Understanding Cost of Conformance: All You Need To Know
Requirements are evolving rapidly, guaranteeing quality and meeting industry protocols underpins survival.
However, compliance comes with a “conformity cost” tag – assets, efforts, and investments maintaining oversight and remedies.
These quality assurance outlays include defect prevention, checks, and non-meeting fixes. Importantly, conformity costs impact enterprises enormously across fields.
Ignoring such expenses risks sizable monetary losses, reputation harm, and even legal troubles.
Well-governed conformity costs streamline processes, cut waste, and boost client happiness though. This uplifts earnings and durable achievements in the end.
Key Highlights
- Grasping conformity’s expenses underpins upholding quality requirements and rules for enterprises.
- These costs cover prevention, testing, and in-network flaw charges alike. Prudently directing them invites upgraded productivity and satisfaction while throwing less away.
- Methods like refining processes, quality administration systems, and worker education minimize compliance fees. Constantly tracking and examining such costs flags upgrade spots and bolsters choices with real insight.
- Industry leaders’ and fields’ prosperous practices grant perception into dependably guiding compliance budgets. None improve alone – our shared comprehension elevates each identity continuously.
- By regularly re-evaluating jointly and bettering cooperatively, enterprises fortify capacity serving ever-evolving urges.
- Their steady focus lifts client and public interest through hindrances unsurprisingly lying ahead on standards’ and desires’ unflagging progression. Progress indeed follows such cooperative dedication.
- Comprehension and betterment together nourish constant enhancements across enterprises, elevating every pursuit and those it serves. Our united strides light pathways for accessibility, optimization and prosperity for all.
What is the Cost of Conformance?
Organizations need to follow strict protocols, standards, and client prerequisites. Failing risks hefty penalties, trust losses, and reputation harm. Accordingly, conformity costs command focus.
These costs cover guaranteeing outputs, administrations, and cycles fulfill necessities, provisions, and desires through arranging, counteractive actions, testing, and references.
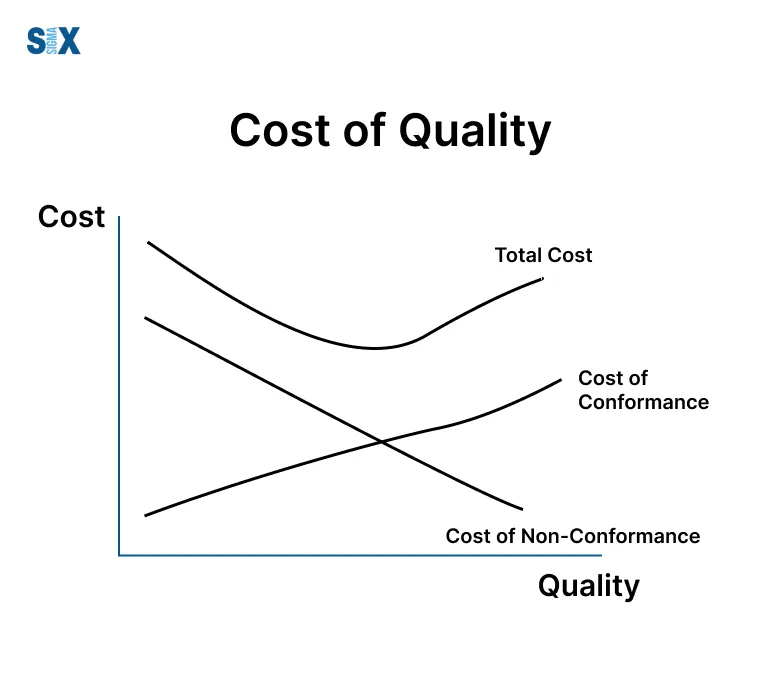
While appearing unavoidable, the cost proves indispensable considering the results of disobedience – returns, lawful issues, penalties, and piece misfortune jeopardizing endurance.
