Integrated Risk Management: Strategies, Tools, and Best Practices for 2025
Organizations widely face an array of risks that demand strategic management and monitoring.
Integrated risk management (IRM) has given the solution for businesses to identify, assess, and control risks across their operations.
This moves beyond traditional siloed approaches to create a unified system that connects risk management activities throughout an organization.
What Makes Integrated Risk Management Different?
Unlike standalone risk management practices, IRM creates a structured framework that brings together various risk-related activities under one umbrella.
Enhance Your Risk Management Capabilities
With our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification join professionals who have reduced process risks by up to 40%.

Key Focus Areas of This Guide
- Building a robust IRM framework tailored to your organization
- Selecting and deploying the right IRM tools and technologies
- Creating risk assessment and monitoring protocols
- Establishing clear communication channels for risk reporting
What is Integrated Risk Management (IRM)?
Modern businesses require sophisticated approaches to manage various risks effectively.
The integrated risk management framework offers organizations a structured method to identify, assess, and control risks across multiple business functions.
The Four Major Components of Integrated Risk Management (IRM)
Strategy development forms the first pillar of integrated risk management.
This involves creating clear policies, setting risk tolerance levels, and establishing governance structures that align with business objectives.
Risk assessment and identification make up the second component. Organizations must systematically evaluate potential threats and opportunities across operations, finance, technology, and compliance areas.
The third element focuses on response planning and execution. This includes developing specific protocols for risk mitigation, creating contingency plans, and implementing control measures to address identified risks.
Monitoring and reporting constitute the fourth component. Regular tracking of risk metrics, performance indicators, and compliance status ensures the effectiveness of risk management efforts while enabling timely adjustments when needed.
How Integrated Risk Management Works in Practice
The integrated risk management approach connects different organizational levels through standardized processes and communication channels.
Senior management sets the overall risk strategy, while operational teams implement specific controls and monitoring procedures.
Risk data flows through centralized systems, allowing real-time visibility into risk status across departments.
This enables quick decision-making and coordinated responses to emerging threats or opportunities.
Technology platforms support these processes by automating data collection, analysis, and reporting tasks.
These tools help organizations maintain consistent risk assessment standards while reducing manual effort in risk monitoring activities.
Comparing IRM, ERM, and GRC
While integrated risk management shares some similarities with Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC), key differences exist in their scope and focus.
ERM typically emphasizes high-level strategic risks and their potential impact on business objectives. It often operates at the executive level, focusing on broad organizational risks.
GRC frameworks primarily address regulatory compliance and governance structures. They ensure organizations meet legal requirements and industry standards while maintaining proper oversight.
IRM combines elements of both approaches while adding operational integration and technological enablement. It creates stronger connections between risk management activities across all organizational levels.
The success of an integrated risk management program depends on proper alignment between these components and consistent execution across the organization.
Regular reviews and updates ensure the framework remains relevant and effective as business conditions change.
Organizations implementing IRM should focus on building strong foundations in each component while maintaining flexibility to adapt to new risks and regulatory requirements.
The Integrated Risk Management Framework
A well-structured integrated risk management framework enables organizations to identify, assess, and respond to risks efficiently.
Key Components of an IRM Framework
Risk governance stands as the foundation of any integrated risk management program.
This includes establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting structures across the organization.
Board members and senior executives must define risk appetite statements and set strategic objectives that guide risk management activities.
The risk assessment methodology forms another crucial component.
Organizations need standardized processes to evaluate and prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood.
This includes tools for risk identification, analysis, and measurement across different business units.
Control mechanisms represent the third vital element.
Learn to identify potential failure points and develop proactive risk mitigation strategies with Failure Mode Effects Analysis.
Implementing Your Integrated Risk Management (IRM) Program
The first step in implementing an integrated risk management process involves conducting a thorough assessment of existing risk management practices.
This helps identify gaps and opportunities for improvement while establishing baseline metrics.
