IDOV: A Systematic Approach to Design Excellence in Six Sigma
The IDOV methodology stands as a cornerstone of Design for Six Sigma (DFSS), offering organizations a structured path to product and process innovation.
This systematic approach breaks down complex design challenges into manageable phases, enabling teams to create solutions that meet exact customer specifications while maintaining quality standards.
Key Highlights
- Step-by-step IDOV implementation guide
- Tools for each design phase
- Real industry case applications
- Integration with modern methodologies
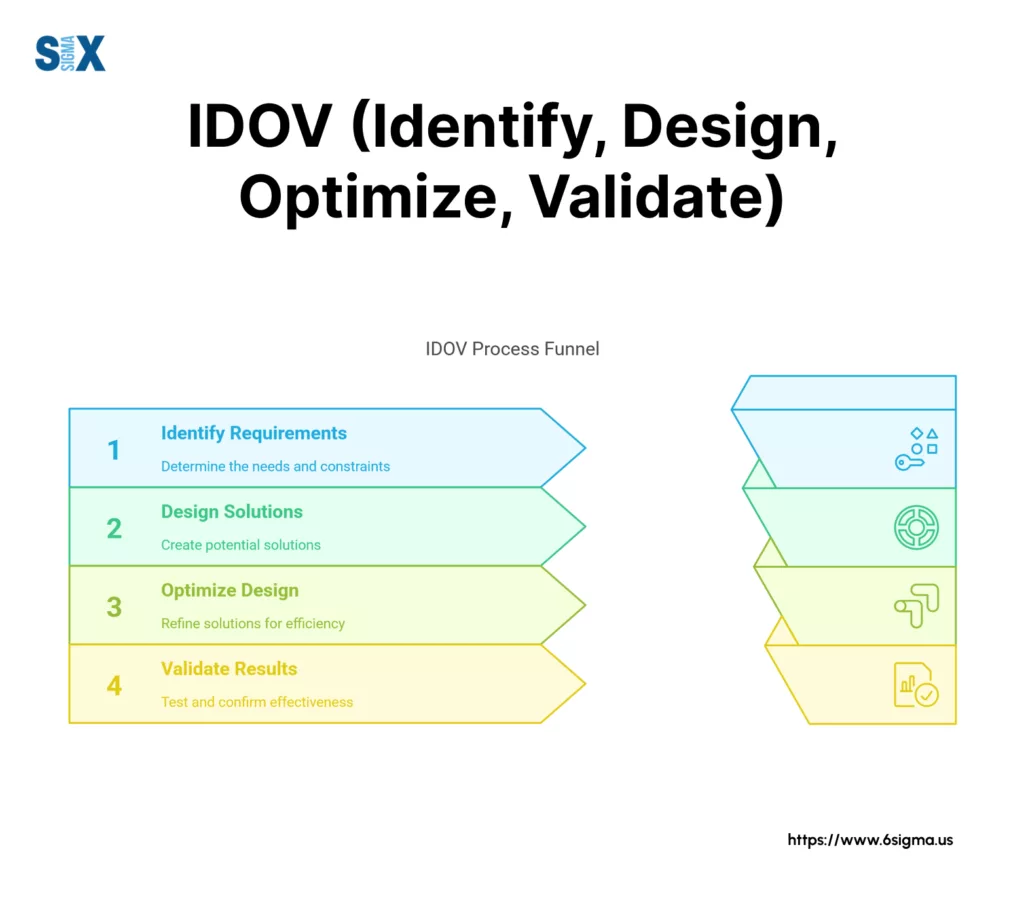
What Is IDOV And Why Does It Matter?
IDOV stands for Identify, Design, Optimize, and Validate – a structured methodology within Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) that guides organizations through new product and process development.
This approach differs from traditional improvement methods by focusing on creating new solutions rather than fixing existing processes.
Origins And Purpose Of IDOV
The IDOV methodology emerged from the Six Sigma movement in the late 1990s when organizations needed a systematic approach to design products that met customer requirements from the start.
Unlike reactive improvement methods, IDOV takes a proactive stance toward quality by building it into the design phase.
