Cost of Non-Conformance in Lean Six Sigma. Everything to Know
Quality amid the present’s intense commercial scenery decides achievement or inability.
Neglecting benchmarks and consumer satisfaction dangers substantive expenses from inconsistencies. These sums come in various like rework, trash, guarantees, obligations, or lost business.
Grasping inconsistency’s expenses remains fundamental for benefit, clients’ joy, and contention.
By distinguishing and tending to fundamental driver quality, organizations execute concentrated enhancements, streamline cycles, and in the end diminish budgetary weights from inconsistencies.
Key Highlights
- Understanding inconsistencies’ expenses proves pivotal for associations distinguishing and mitigating quality issues, diminishing waste, and improving benefits.
- Such expenses incorporate avoidance, evaluation, inside disappointment, and outside disappointment expenses.
- Exact inconsistency estimating permits powerful quality administration and expense advantage examinations.
- Distinguishing essential drivers and amendable activities battle fundamental issues causing inconsistencies.
- Six Sigma, Lean Making, and Total Quality the board essentially decreases inconsistencies’ expenses.
What is the Cost of Non-Conformance?
Guaranteeing items and administrations meet prerequisites remains fundamental for any endeavor achievement. Then again, deviations from these standards can lead to gigantic inconsistencies in expenses.
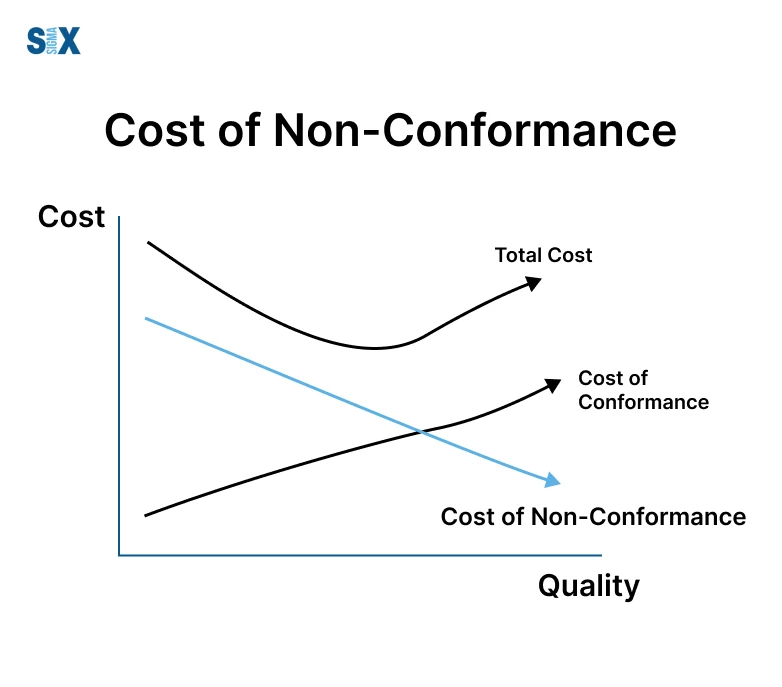
This involves direct and roundabout outflows because of item or administration imperfections, mistakes, or disappointment in meeting client desires.
Non-conformance costs assume a basic part in quality administration as they reflect the monetary effect of poor quality. It remembers costs like rework, trash, guarantees, client displeasure, or potential lawful liabilities.
Neglecting inconsistencies deteriorates benefits, harms image, and hinders challenge.
Understanding inconsistencies’ expenses empower focusing upgrade, and asset designation accurately.
By recognizing and limiting fundamental drivers, organizations decrease waste and enhance client fulfillment, and trustworthiness enduringly.
Types of Cost of Non-Conformance
Non-conformance costs can be broadly categorized into four main types:
- Prevention Costs
These are the costs associated with preventing defects or non-conformities from occurring in the first place. Prevention costs include quality planning, employee training, process design and documentation, supplier evaluations, and other proactive quality management activities. - Appraisal Costs
Appraisal costs are incurred to evaluate processes, products, or services for conformance with quality standards. Examples include costs for inspection, testing, audits, calibration of measuring equipment, and associated supplies and materials. - Internal Failure Costs
Internal failure costs arise from non-conformities discovered before delivery to the customer. This includes costs of rework or repair, scrap, re-inspection, process downtimes, and failure analysis efforts. - External Failure Costs
These are the most critical non-conformance costs as they occur after delivery to the customer. External failure costs cover returned products, warranty claims, complaint handling, product liability costs, lost sales due to defects, and costs associated with a damaged reputation.
