Nominal Group Technique: A Strategic Decision-Making Tool in Six Sigma
The Nominal Group Technique (NGT) stands as a structured method for group decision-making that transforms individual ideas into actionable solutions.
This systematic approach helps teams prioritize options and reach consensus while ensuring every voice gets heard.
Key Highlights
- Step-by-step NGT implementation guide
- Real Six Sigma project applications
- Digital adaptation strategies
- Decision-making framework examples
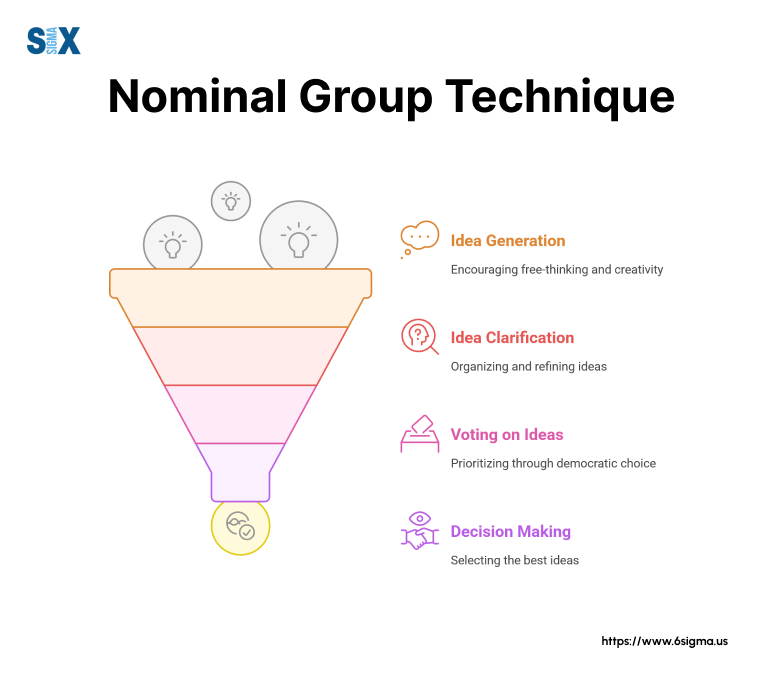
What is Nominal Group Technique?
The Nominal Group Technique (NGT) represents a structured decision-making method that organizations use to generate, prioritize, and evaluate ideas within teams.
This technique emerged in the 1970s when researchers Andre Delbecq and Andrew Van de Ven developed it to enhance group productivity and decision-making quality.
Breaking Down The Nominal Group Technique Definition
NGT functions as a voting-based system where team members first work independently to generate ideas, then come together to discuss and rank these ideas systematically.
The term “nominal” refers to the limited interaction between participants during the initial ideation phase, setting it apart from traditional group discussions.
Evolution In Six Sigma Applications
Six Sigma practitioners have adapted the Nominal Group Technique to solve complex process improvement challenges.
The method fits naturally within the DMAIC framework, particularly during problem identification and solution generation phases.
Project teams use NGT to:
- Define critical customer requirements
- Identify potential process improvements
- Select optimal solutions from multiple alternatives
- Prioritize implementation strategies
Key Components Of The Process
The technique follows a structured format that includes silent ideation, round-robin sharing, group discussion, and weighted voting.
This systematic approach ensures equal participation while minimizing the influence of dominant personalities or organizational hierarchy.
Modern Adaptations For Today’s Teams
Digital tools have transformed how teams implement the Nominal Group Technique.
Virtual whiteboards, online polling systems, and collaboration platforms enable remote teams to conduct effective NGT sessions while maintaining the method’s core principles.
Integration of Nominal Group Technique with Lean Principles
Within Lean Six Sigma, NGT serves as a valuable tool for waste elimination and process optimization.
Teams apply this technique to identify value-adding activities, streamline workflows, and develop sustainable improvements.
The method’s structured nature aligns with Lean’s focus on systematic problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Through careful application of NGT principles, organizations can harness collective wisdom while avoiding common group decision-making pitfalls.
This balanced approach leads to better solutions and stronger team buy-in for implemented changes.
The Critical Role Of NGT In Six Sigma Problem-Solving
The Nominal Group Technique plays a vital role in Six Sigma projects by providing teams with a structured approach to problem-solving and decision-making.
Project managers and Six Sigma practitioners regularly employ this method to gather valuable insights and drive process improvements.
When To Use Nominal Group Technique (NGT) In Six Sigma Projects
Six Sigma teams turn to the Nominal Group Technique during crucial decision points that require diverse perspectives and clear consensus.
The method proves particularly valuable when:
- Teams face complex technical challenges
- Projects require stakeholder buy-in
- Process improvements need prioritization
- Root causes remain unclear
Nominal Group Technique (NGT) Application Across DMAIC Phases
Define Phase:
Teams use the Nominal Group Technique to clarify project scope and identify critical customer requirements.
This phase often involves stakeholder analysis and problem definition workshops where NGT helps teams align on project goals.
Measure Phase:
During measurement planning, NGT assists teams in selecting appropriate metrics and data collection methods. Teams prioritize measurement points and determine which process variables require monitoring.
Analyze Phase:
Root cause analysis benefits from NGT’s structured approach. Teams generate potential cause theories and systematically evaluate each possibility using data and expert knowledge.
Improve Phase:
The technique guides solution selection and implementation planning. Teams use NGT to:
- Generate improvement ideas
- Evaluate potential solutions
- Select optimal implementation strategies
- Plan pilot studies
Control Phase:
NGT supports the development of control mechanisms by helping teams:
- Identify critical control points
- Select appropriate monitoring methods
- Design response plans
- Establish review procedures
Real-World Implementation Examples
Manufacturing Sector:
A automotive parts manufacturer used NGT to identify quality control improvements, resulting in a 30% defect reduction.
Healthcare Industry:
Medical teams applied NGT to streamline patient flow processes, reducing wait times and improving satisfaction scores.
Service Operations:
Call centers implemented NGT to optimize customer service protocols, leading to improved resolution rates and reduced handling times.
Integration With Project Management
Project Management Professionals (PMPs) integrate NGT with traditional project management tools to enhance:
- Risk assessment procedures
- Stakeholder engagement
- Resource allocation decisions
- Change management processes
This systematic approach ensures projects stay aligned with Six Sigma principles while maintaining efficient progress toward improvement goals.
Detailed Steps Of Nominal Group Technique
The success of any Nominal Group Technique session depends on following a structured process. Each step builds upon the previous one, creating a logical flow that leads to actionable results.
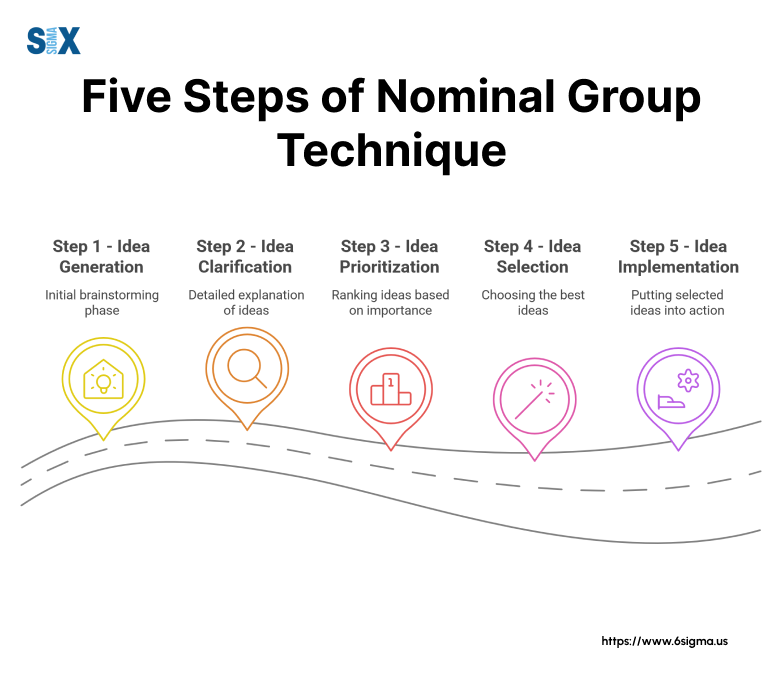
Step 1: Problem Identification
The facilitator presents a clear problem statement to the group.
This step requires:
- Writing the problem on a visible board
- Ensuring all participants understand the issue
- Clarifying any technical terms or ambiguities
- Setting specific objectives for the session
Step 2: Silent Idea Generation
Participants work independently for 10-15 minutes to generate solutions.
During this phase:
- Each person writes their ideas privately
- No discussion occurs between team members
- Participants focus on quantity over quality
- Ideas remain anonymous
Step 3: Round Robin Idea Sharing
Team members take turns sharing one idea at a time until all ideas are recorded.
The process involves:
- Recording each idea on a central board
- Avoiding discussion or criticism
- Numbering ideas for easy reference
- Continuing until all ideas are shared
Step 4: Group Discussion And Clarification
The team reviews and discusses each recorded idea.
This phase includes:
- Asking questions for clarity
- Combining similar suggestions
- Eliminating duplicate entries
- Refining idea descriptions
Step 5: Voting And Prioritization
Participants rank or vote on the ideas using a predetermined system.