Quality management professionals use IDOV to ensure new products and processes achieve Six Sigma quality levels before launch.
This preventive approach reduces the need for costly corrections and improvements after implementation.
Role of IDOV In Design For Six Sigma
Within the DFSS framework, IDOV serves as the primary roadmap for design projects.
The methodology connects customer requirements directly to design specifications, ensuring final products meet market needs while maintaining manufacturing feasibility.
Manufacturing engineers and process specialists rely on IDOV to:
- Transform customer requirements into technical specifications
- Create designs that meet quality targets
- Develop processes capable of consistent production
- Validate designs before full-scale implementation
IDOV vs Traditional Design Approaches
Traditional design methods often rely on intuition and experience, leading to multiple revision cycles. IDOV brings statistical rigor and data-driven decision-making to the design process.
Project managers appreciate this structured approach as it provides clear metrics and milestone checks throughout development.
Implementation Framework
The IDOV methodology follows a logical progression through each phase:
Identify Phase: Teams gather customer requirements and translate them into measurable specifications.
Design Phase: Engineers develop solutions that meet identified requirements while considering manufacturing capabilities.
Optimize Phase: Statistical tools fine-tune designs for maximum performance and reliability.
Validate Phase: Testing confirms that designs meet all requirements under actual conditions.
This systematic progression helps Six Sigma practitioners maintain control over complex design projects while ensuring quality outcomes.
Each phase builds upon previous work, creating a solid foundation for successful product launches.
Master the IDOV Methodology with Green Belt Certification
Transform your design approach with structured Six Sigma techniques

The Four Phases Of IDOV Methodology
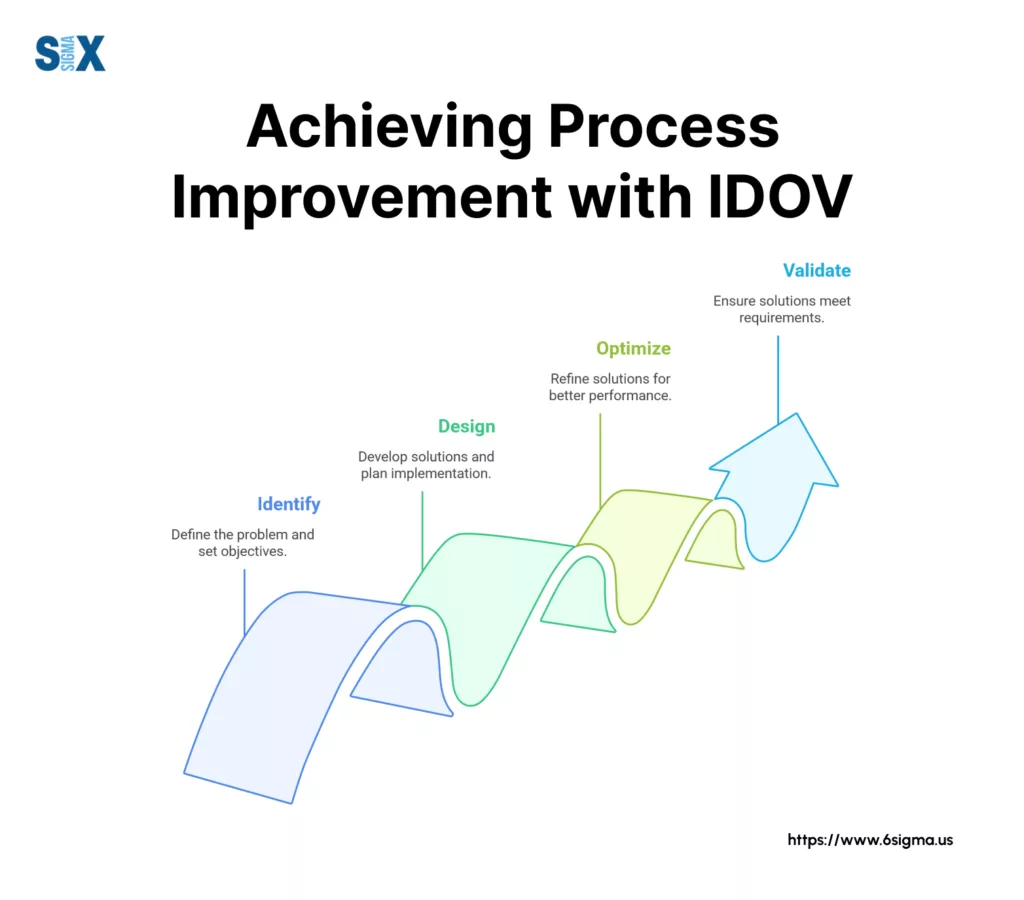
The IDOV methodology breaks down complex design projects into four distinct phases. Each phase builds upon the previous one, creating a logical progression from customer needs to validated solutions.