Of these four categories, the prevention costs are voluntary while the other three (appraisal, internal failures, external failures) are unavoidable once non-conformances exist.
Effective quality management optimizes prevention costs to minimize the other non-conformance costs.
Some key examples of internal and external non-conformance costs include:
Internal:
- Rework/repair labor and material costs
- Costs of scrap, spoilage, waste
- Re-inspection and re-testing costs
- Production downtime costs
External:
- Customer returns, refunds, replacements
- Warranty service and repair costs
- Liability costs from product safety issues
- Lost sales and lost customer goodwill
Measuring and Quantifying Cost of Non-Conformance
To effectively manage and reduce the cost of non-conformance, it is crucial to accurately measure and quantify these costs within an organization. Quantifying non-conformance costs allows companies to understand the true financial impact and prioritize areas for improvement.
There are several methods and techniques used to measure non-conformance costs:
- Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) Measurement: This approach categorizes and tracks the costs associated with non-conformances, including prevention costs, appraisal costs, internal failure costs, and external failure costs. By capturing data on rework, scrap, warranty claims, and customer complaints, organizations can calculate the total cost of poor quality.
- Process Mapping and Activity-Based Costing: By mapping out processes and identifying non-conformance points, companies can use activity-based costing to assign costs to specific activities related to non-conformances, such as rework, inspection, and corrective actions.
- Quality Cost Reporting System: Implementing a formal quality cost reporting system allows organizations to systematically collect, analyze, and report on quality-related costs, including those associated with non-conformances. This data can be used to identify trends, set benchmarks, and track improvement initiatives.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): FMEA is a risk analysis tool used to identify potential failure modes, their causes, and effects. By quantifying the risk priority numbers (RPNs) associated with each failure mode, organizations can prioritize non-conformance areas that have the highest potential impact.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC techniques, such as control charts, can help detect process variations and non-conformances in real time. By monitoring and analyzing SPC data, companies can quantify the costs associated with process non-conformities and take corrective actions.
Accurate measurement and quantification of non-conformance costs are essential for effective quality management and cost reduction efforts. By understanding the true financial impact of non-conformances, organizations can prioritize improvement initiatives, allocate resources effectively, and track the return on investment (ROI) of quality programs.
Root Cause Analysis and Corrective Actions
Identifying and addressing the root causes of non-conformances is crucial for effectively reducing associated costs in the long run. Root cause analysis (RCA) is a structured approach to identifying the underlying sources of problems or defects that lead to non-conformances.
The goal of RCA is to go beyond merely treating the symptoms and instead uncover the systemic issues contributing to non-conformances. Common root cause analysis techniques include:
- 5 Whys Analysis: Repeatedly asking “why” to peel back layers of symptoms.
- Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagrams: Visually mapping potential causes across categories like people, methods, materials, etc.
- Fault Tree Analysis: Using logic gates to identify combinations of events leading to failures.
Once root causes are identified, organizations can develop and implement targeted corrective actions and preventive actions (CAPA) to address those root causes systematically.
Corrective actions focus on eliminating detected non-conformances and preventing their recurrence. This could involve process improvements, additional controls, training, updating documentation, etc.
Preventive actions aim to proactively prevent potential non-conformances from occurring in the first place by addressing root causes before issues manifest. Examples include design changes, mistake-proofing, enhanced inspections, etc.
Rigorous root cause analysis combined with robust corrective and preventive actions enables organizations to address non-conformances at their source rather than dealing with costly symptoms perpetually. This closed-loop quality system is essential for driving down the cost of non-conformance over time.
Reducing Cost of Non-Conformance through Quality Initiatives
Implementing robust quality initiatives is critical for organizations to reduce non-conformance costs and improve profitability. Some proven strategies include:
Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims to minimize defects and variability in processes.
