A Complete Guide to Quality Management Process
Ensuring top-quality products or services is key to success.
Customers now want more and expect higher quality standards. To keep up, companies must have robust quality systems that make certain everything stays consistent with quality guidelines across operations.
The quality management method is a systematic, coordinated approach combining various practices and activities aimed at achieving quality targets.
It includes setting quality policies, planning how to achieve them, quality assurance, control, and continuous improvement to consistently meet or exceed customer needs while boosting performance over time.
Above all, the system strives to foresee and stop defects, cut down on waste, and optimize resource use by proactively identifying and fixing quality issues before they arise.
By properly harnessing quality management, organizations can boost customer satisfaction, lower expenses from re-work and defects, improve workflows, and gain an edge in their various markets. It’s a win for both the business and customers in the end.
Key Highlights
- The quality management process covers the coordinated methods and practices companies use to ensure everything hits the targeted quality levels and meets what customers want.
- It revolves around setting quality policies and objectives, then planning, assuring, controlling, and continuously refining how the work gets done. The aim is to reliably deliver high-quality results that keep customers happy while also boosting how the organization performs over time.
- Some big parts are quality planning, quality assurance, quality control, and always-improving methodologies like Six Sigma certification programs and Lean approaches.
- When quality management is done right, it leads to benefits like higher customer satisfaction, lower costs, better efficiency, and competitive differentiation compared to industry peers.
- Overall it creates a “win-win” scenario for both the business and customers in the short and long run.
What is Quality Management Process?
Quality management is an ongoing effort that organizations use to always deliver products and services meeting customer needs and expectations.
The quality management process refers to all the coordinated steps that guide and control efforts around quality.
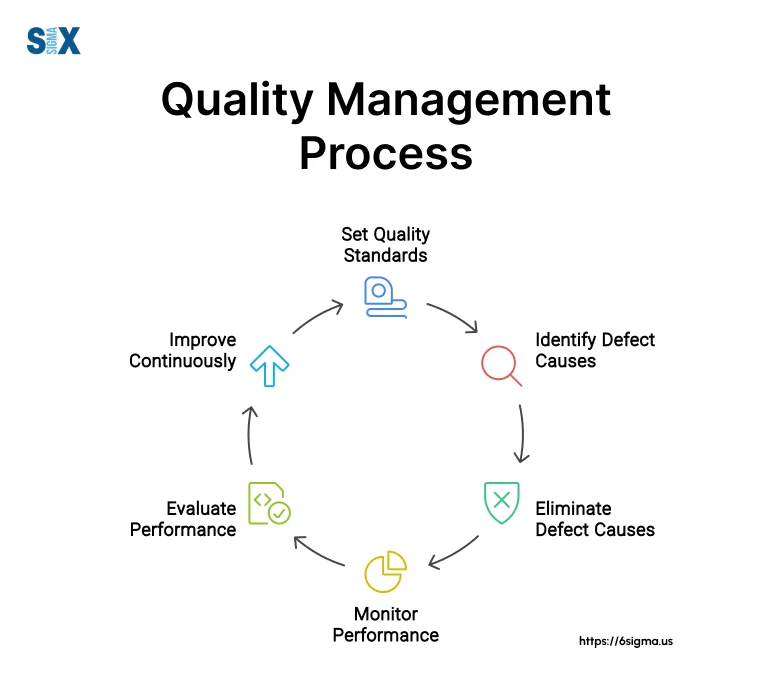
Essentially, it aims to put in place an overall quality system handling everything from identifying what customers want to ensuring satisfaction with the final offering.
It revolves around setting quality policies, aims, plans, and documented procedures establishing an operational framework for properly managing quality within.
Having a robust quality process down is crucial for any company wanting to stay competitive today. Customers now demand higher and higher quality. It allows for meeting, sometimes exceeding those ever-increasing quality benchmarks.
Following a structured process brings benefits like lower costs from fixing defects, smoother operations, and greater customer satisfaction and retention, ultimately boosting the bottom line.
Most importantly, it lays out best practices, tools, and techniques for monitoring everything impacting product or service quality at a consistent level of excellence.
Seven Principles of Quality Management
The quality management process is guided by seven key principles that provide a framework for organizations to implement effective quality practices. These principles are:
- Customer Focus: Organizations depend on their customers, so understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations should be the primary focus. This involves determining customer requirements, ensuring customer satisfaction, and striving to exceed customer expectations.