The Identify Phase: Setting The Foundation
The Identify phase focuses on gathering and analyzing customer requirements. Quality management teams start by collecting Voice of Customer (VOC) data through surveys, interviews, and market research.
This data transforms into Critical to Quality (CTQ) characteristics, which become the measurable targets for the design process.
Project managers develop the charter during this phase, outlining:
- Project scope and objectives
- Team roles and responsibilities
- Resource requirements
- Timeline milestones
Key tools used in the Identify phase include Quality Function Deployment (QFD), SIPOC diagrams, and CTQ trees.
The Design Phase: Creating Solutions
During the Design phase, engineering teams develop potential solutions that meet the identified requirements.
This phase emphasizes creative problem-solving while maintaining technical feasibility.
Design activities include:
- Generating multiple concept designs
- Evaluating technical feasibility
- Conducting risk assessments
- Creating detailed specifications
Teams use tools like FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis), CAD software, and simulation models to support design decisions.
The Optimize Phase: Refining The Design
The Optimize phase focuses on maximizing design performance while considering manufacturing capabilities and cost constraints. Process improvement specialists use statistical tools to fine-tune design parameters.
- Optimization activities involve:
- Statistical Design of Experiments (DOE)
- Process capability studies
- Tolerance analysis
- Cost-benefit evaluations
Manufacturing engineers play a crucial role in ensuring designs meet production requirements while maintaining quality standards.
The Validate Phase: Ensuring Success
The final phase confirms that the design meets all requirements under actual conditions. Six Sigma practitioners conduct rigorous testing and verification procedures.
- Validation includes:
- Prototype testing
- Performance verification
- Process capability confirmation
- Documentation completion
Teams use reliability testing, measurement system analysis, and control plans to ensure sustained quality performance.
Each IDOV phase requires specific tools and techniques, creating a structured approach to design excellence.
This methodology helps organizations deliver products and processes that consistently meet customer requirements while maintaining efficiency in development and production.
The success of IDOV implementation depends on proper execution of each phase, with careful attention to documentation and data-driven decision-making.
Modern digital tools enhance these activities, enabling faster development cycles and more accurate predictions of design performance.
IDOV vs. DMAIC: Understanding The Key Differences
While both IDOV and DMAIC belong to the Six Sigma family, they serve distinctly different purposes in quality improvement.
IDOV focuses on creating new products or processes, while DMAIC addresses existing process improvements.
Fundamental Methodology Differences
IDOV emphasizes design excellence from the start, making it ideal for new product development. The methodology prevents quality issues through careful planning and validation before implementation.
DMAIC, however, tackles existing processes that need improvement, focusing on identifying and eliminating defects.
Quality management professionals select between these methodologies based on project goals.
IDOV suits greenfield projects where teams start from scratch, while DMAIC excels in improving established operations.
When To Use Each Approach
IDOV proves most effective when:
- Developing new products
- Creating new processes
- Designing services from scratch
- Implementing revolutionary changes
DMAIC delivers better results for:
- Improving existing processes
- Reducing current defects
- Optimizing operational efficiency
- Making incremental improvements
Benefits And Trade-offs with IDOV
The IDOV methodology offers several advantages:
- Prevents quality issues before production
- Reduces long-term improvement costs
- Creates optimized designs from the start
- Ensures customer requirements drive development
However, IDOV requires:
- Longer initial development time
- Higher upfront investment
- More extensive planning
- Specialized expertise
Integration With Modern Practices
Modern Six Sigma practitioners often combine elements of both methodologies.