Next, organizations should develop their risk taxonomy and assessment criteria. This creates a common language for discussing and evaluating risks across different departments and functions.
The third phase focuses on selecting and implementing appropriate technology solutions. These tools should support risk assessment, monitoring, and reporting activities while integrating with existing business systems.
Finally, organizations must establish ongoing monitoring and review processes. Regular assessments help ensure the program remains effective and adapts to changing business conditions.
Integration With Business Operations
Successful integration of the integrated risk management program requires alignment with existing business processes.
This includes incorporating risk assessments into strategic planning, project management, and operational decision-making.
Risk data should flow seamlessly between different business units and systems. This enables real-time risk monitoring and faster response to emerging threats or opportunities.
Training and communication play vital roles in program integration. All employees need to understand their responsibilities within the risk management framework and how to use available tools and resources effectively.
Regular reviews and updates ensure the framework continues to meet organizational needs. This includes assessing the effectiveness of controls, updating risk assessments, and refining processes based on lessons learned.
Performance metrics help track the success of the integrated risk management program.
These might include reduced incident rates, improved regulatory compliance, or enhanced decision-making capabilities.
By following these guidelines, organizations can build and maintain an effective integrated risk management framework that supports their business objectives while managing risks appropriately.
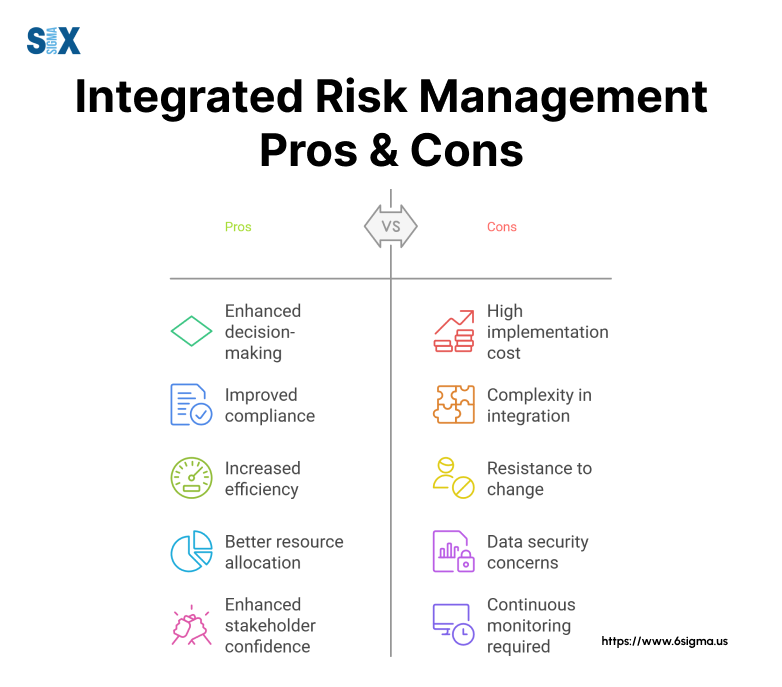
Benefits and Challenges of Implementing Integrated Risk Management (IRM)
Organizations implementing integrated risk management often experience significant improvements in their risk oversight capabilities.
However, the journey involves both notable advantages and potential hurdles that require careful navigation.
Strategic Advantages of an Integrated Approach
Enhanced decision-making stands out as a primary benefit of integrated risk management.
When organizations connect risk data across departments, leaders gain clearer insights for strategic planning and resource allocation.
Cost reduction represents another key advantage. By eliminating duplicate risk management efforts and streamlining processes, organizations typically see decreased operational expenses and improved resource utilization.
Improved regulatory compliance emerges naturally from a well-executed integrated approach to risk management.
The unified view of risk activities helps organizations stay ahead of regulatory requirements while reducing compliance-related costs.
Better stakeholder confidence results from more transparent risk reporting and management.
This enhanced visibility often leads to improved relationships with investors, regulators, and other key stakeholders.