- Leadership: Leaders at all levels of the organization need to establish unity of purpose, direction, and an environment where people can become fully involved in achieving quality objectives. Their commitment and active involvement are crucial.
- Engagement of People: Competent, empowered, and engaged people at all levels throughout the organization are essential for enhancing its capabilities. Their full involvement allows their abilities to be used for the organization’s benefit.
- Process Approach: Desired results are achieved more efficiently when activities and related resources are managed as a process. Understanding how results are produced by the organization’s interlinked processes allows their integration and alignment.
- Improvement: Successful organizations have an ongoing focus on improvement. Continually improving products, services, and processes is a permanent objective.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making: Effective decisions are based on the logical and intuitive analysis of data and information. This helps ensure objectivity and confidence in decision-making.
- Relationship Management: An organization and its external providers (suppliers, contractors, partners) are interdependent. Mutually beneficial relationships enhance the ability to create value.
Quality Management Methodologies
There are several well-established methodologies that organizations can implement as part of their quality management process. Some of the most widely adopted include:
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims to improve processes by reducing defects and variations. Professionals often pursue Six Sigma certification to master a structured approach of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC) to identify and eliminate causes of errors or defects in processes.
Six Sigma emphasizes the rigorous use of statistical analysis to measure process performance and make data-driven decisions. Combined with root cause analysis training, practitioners can systematically identify and resolve underlying quality issues. Achieving the Six Sigma level means having no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing principles focus on maximizing value for the customer while minimizing waste. For teams new to this approach, Lean fundamentals training provides a foundational understanding of core concepts like value stream mapping and 5S.
It involves identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities (waste) in processes through techniques like value stream mapping, 5S (Sort, Set, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), just-in-time production, and pull systems.
Lean thinking aims to create more efficient and responsive processes that deliver value faster at a lower cost.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM is a comprehensive management approach centered on creating an organization-wide culture of continuous improvement in all areas.
It emphasizes leadership commitment, strategic quality planning, customer focus, employee involvement, training, supplier partnerships, and a systematic view of managing processes to achieve high-quality products and services.
The core principles of TQM include customer satisfaction, continuous improvement, total involvement, an integrated system, and a factual approach to decision-making.
ISO 9000 Standards
The ISO 9000 family of quality management standards provides guidelines and requirements for establishing a quality management system within an organization.
These internationally recognized standards outline best practices for areas such as leadership, planning, support, operations, performance evaluation, and improvement.
Becoming ISO 9001 certified demonstrates an organization’s ability to consistently meet customer requirements and enhance customer satisfaction.
Implementing a Quality Management Process
Successfully implementing a quality management process requires a systematic approach and commitment from all levels of an organization. Here are some key steps to effectively implement quality management:
Define Quality Objectives and Metrics
The first step is to clearly define what quality means for your products/services and establish measurable objectives and metrics. This could include defect rates, customer satisfaction scores, on-time delivery percentages, etc. Having well-defined quality targets provides a roadmap.
Establish Quality Management System
Put a formal quality management system (QMS) in place that documents all the processes, procedures, responsibilities, and resources required to achieve your quality objectives. Common QMS frameworks include ISO 9001, Six Sigma Certification, Lean, etc.
Provide Training and Resources
Ensure all employees involved in quality processes receive comprehensive training on quality concepts, tools, and the implemented QMS. Allocate sufficient resources like quality management software, testing equipment, etc.
Monitor and Control Processes
Continuously monitor quality performance metrics across all processes using statistical tools. Identify areas of non-conformance and take corrective/preventive actions to control processes.
Conduct Quality Audits
Perform regular internal and external audits to evaluate how effectively the QMS is being implemented and maintained across the organization. Audits help identify improvement opportunities.
Adopt Continuous Improvement
Embed a culture of continuous improvement by capturing feedback from quality audits, customer complaints, employee suggestions, etc. Implement improvement initiatives using techniques like the PDCA cycle.
Management Leadership and Review
Active leadership and commitment from top management are crucial. They should conduct periodic reviews of the QMS performance and make key decisions to improve its effectiveness.
Benefits and Challenges of Quality Management
The quality management process provides numerous benefits to organizations that implement it effectively. Some key advantages include:
- Customer Satisfaction: By focusing on meeting customer requirements and expectations consistently, quality management helps increase customer satisfaction levels. This leads to higher customer retention and loyalty.
- Improved Efficiency: The continuous improvement aspect of quality management methodologies like Lean and Six Sigma helps streamline processes. This eliminates waste, reduces costs, and improves overall operational efficiency.
- Better Products/Services: Quality management emphasizes defect prevention rather than defect detection. This proactive approach results in higher quality products and services that meet specifications.
- Competitive Advantage: Providing superior quality products/services can differentiate a company from its competitors and give it a powerful competitive edge in the marketplace.
- Employee Engagement: Involving employees in quality initiatives, providing training, and encouraging their suggestions cultivates a sense of ownership and engagement.
Despite its manifold benefits, implementing an effective quality management process has its own set of challenges:
- Cultural Resistance: Adopting a quality-focused mindset requires a cultural transformation which can face resistance from employees accustomed to the old way of working.
- Training Costs: Extensive training is required for employees at all levels on quality concepts, tools, and methodologies. This can involve significant costs, especially initially. Tiered programs like Six Sigma Green Belt certification for operational teams and Six Sigma Black Belt certification for project leaders allow organizations to scale expertise effectively.
- Management Commitment: Sustaining quality initiatives requires ongoing leadership commitment and allocation of sufficient resources over the long term.
- Data Quality Issues: Many quality improvement efforts rely on accurate data. Poor data quality can derail analysis and impede effective decision-making.
- Maintaining Momentum: Once initial quality gains are achieved, it becomes challenging to continuously identify new opportunities and maintain the improvement momentum.
By being aware of these potential challenges, organizations can proactively plan and take steps to overcome hurdles in their quality journey. The long-term benefits of an effective quality management process make it a worthwhile investment.
Future of Quality Management
The field of quality management is continuously evolving to keep pace with changing business environments, customer expectations, and technological advancements.
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of quality management processes:
Quality 4.0 and Digital Transformation
The fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0, is driving the digital transformation of quality management.
Technologies like the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), big data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) are being integrated into quality management systems. This enables real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making for quality control.
Increased Focus on Customer Experience
With growing competition and customer expectations, organizations are shifting their quality management focus from just product/service quality to overall customer experience quality.
This holistic approach considers all touchpoints in the customer journey and aims to deliver consistently excellent experiences.
Risk-Based Quality Management
Traditional quality management relied heavily on product inspection and testing. The future points toward a risk-based approach that identifies, analyzes, and mitigates potential quality risks proactively across the entire value chain using tools like Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
Quality Intelligence and Data-Driven Decisions
The integration of quality data from multiple sources, including customer feedback, supplier data, and production data, is enabling organizations to gain deeper quality intelligence. This data-driven approach allows for more informed decision-making and continuous improvement of quality management processes.
Emphasis on Agility and Adaptability
In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, quality management processes need to be agile and adaptable.
Methodologies like Agile Quality Management focus on iterative development, cross-functional collaboration, and the ability to quickly respond to changing requirements and market demands.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Increasingly, quality management is expanding beyond traditional parameters to include sustainability and social responsibility factors.
This involves considering the environmental impact, ethical sourcing, and corporate social responsibility aspects throughout the product/service lifecycle.
Upskilling and Quality Culture
As quality management evolves, there is a growing need for upskilling and fostering a strong quality culture within organizations.
Continuous training, knowledge sharing, and fostering a mindset of quality at every level will be crucial for successful quality management implementation.
Conclusion
Having a solid quality management process locked in is key for companies to reliably ship great products/services meeting customer needs.
Guidance from the seven quality principles and methods like Six Sigma, Lean, and TQM help drive non-stop improvement and the quest for workflow perfection.
But managing quality isn’t a one-and-done deal—it takes leaders fully committed plus a culture where quality forms the core identity.
Companies must review and refine their quality systems too, adapting to shifting markets, customer requirements, and the industry’s leading-edge approaches.
As quality management evolves, staying in the know about new technologies, tools, and frameworks maintains quality efforts at their best.
Quality management software, for one, streamlines things, boosts data collection/analysis, and provides real-time insights for smarter choices.
Ultimately, the benefits of quality done right—happier customers, lower costs, better efficiency, competitive separation—far outweigh any challenges in implementing it all.
By constantly prioritizing quality and upgrading processes, businesses set themselves up for long-haul success in ever more cutthroat global markets.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