The steps include:
- Assigning ranking criteria
- Individual voting by participants
- Tallying the results
- Creating a prioritized list
Digital Implementation Tips
Modern teams often conduct NGT sessions virtually using:
- Online whiteboarding tools
- Digital voting platforms
- Video conferencing software
- Collaborative documentation systems
Time Management Guidelines of Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
Effective NGT sessions typically follow this timeline:
- Problem presentation: 5-10 minutes
- Silent generation: 10-15 minutes
- Idea sharing: 15-20 minutes
- Discussion: 30-45 minutes
- Voting: 15-20 minutes
Facilitator Responsibilities
The session leader must:
- Keep time for each phase
- Maintain equal participation
- Record ideas accurately
- Guide discussion flow
- Manage voting process
Following these structured steps of the Nominal Group Technique ensures efficient idea generation and decision-making while maintaining team engagement throughout the process.
Psychological And Practical Advantages Of Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
The Nominal Group Technique offers distinct benefits that set it apart from traditional decision-making methods.
These advantages make it particularly valuable for project teams tackling complex challenges.
Equal Participation In Decision Making
The structured nature of NGT eliminates common meeting dynamics that often silence quieter team members.
This approach delivers several key benefits:
- Every participant contributes ideas independently
- Senior team members cannot dominate discussions
- Introverted members share thoughts without pressure
- Cultural and language barriers become less significant
Breaking Free From Groupthink
NGT effectively counters groupthink through its built-in mechanisms:
- Individual ideation prevents bandwagon effects
- Anonymous voting reduces peer pressure
- Structured discussion promotes critical thinking
- Multiple perspectives receive equal consideration
Diversity In Solution Generation with Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
Teams using the Nominal Group Technique typically generate more varied solutions because:
- Independent thinking encourages unique perspectives
- Silent brainstorming removes social barriers
- Round-robin sharing ensures all ideas surface
- Discussion phase combines different viewpoints
Data-Driven Decision Making
The quantitative aspects of NGT provide concrete advantages:
- Numerical rankings create clear priorities
- Voting results offer objective decision criteria
- Documentation provides traceable rationale
- Metrics enable progress tracking
Time And Resource Efficiency
NGT streamlines the decision-making process by:
- Setting clear time boundaries
- Following structured steps
- Focusing discussions effectively
- Reaching conclusions systematically
Enhanced Team Dynamics with Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
Regular use of the Nominal Group Technique improves:
- Team communication patterns
- Mutual respect among members
- Problem-solving capabilities
- Group cohesion levels
Implementation Benefits
Projects using NGT often experience:
- Higher solution quality
- Stronger team buy-in
- Better implementation rates
- Reduced resistance to change
Long-Term Organizational Impact
Organizations that adopt NGT regularly see improvements in:
- Decision-making culture
- Innovation capabilities
- Team collaboration
- Project success rates
These advantages make the Nominal Group Technique a powerful tool for teams seeking efficient, inclusive, and effective decision-making processes.
The method’s structured approach ensures both psychological safety and practical results, leading to better outcomes across various project types.
Master the Nominal Group Technique with Our Six Sigma Training
Implementing NGT In Different Six Sigma Scenarios
The Nominal Group Technique proves valuable across various industries, each with unique challenges and requirements. These real-world applications demonstrate the technique’s versatility and effectiveness in Six Sigma projects.
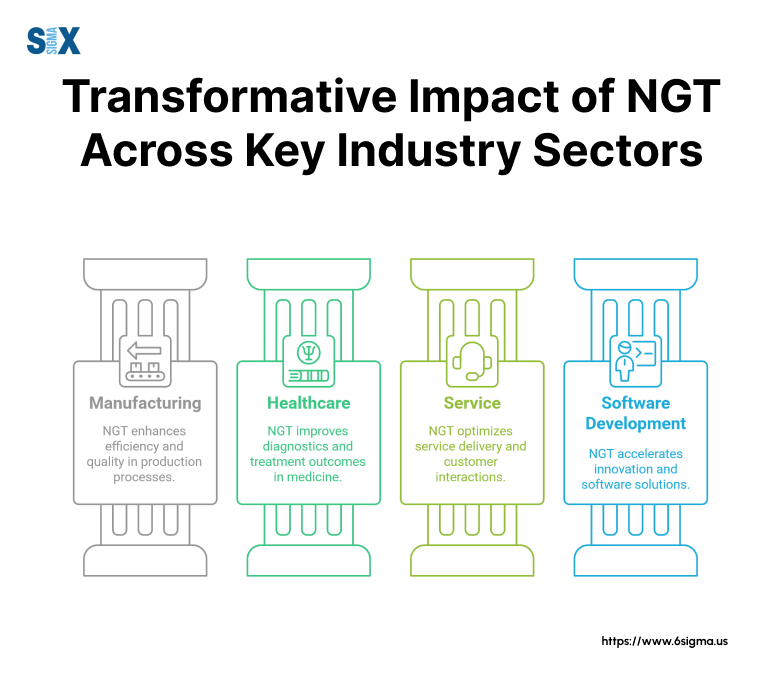
Manufacturing Process Improvement with Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
A leading automotive parts manufacturer implemented the Nominal Group Technique to address quality control issues. The team focused on reducing defect rates in their production line.
Results achieved:
- 35% reduction in defect rates
- $2.1 million annual cost savings
- 22% improvement in process efficiency
- Enhanced team collaboration
Key success factors included structured idea generation from floor workers and engineering staff, leading to practical solutions grounded in daily operations.
Healthcare Quality Enhancement
Regional medical centers utilized NGT to streamline patient care protocols. The project targeted emergency department wait times and patient satisfaction scores.
The process revealed:
- Hidden bottlenecks in patient flow
- Communication gaps between departments
- Resource allocation opportunities
- Staff training needs
Implementation led to a 40% reduction in wait times and improved patient satisfaction ratings from 3.2 to 4.6 out of 5.
Service Industry Problem-Solving
A national retail chain employed NGT to enhance customer service operations. The focus centered on improving first-call resolution rates and customer satisfaction.
Project outcomes included:
- 28% increase in first-call resolution
- Reduced customer complaints by 45%
- Improved employee satisfaction scores
- Standardized service protocols
The structured NGT approach helped identify and prioritize key service improvements while maintaining team engagement throughout the process.
Software Development Optimization with Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
Tech companies have adapted NGT for agile development environments. One project focused on reducing bug rates in new releases.
The team achieved:
- 50% reduction in post-release bugs
- Faster development cycles
- Better code quality metrics
- Enhanced team collaboration
Digital tools facilitated remote NGT sessions, allowing distributed teams to participate effectively in the improvement process.
Cross-Industry Success Factors
Several common elements emerged across successful implementations:
- Clear problem definition
- Strong facilitator guidance
- Active stakeholder engagement
- Systematic follow-through
- Regular progress monitoring
These case studies demonstrate how the Nominal Group Technique adapts to different business environments while maintaining its core benefits of structured decision-making and team engagement.
Learn Structured Techniques Like NGT to Drive Organizational Excellence
Become a certified problem-solving expert!

Potential Challenges And Mitigation Strategies
While the Nominal Group Technique offers numerous benefits, teams often encounter specific challenges during implementation.
Understanding these obstacles and their solutions ensures successful outcomes in Six Sigma projects.
Maintaining Participant Engagement
Low engagement can derail NGT sessions. Project managers must address participation barriers through strategic approaches.
Common Engagement Issues:
- Silent participants during discussions
- Dominant personalities taking over
- Loss of focus during lengthy sessions
- Resistance to structured processes
Mitigation Strategies:
The facilitator should establish clear ground rules, rotate speaking order, and use targeted questions to draw out quieter participants.
Breaking longer sessions into smaller segments helps maintain energy levels and focus.
Effective Time Management with Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
Poor time management often leads to rushed decisions or incomplete processes. Successful NGT sessions require careful planning and pacing.
Key Time Management Solutions:
- Set realistic timeframes for each phase
- Use visible timers during sessions
- Prepare materials in advance
- Schedule breaks strategically
Building True Consensus
Reaching genuine agreement rather than forced consensus presents a significant challenge in NGT implementation.
Effective consensus-building requires:
- Clear voting criteria
- Transparent ranking systems
- Open discussion periods
- Documentation of decision rationale
Remote And Virtual Adaptations
Digital transformation demands new approaches to NGT facilitation. Teams must adapt traditional methods for virtual environments.
Virtual Implementation Tools:
- Digital whiteboarding platforms
- Online voting systems
- Video conferencing software
- Collaborative documentation tools
Success factors include selecting appropriate technology, providing technical training, and establishing clear virtual participation guidelines.
Maximizing NGT’s Potential In Six Sigma
The Nominal Group Technique serves as a powerful tool within Six Sigma methodology when properly implemented.
Teams achieve optimal results by:
- Selecting appropriate projects for NGT application
- Preparing thoroughly for each session
- Following structured processes consistently
- Monitoring and measuring outcomes
- Adapting methods based on feedback
Future Considerations:
- Integration with emerging technologies
- Adaptation for hybrid work environments
- Enhanced data analytics capabilities
- Improved visualization tools
Success Metrics:
Teams should track specific indicators including:
- Participation rates
- Decision implementation success
- Time efficiency improvements
- Team satisfaction scores
By addressing these challenges proactively and implementing targeted solutions, organizations can maximize the benefits of the Nominal Group Technique in their Six Sigma initiatives.
Regular evaluation and adjustment of approaches ensure continuous improvement in NGT effectiveness.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