Lean manufacturing principles focus on eliminating waste and optimizing workflow. Combining these approaches leads to streamlined processes with fewer non-conformities, resulting in significant cost savings from reduced rework, scrap, and failure costs.
Total Quality Management (TQM) & Cost of Non-Conformance
TQM is a comprehensive management approach centered on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
It involves processes like quality planning, quality assurance, quality control, and quality improvement. Effective TQM implementation drives down costs of non-conformance through prevention, early detection, and systematic elimination of root causes.
Advanced Quality Planning
Rigorous quality planning like Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) enables organizations to anticipate potential non-conformities proactively. Developing control plans with statistical process control and control charts allows monitoring of critical quality characteristics to prevent issues.
Quality Audits and Standards
Conducting regular internal and external quality audits ensures processes conform to requirements and standards like ISO 9001. This helps identify non-conformances early for correction before they result in major failure costs.
Employee Training and Culture with Cost of Non-Conformance
A quality-focused culture backed by comprehensive training equips employees with skills for quality assurance and control. This empowers them to prevent, identify, and address non-conformities effectively.
By deploying a strategic mix of these quality initiatives, organizations can drastically reduce the costs stemming from non-conformances across their operations and product lines. However, prioritizing initiatives requires a cost-benefit analysis as covered next.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Quality Improvement
Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis is crucial when evaluating quality improvement initiatives aimed at reducing the cost of non-conformance. This analysis weighs the potential benefits of decreased quality costs against the investment required to implement the improvement measures.
When considering quality improvement programs like Six Sigma, Lean Manufacturing, or Total Quality Management (TQM), organizations must assess the cost of poor quality they are currently experiencing.
The cost of non-conformance, including rework, scrap, warranty claims, and liability costs, provides a baseline to compare against the projected costs of rolling out quality initiatives.
Potential cost savings from reducing defects, increasing efficiency, and improving customer satisfaction can be substantial.
However, training employees, investing in new technology, restructuring processes, and hiring quality experts involves upfront and ongoing expenditures. Cost-benefit analysis helps determine if the projected return on investment justifies the costs.
Quality tools like failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) and statistical process control (SPC) methods enable more accurate forecasting of potential improvements. Modeling different scenarios and their associated costs versus benefits over time provides better visibility for decision-making.
Ultimately, the cost-benefit analysis should extend beyond just short-term financial impacts. The long-term competitive advantages of a robust quality management system – improved reputation, increased customer loyalty, higher employee engagement, etc. – are critical considerations. Organizations must weigh both the tangible and intangible factors holistically.
Conclusion and Best Practices for Cost of Non-Conformance
Minimizing the cost of non-conformance should be a top priority for any organization committed to quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
By understanding the different types of non-conformance costs, accurately measuring and quantifying them, conducting thorough root cause analysis, and implementing proven quality initiatives, companies can significantly reduce these costs and improve their bottom line.
Some best practices to reduce the cost of non-conformance include:
- Foster a culture of quality: Embed quality principles and practices throughout the organization, from top leadership to front-line employees. Encourage everyone to take ownership of quality and continuously seek ways to improve processes and products.
- Invest in employee training: Provide comprehensive training programs to ensure employees have the knowledge and skills necessary to perform their jobs effectively and consistently meet quality standards.
- Implement robust quality management systems: Establish a comprehensive quality management system that encompasses quality planning, control, assurance, and improvement activities. Regularly review and update these systems to align with industry best practices and evolving customer needs.
- Leverage data and analytics: Collect and analyze data on non-conformance incidents, root causes, and associated costs. Use this information to identify trends, prioritize improvement efforts, and measure the effectiveness of corrective actions.
- Encourage continuous improvement: Promote a mindset of continuous improvement and empower employees to identify and address non-conformities proactively. Implement programs like Six Sigma, Lean Manufacturing, or Kaizen events to drive ongoing process optimization.
- Collaborate with suppliers and customers: Engage with suppliers to ensure they meet quality requirements and provide them with feedback and support for improvement. Similarly, work closely with customers to understand their evolving needs and incorporate their feedback into quality initiatives.
By adopting these best practices and remaining vigilant in their pursuit of quality excellence, organizations can minimize the costly impact of non-conformance and gain a competitive advantage in their respective markets.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