Common Implementation Challenges
Cultural resistance often poses the first major hurdle in implementing best integrated risk management practices.
Employees and managers may resist changes to established processes or struggle with new responsibilities.
Technology integration challenges frequently arise when connecting various systems and data sources.
Legacy systems might not easily share data, requiring additional investment in integration solutions or system upgrades.
Resource constraints can limit implementation effectiveness. Organizations must balance the need for new tools and training against budget limitations and competing priorities.
Data quality issues may surface during integration efforts. Inconsistent data formats, outdated information, and gaps in risk documentation can complicate the implementation process.
Struggling with risk management implementation? Transform your approach with our Green Belt certification.
Measuring Success and ROI with Integrated Risk Management
Financial metrics provide concrete evidence of program success.
Organizations should track risk-related losses, compliance costs, and operational efficiencies to demonstrate ROI.
Operational improvements offer another measurement area.
This includes tracking metrics like:
- Reduced incident response times
- Decreased duplicate risk assessments
- Improved audit outcomes
- Enhanced regulatory compliance rates
Risk management maturity scores help organizations gauge their progress. Regular assessments can show advancement in risk identification, assessment, and response capabilities.
Stakeholder satisfaction provides valuable feedback on program effectiveness.
Regular surveys of business units, board members, and external stakeholders can reveal areas of success and improvement opportunities.
Process efficiency metrics highlight operational gains. Organizations should monitor improvements in risk assessment completion times, control testing efficiency, and reporting accuracy.
Integrated Risk Management Solutions and Tools
Modern integrated risk management demands robust technological support to handle complex risk data and processes effectively.
The right combination of tools and platforms can significantly enhance an organization’s risk management capabilities.
Essential IRM Technologies
Risk assessment platforms form the backbone of integrated risk management solutions.
These systems enable organizations to identify, evaluate, and track risks across multiple business units.
Advanced analytics capabilities help predict potential risks and their impact on business operations.
Automated workflow tools streamline risk management processes by coordinating activities between different stakeholders.
These systems handle everything from initial risk identification to final approval and monitoring stages.
Data visualization technologies transform complex risk information into actionable insights.
Interactive dashboards and reporting tools help stakeholders understand risk patterns and make informed decisions quickly.
Real-time monitoring systems provide continuous oversight of risk indicators. These tools alert relevant personnel when risk thresholds are breached, enabling swift response to emerging threats.
Selecting the Right Integrated Risk Management Solution
Integration capabilities should top the list of selection criteria for integrated risk management tools. The chosen solution must work seamlessly with existing business systems and data sources.
Scalability ensures the platform can grow with organizational needs. The solution should handle increasing data volumes and user numbers without performance degradation.
User experience matters significantly in adoption rates. The interface should be intuitive enough for occasional users while providing advanced features for risk management professionals.
Security features must meet both internal standards and regulatory requirements. This includes robust access controls, data encryption, and audit trails for all risk-related activities.
Leading IRM Platforms and Applications
Enterprise-grade solutions offer full-featured integrated risk management applications.
These platforms typically include:
- Risk assessment modules
- Compliance management tools
- Incident tracking systems
- Performance analytics
- Regulatory reporting capabilities
Mid-market solutions provide balanced functionality for growing organizations. These tools often focus on core risk management features while maintaining reasonable cost structures.
Industry-specific applications address unique requirements in sectors like financial services, healthcare, and manufacturing.
These specialized tools include pre-built templates and workflows tailored to specific regulatory frameworks.
Cloud-based solutions continue gaining popularity in the integrated risk management space. These platforms offer advantages in accessibility, updates, and maintenance while reducing infrastructure costs.
Mobile applications extend risk management capabilities to field personnel. These tools enable real-time incident reporting and risk assessments from any location.
When evaluating integrated risk management solutions, organizations should consider their specific needs, budget constraints, and growth plans.
A thorough assessment of available options helps ensure the selected tool aligns with both current requirements and future objectives.
