evolving to address new business challenges. Environmental sustainability requirements influence policy development.
Remote work environments demand updated quality control measures. Digital transformation introduces additional considerations for data management and cyber security.
Taking Action on Quality Policy
Organizations should regularly review and update their quality policies to maintain effectiveness.
Consider current business needs, emerging industry trends, and stakeholder feedback during updates.
Remember that successful implementation requires clear communication, consistent monitoring, and ongoing adjustment based on results.
Final Recommendations
- Review your quality policy annually
- Involve all stakeholders in updates
- Measure policy effectiveness regularly
- Adapt to changing business needs
- Maintain clear documentation
Quality policies serve as foundational documents for organizational success. They guide quality initiatives, support continuous improvement, and help maintain consistent standards across operations.
Regular review and updates ensure these policies remain effective tools for quality management.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs








