LTPD (Lot Tolerance Percent Defective) in Lean Six Sigma
Quality checks assume pivotal jobs in each assembling or creation process. Representative testing utilizes tests on item tests rather than each. Inside this, the Lot Endurance Percent Detrimental (LTPD) assumes a basic part in choosing regardless of whether a delivery or outfit ought to be acknowledged or dismissed given imperfection levels.
Key Highlights
- Understanding LTPD’s meaning, its significance in acknowledgment testing, and its relationship with AQL gives a strong establishment for quality administration cycles.
- The benefits of utilizing its incorporate sparing time and assets, overseeing testing dangers, and serving as an industry norm for ensuring deliverable quality.
- Distinctive testing strategies, for example, quality testing and fluctuating testing, and the notion of Operation Characteristic curves and assembling and shopper dangers are investigations.
- Learning its esteem determination, fitting it into testing designs and acknowledgment/dismissal guidelines for item masses is imperative.
- Genuine world applications incorporate assembling, quality control, provider assessment, and different enterprises.
- Best hones incorporate coupling it with Statistical Process Control, adjusting makers’ and shoppers’ dangers, and advancing constant upgrades and streamlining.
What is Lot Tolerance Percent Defective (LTPD)?
In quality oversight and acknowledgment testing, Lot Tolerance Percent Deleterious (LTPD) represents a basic pointer helping decide on conveying or dismissing a thing bundle or outfit in view of imperfection levels.
It portrays the most extreme permittable rate of flaws expected for acknowledgment, normally 90%.
Acknowledgment testing utilizes tests to assess an outfit rather than each part. This fills a significant job, assisting with setting the most extreme flaw rates.
It relates to Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL) which is the most extreme imperfections rate a testing design will acknowledge with 95% possibility.
Benefits of Using LTPD
Incorporating LTPD into quality control processes offers several significant benefits for businesses and organizations:
Time and resource savings
By utilizing this and acceptance sampling, businesses can save valuable time and resources that would otherwise be spent on inspecting every single item in a lot. This approach is particularly beneficial when 100% inspection is not feasible due to time constraints, costs, or the potential for human error.
Risk control in sampling plans
LTPD helps control the risks associated with accepting or rejecting lots based on a sample. By setting an appropriate value, businesses can minimize the risk of accepting defective lots while also reducing the risk of rejecting acceptable lots unnecessarily.
Industry-standard metric
LTPD is widely recognized and used as an industry-standard metric for acceptance sampling and quality control. By adopting it, businesses can align their processes with established best practices and facilitate communication and collaboration with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders.
Sampling Plans and LTPD
LTPD is closely tied to the development and implementation of sampling plans, which are essential for effective acceptance sampling.
Attribute sampling vs variable sampling
Acceptance sampling can be broadly categorized into two types: attribute sampling and variable sampling. Attribute sampling involves classifying units as either conforming or nonconforming based on specific criteria, while variable sampling involves measuring a continuous characteristic of the units.
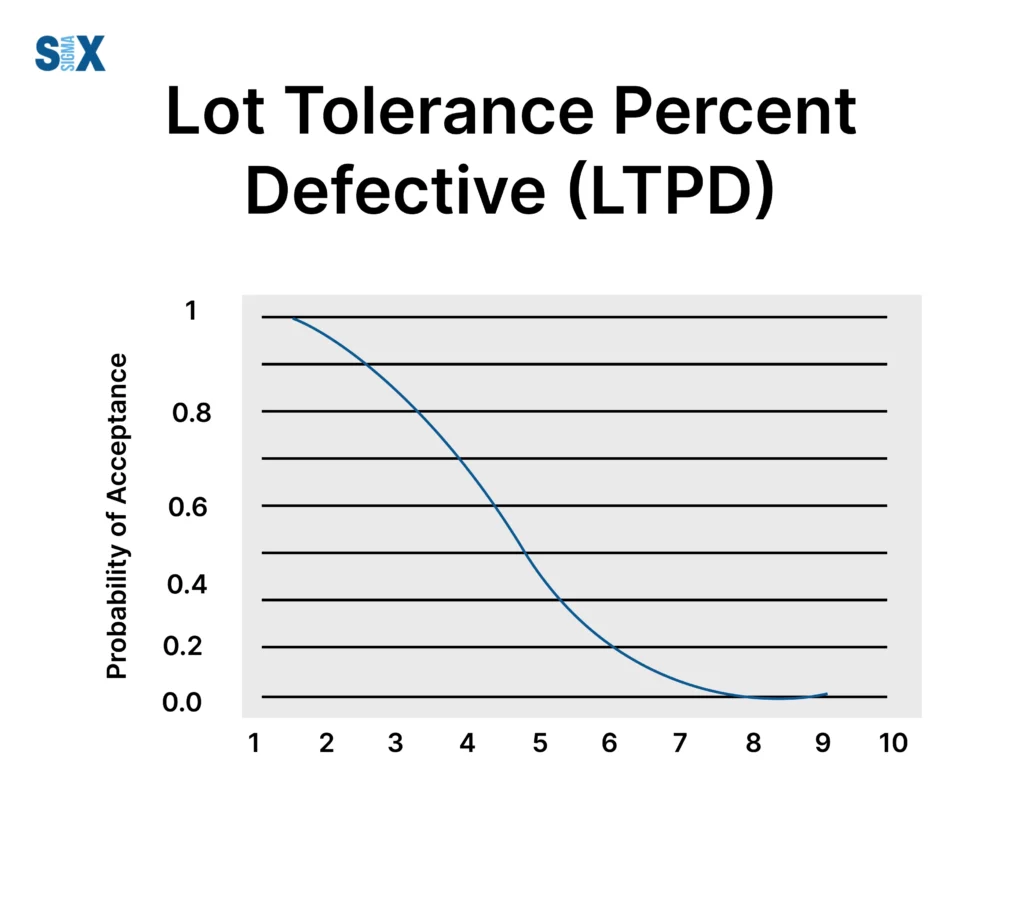
Operating Characteristic (OC) curve
The Operating Characteristic (OC) curve is a graphical representation that shows the probability of accepting a lot for various percentages of defective units. The OC curve is used to determine the LTPD and AQL values for a sampling plan, as well as other important parameters.