Comprehending and prudently handling such costs remains vital for focused survival and request serving. None enhance alone – joined comprehension elevates benefit for all through consistent cooperative strides amidst unforeseen difficulties progressively encountered.
Through shared duty and upgraded comprehension, enterprises enhance resilience by serving evolving needs.
Their constant upgrades through joint exams and betterment champion accessibility, supportability, and prosperity enduringly. Progress pursues the way of numerous personalities and hearts as one.
Components of Cost of Conformance
The cost of conformance refers to the expenses incurred by an organization to ensure its products, services, or operations comply with relevant standards, regulations, and customer requirements. It encompasses various cost elements that can be categorized into four main groups:
Prevention Costs
These are the costs associated with activities aimed at preventing defects or non-conformities from occurring in the first place. Examples include:
- Quality planning and system design
- Product or process design reviews
- Quality training for employees
- Supplier evaluation and qualification
Appraisal Costs
Appraisal costs are incurred to evaluate products, services, or processes to ensure they meet specified requirements. These costs cover activities such as:
- Incoming material inspection
- In-process and final inspections
- Product testing and validation
- Quality audits (internal and external)
- Calibration of measuring and test equipment
Internal Failure Costs within Cost of Conformance
These costs arise when defects or non-conformities are detected before the product or service is delivered to the customer. Internal failure costs may include:
- Rework or rectification of defective items
- Waste and scrap from defective production
- Re-inspection or retesting after rework
- Downtime due to process failures
External Failure Costs within Cost of Conformance
External failure costs are incurred when defects or non-conformities are discovered after the product or service has been delivered to the customer. These costs can be significant and may involve:
- Processing customer complaints and returns
- Product recalls or replacements
- Warranty claims and repairs
- Potential legal liabilities or fines
Benefits of Managing Cost of Conformance
Effectively managing the cost of conformance can provide significant benefits to organizations across industries. By proactively controlling conformance costs, companies can improve profitability, enhance customer satisfaction, and mitigate risks.
Improved Profitability
One of the primary advantages is increased profitability. By optimizing quality processes and minimizing costs associated with prevention, appraisal, and failure, organizations can reduce their overall operational expenses.
Efficient quality management systems help eliminate waste, rework, and product defects, leading to cost savings that directly impact the bottom line.
Competitive Advantage with Cost of Conformance
Managing conformance costs effectively can also give companies a competitive edge in the market.
By delivering high-quality products and services consistently, organizations can build a reputation for excellence, fostering customer loyalty and attracting new business opportunities. This can lead to increased market share and a stronger brand image.
Regulatory Compliance
In many industries, adhering to quality standards and regulatory requirements is essential. Failure to comply can result in costly fines, legal issues, and damage to a company’s reputation.
By implementing robust quality management systems and controlling conformance costs, organizations can ensure compliance with relevant regulations, avoiding potential penalties and legal complications.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction with Cost of Conformance
Customers expect products and services to meet their expectations and conform to specified requirements.
By managing conformance costs effectively, companies can consistently deliver high-quality offerings, leading to increased customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and provide positive word-of-mouth, contributing to business growth and success.
Risk Mitigation
Uncontrolled conformance costs can expose organizations to various risks, such as product recalls, liability claims, and reputational damage.
By proactively managing these costs through quality assurance, quality control, and process improvement initiatives, companies can identify and address potential issues before they escalate, mitigating risks and protecting their brand reputation.
Continuous Improvement
Effective management of conformance costs often involves implementing continuous improvement processes.
By regularly analyzing quality data, identifying areas for optimization, and implementing corrective actions, organizations can foster a culture of ongoing improvement. This can lead to increased efficiency, reduced waste, and a competitive advantage in the long run.
Strategies for Reducing Cost of Conformance
Implementing effective strategies to reduce the cost of conformance can lead to significant savings and improved profitability for organizations. Here are some key strategies to consider:
Process Standardization and Optimization
Standardizing and optimizing processes can streamline operations, reduce errors and rework, and increase efficiency.