Digital tools enable teams to simulate and test designs virtually, reducing the traditional time constraints of IDOV implementation.
Project managers increasingly integrate Agile principles with IDOV, creating hybrid approaches that maintain quality while increasing development speed.
Impact of IDOV and DMAIC On Project Success
Manufacturing engineers and process specialists report higher first-time success rates with IDOV for new designs.
The structured approach reduces the need for post-implementation fixes, leading to lower total project costs despite higher initial investment.
DMAIC remains essential for continuous improvement initiatives, complementing IDOV by addressing issues that emerge after implementation.
Together, these methodologies provide a complete toolkit for quality management across the product lifecycle.
Resource Requirements
Teams implementing IDOV need:
- Design expertise
- Statistical analysis capabilities
- Advanced modeling tools
- Cross-functional collaboration
This resource intensity often influences methodology selection, particularly in smaller organizations or time-sensitive projects.
The choice between IDOV and DMAIC significantly impacts project outcomes.
Understanding these differences helps quality professionals select the most appropriate methodology for their specific needs, ensuring efficient use of resources and optimal results.
Elevate Your Quality Management Skills with Black Belt Expertise
Implementing IDOV: Best Practices And Challenges
Common Implementation Hurdles
Organizations often face several challenges when implementing IDOV methodology. Resource allocation typically presents the first major obstacle, as teams must balance detailed analysis with project timelines.
Quality management professionals frequently encounter resistance from stakeholders who prefer traditional development approaches.
Technical teams struggle with data collection during the Identify phase, particularly when gathering accurate Voice of Customer information.
The translation of customer requirements into measurable specifications demands significant expertise and time investment.
Critical Success Factors of IDOV
Successful IDOV implementation relies on several key elements. Strong executive sponsorship proves essential for securing necessary resources and maintaining project momentum.
Cross-functional team collaboration enables better decision-making throughout the design process.
Process improvement specialists emphasize the importance of:
- Clear project scope definition
- Regular stakeholder communication
- Robust data collection methods
- Proper tool selection and usage
Industry-Tested Best Practices
Manufacturing engineers have developed effective practices for IDOV implementation. Starting with pilot projects helps teams gain experience while managing risks.
Digital simulation tools reduce physical prototyping needs, accelerating the validation phase.
Project managers should establish:
- Regular review checkpoints
- Clear decision-making protocols
- Documentation standards
- Performance metrics tracking
Digital Integration Strategies of IDOV
Modern IDOV implementation increasingly relies on digital tools. Virtual modeling and simulation software enable teams to test designs before physical prototyping.
Cloud-based collaboration platforms facilitate remote team coordination and documentation sharing.
Agile Integration Techniques
Organizations now combine IDOV with Agile principles to increase flexibility. Sprint-based approaches within each IDOV phase allow for faster iterations while maintaining quality standards.
This hybrid model particularly benefits software and technology projects.
Risk Mitigation Approaches of IDOV
Successful teams develop robust risk management strategies. Early identification of potential issues through FMEA helps prevent costly delays.
Regular validation of assumptions throughout the process ensures alignment with project goals.
Training And Skill Development
Teams require specific skills for effective IDOV implementation:
- Statistical analysis capabilities
- Design thinking methodologies
- Project management expertise
- Quality tools proficiency
Organizations should invest in training programs to build these competencies across their teams.
Measuring Implementation Success with IDOV
Key performance indicators help track IDOV effectiveness:
- Design cycle time reduction
- First-time quality rates
- Customer satisfaction scores
- Development cost metrics
Regular monitoring of these metrics enables continuous improvement of the IDOV process itself.
Remote Implementation Considerations
Modern work environments demand adapted IDOV practices. Virtual collaboration tools support remote team coordination.
Digital documentation systems ensure information accessibility across locations. Regular virtual check-ins maintain team alignment and progress tracking.
The success of IDOV implementation depends on careful attention to these elements while maintaining flexibility to adapt to specific organizational needs.