Setting producer’s risk and consumer’s risk
When developing a sampling plan, it is necessary to consider the producer’s risk (the probability of rejecting an acceptable lot) and the consumer’s risk (the probability of accepting a defective lot). These risks are typically set at 5% and 10%, respectively, but can be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the situation.
Calculating and Implementing LTPD
To effectively utilize it in quality control processes, it is essential to understand how to calculate and implement this metric properly.
Determining LTPD value
The LTPD value is typically determined using statistical methods and tables, taking into account factors such as the sample size, the desired level of protection, and the acceptable quality level. Various software tools and online calculators are available to assist with these calculations.
Creating a sampling plan with LTPD
Once the LTPD value has been determined, it can be used to create a comprehensive sampling plan that outlines the sample size, acceptance criteria, and other relevant parameters. This plan serves as a guide for conducting acceptance sampling and making decisions about accepting or rejecting lots.
Acceptance/rejection criteria
The sampling plan will specify the acceptance and rejection criteria based on the LTPD value and the number of defective units found in the sample. If the number of defective units in the sample is equal to or greater than the rejection limit, the lot is rejected; otherwise, it is accepted.
Applications of LTPD
LTPD finds applications in various industries and sectors where quality control and acceptance sampling are essential:
Manufacturing and quality control
It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, to ensure that products meet quality standards before being released to the market. It helps streamline quality control processes and minimize the risk of defective products reaching customers.
Supplier evaluation and selection
Companies often use this and acceptance sampling plans to evaluate and select suppliers based on the quality of their products or materials. By setting appropriate LTPD values, businesses can ensure that they receive high-quality goods from their suppliers and maintain their own quality standards.
Other industries using sampling
LTPD and acceptance sampling techniques are also employed in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and construction, where quality control is critical for ensuring safety, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for LTPD
To maximize the benefits of using LTPD and ensure its effective implementation, it is important to follow the best practices:
Complementing Statistical Process Control (SPC)
While Lot Tolerance Percent Defective and acceptance sampling are valuable tools for evaluating finished products, they should be complemented by Statistical Process Control (SPC) techniques to identify and address issues during the production process. SPC helps ensure consistent quality and continuous improvement.
Balancing producer’s and consumer’s risks
When setting LTPD values and developing sampling plans, it is crucial to strike a balance between the producer’s risk and the consumer’s risk. This balance ensures that both the producer and the consumer are adequately protected while maintaining reasonable costs and efficiency.
Continuous improvement and process optimization
The implementation of Lot Tolerance Percent Defective and acceptance sampling should be part of an ongoing effort towards continuous improvement and process optimization.
Regular reviews and adjustments to sampling plans, LTPD values, and quality control processes should be undertaken to ensure they remain effective and aligned with changing requirements and industry best practices.
Conclusion
The Lot Tolerance Percent Defective is a critical metric in the realm of quality control and acceptance sampling. By understanding and effectively utilizing LTPD, businesses can streamline their quality control processes, ensure consistent product quality, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Key Points on Lot Tolerance Percent Defective
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of Lot Tolerance Percent Defective, its importance in acceptance sampling, its relationship with the Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL), and the benefits of using Lot Tolerance Percent Defective, such as time and resource savings, risk control, and industry standardization.
We have also delved into sampling plans, the Operating Characteristic (OC) curve, and the calculation and implementation of LTPD values.
Importance of LTPD in Modern Businesses
The use of Lot Tolerance Percent Defective and acceptance sampling techniques has become increasingly important.
By adopting these methods, companies can ensure that their products meet the highest standards, build trust with customers, and maintain a strong reputation in the market.
Future Trends and Developments
As technology continues to advance and industries evolve, the application of LTPD and acceptance sampling is likely to expand further.
Emerging technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, may enable more sophisticated sampling techniques and quality control processes. Additionally, as global supply chains become more complex, the need for robust and standardized quality control measures like LTPD will become even more crucial.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