Regular evaluation of tool effectiveness ensures continued alignment with organizational needs.
This includes monitoring user adoption rates, process efficiency improvements, and overall risk management performance.
Industry-Specific Applications of IRM
Different industries face unique risk challenges that require tailored integrated risk management approaches.
Financial Services Sector
Banks and financial institutions deploy integrated risk management to address market volatility, credit risks, and regulatory compliance.
Their focus often centers on maintaining capital adequacy while managing operational risks across multiple business lines.
Third-party risk management plays a crucial role in financial services, particularly when dealing with vendors, payment processors, and technology providers.
Financial institutions must monitor and assess these relationships continuously to maintain regulatory compliance and operational stability.
Credit risk assessment represents another key application area.
Banks use integrated risk management systems to evaluate borrower creditworthiness, monitor loan portfolios, and manage potential defaults across different market segments.
Healthcare Industry Applications
Healthcare organizations prioritize patient safety and data protection in their integrated risk management programs.
These institutions must balance clinical risks with operational efficiency while maintaining strict regulatory compliance.
Privacy protection demands significant attention due to sensitive patient data.
Healthcare providers implement specialized risk controls to safeguard electronic health records and ensure HIPAA compliance across all operations.
Manufacturing Sector Implementation
Manufacturing companies focus their integrated risk management efforts on operational safety, supply chain reliability, and quality control.
These organizations often deal with complex international operations requiring coordinated risk oversight.
Production line risk monitoring helps prevent costly disruptions. Manufacturers use integrated systems to track equipment performance, maintenance schedules, and potential failure points across their facilities.
Technology Sector Approaches
Technology companies emphasize cybersecurity and intellectual property protection in their integrated risk management strategies.
These organizations face rapidly evolving threats requiring dynamic risk assessment and response capabilities.
Product development risks require careful monitoring throughout the lifecycle. Tech companies use integrated systems to track technical debt, security vulnerabilities, and potential compliance issues during development.
Each industry’s integrated risk management example demonstrates how organizations adapt standard frameworks to address sector-specific challenges.
Success often depends on selecting appropriate tools and methodologies that align with industry requirements while maintaining flexibility for emerging risks.
Regular assessment and updating of industry-specific risk management practices ensure continued effectiveness.
The Future of Integrated Risk Management
The evolution of integrated risk-management continues to shape how organizations approach their risk management programs.
Key Takeaways for Risk Management Success
Effective risk management requires organization-wide commitment and clear strategic direction.
The most successful programs demonstrate strong leadership support, well-defined processes, and consistent execution across all business units.
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern risk management programs.
Organizations must leverage advanced tools and analytics to identify, assess, and monitor risks effectively while maintaining operational efficiency.
Staff engagement and training remain essential elements for program success. Regular education and clear communication help ensure all employees understand their roles in risk management activities.
Looking Ahead: The Evolution of IRM
Digital transformation continues to drive changes in integrated risk management practices.
Regulatory requirements grow more complex each year, demanding greater sophistication in risk management approaches.
Organizations need flexible frameworks that can adapt to new compliance demands without disrupting business operations.
Data analytics and artificial intelligence will reshape risk assessment capabilities. These technologies enable more accurate risk predictions and faster response times to emerging threats.
Environmental and social governance factors gain prominence in risk considerations. Organizations must expand their risk management programs to address these evolving stakeholder priorities.
Building for Tomorrow
Success in integrated risk management requires continuous improvement and adaptation.
Investment in risk management capabilities delivers long-term value.
Organizations that prioritize risk management development often see improved operational efficiency and stronger stakeholder relationships.
Cross-functional collaboration becomes increasingly important as risks become more interconnected.
Organizations must break down silos and foster cooperation between different business units and risk management teams.
The future of integrated risk management lies in balancing technological advancement with human expertise.
While automation and analytics provide powerful tools, experienced risk professionals remain essential for effective decision-making.
The journey toward mature integrated risk management never truly ends.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