Regular assessment and adjustment of implementation strategies ensure continuous improvement of the methodology’s effectiveness.
Industry-Specific Applications Of IDOV
Manufacturing Sector Implementation
Manufacturing organizations utilize IDOV methodology to design new production processes and products.
Automotive manufacturers apply IDOV principles when developing new vehicle components, ensuring quality standards from initial design through final production.
The methodology proves particularly effective in reducing prototype iterations and manufacturing defects.
Process improvement specialists in electronics manufacturing leverage IDOV to design assembly lines that meet Six Sigma quality levels.
These implementations focus heavily on automation integration and quality control systems, resulting in significantly reduced defect rates and improved production efficiency.
Service Industry Adaptations
Service organizations modify IDOV to address unique customer experience challenges. Banking institutions apply the methodology when designing new financial products, focusing on customer interaction points and regulatory compliance.
he Identify phase receives particular attention, with extensive Voice of Customer analysis shaping service delivery models.
Quality management professionals in hospitality sectors adapt IDOV for service process design.
Hotels use the methodology to create check-in procedures and guest experience protocols, measuring success through customer satisfaction metrics and operational efficiency.
Healthcare Applications
Healthcare facilities implement IDOV when designing patient care protocols and medical procedures. The methodology helps ensure patient safety while optimizing resource utilization.
Hospitals apply these principles to design emergency response procedures and patient flow systems.
Medical device manufacturers combine IDOV with regulatory requirements to create products that meet both quality standards and compliance needs.
The Validate phase becomes particularly crucial, incorporating extensive testing and documentation requirements specific to healthcare regulations.
Technology Sector Innovation
Software development teams adapt IDOV principles to create robust applications and systems.
The methodology integrates with Agile practices, allowing for rapid iteration while maintaining quality standards.
Development teams focus on user experience metrics during the Identify phase and automated testing during Validation.
Technology hardware manufacturers employ IDOV in product development cycles. The methodology guides the creation of quality-focused design specifications and testing protocols.
These implementations often emphasize the Optimize phase, using advanced simulation tools to predict performance.
Cross-Industry Success Factors
Several elements remain consistent across successful IDOV implementations:
- Clear alignment with industry-specific regulations
- Customized measurement systems
- Adapted validation procedures
- Industry-appropriate tools and techniques
Digital Transformation Impact of IDOV
Modern IDOV implementations across industries increasingly incorporate digital tools. Manufacturing plants utilize digital twins for process design.
Healthcare facilities employ simulation software for procedure development. Service organizations leverage data analytics for customer experience optimization.
Industry-Specific Challenges
Each sector faces unique challenges in IDOV implementation:
- Manufacturing requires extensive equipment validation
- Healthcare demands strict compliance documentation
- Service industries need flexible adaptation capabilities
- Technology sectors require rapid implementation cycles
Project managers must address these challenges while maintaining IDOV methodology integrity.
Future Industry Trends
Emerging trends shape IDOV applications across sectors. Remote implementation capabilities grow increasingly important.
Integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning tools enhances predictive capabilities. Industry-specific digital platforms facilitate methodology deployment.
The versatility of IDOV methodology allows for effective adaptation across diverse industries while maintaining core quality principles.
Success depends on proper customization to industry-specific requirements while preserving the fundamental structure of the methodology.
Unlock Design Innovation with Our DFSS Certification Program
Moving Forward With IDOV Implementation
The IDOV methodology continues to grow as organizations adapt it to modern business challenges.
This structured approach to design excellence proves valuable across industries, from manufacturing to healthcare and technology sectors.
The integration of digital tools and Agile principles has enhanced its effectiveness while maintaining the core focus on quality and customer satisfaction.
Quality management professionals should focus on tailoring IDOV implementation to their specific organizational needs.
Success depends on proper resource allocation, team training, and stakeholder engagement throughout all phases.
The growing emphasis on remote work necessitates adapted implementation strategies that maintain methodology effectiveness across distributed teams.
Organizations starting their IDOV journey should begin with pilot projects, gradually expanding application as teams gain experience and expertise.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