This involves mapping out processes, identifying bottlenecks and redundancies, and implementing lean methodologies to eliminate waste and non-value-added activities. Automation and digitization can also play a crucial role in optimizing processes and reducing conformance costs.
Employee Training and Awareness
Investing in employee training and awareness programs can significantly reduce the cost of conformance.
Well-trained employees are less likely to make mistakes, leading to fewer defects, reworks, and non-conformances. Training should cover quality standards, compliance requirements, and the importance of adhering to established processes and procedures.
Supplier Management and Collaboration
Effective supplier management and collaboration can help reduce the cost of conformance by ensuring that raw materials, components, and services meet the required quality standards.
This involves establishing clear quality requirements, conducting supplier audits and evaluations, and fostering open communication and collaboration with suppliers.
Continuous Improvement Culture
Fostering a culture of continuous improvement is essential for reducing the cost of conformance over the long term.
This involves encouraging employees to identify opportunities for improvement, implementing quality circles or kaizen events, and continuously refining processes and procedures based on feedback and lessons learned.
Preventive Maintenance and Calibration
Regular preventive maintenance and calibration of equipment and instruments can help prevent breakdowns, errors, and non-conformances.
This not only reduces the cost of conformance but also improves product quality, reduces downtime, and extends the lifespan of equipment.
Quality Management System (QMS) Implementation
Implementing a robust Quality Management System (QMS) can provide a structured framework for managing quality and conformance processes.
A well-designed QMS can help streamline documentation, ensure compliance with regulations and standards, and facilitate continuous improvement efforts.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Leveraging data and analytics can help organizations make informed decisions about where to focus their efforts to reduce the cost of conformance.
This involves collecting and analyzing data related to non-conformances, defects, reworks, and other quality-related metrics to identify root causes and implement targeted improvements.
Measuring and Monitoring Cost of Conformance
Accurately measuring and monitoring the cost of conformance is crucial for organizations to gain insights into their quality management efforts and identify areas for improvement.
By tracking conformance costs, companies can make data-driven decisions to optimize their processes and allocate resources more effectively.
There are several methods and metrics organizations can use to measure the cost of conformance:
- Cost of Quality (COQ) Reporting: COQ reporting involves systematically collecting and analyzing data related to conformance and non-conformance costs. This includes prevention costs (e.g., quality planning, training), appraisal costs (e.g., inspections, audits), and internal/external failure costs.
- Quality Cost Metrics: Specific metrics like the Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) as a percentage of sales, prevention/appraisal cost ratios, and defect rates can provide quantifiable measures of conformance performance.
- Process Capability Analysis: Statistical tools like process capability indices (Cp, Cpk) assess how well a process is performing relative to its specified requirements, indicating the likelihood and associated costs of non-conformances.
- Quality Audits: Regular internal and external audits can identify non-conformances and estimate their costs based on rework, scrap, penalties, etc.
- Customer Feedback: Monitoring customer complaints, returns, and satisfaction levels offers insights into conformance from the customer’s perspective and associated costs.
Monitoring conformance costs is an ongoing process. Leading organizations establish review cycles (e.g., monthly, quarterly) to analyze cost data, identify trends, and benchmark against targets or industry standards.
Management tools like quality dashboards and scorecards provide visual overviews of key conformance metrics.
Best Practices and Examples of Cost of Conformance
Implementing best practices for managing the cost of conformance can significantly improve efficiency and profitability.
Leading companies across various industries have adopted strategies to minimize conformance costs while maintaining high-quality standards.
Manufacturing Industry: Toyota’s renowned Toyota Production System (TPS) places a strong emphasis on eliminating waste and promoting continuous improvement.
By empowering employees to identify and address quality issues at the source, Toyota has been able to minimize costs associated with non-conformance, such as rework, scrap, and customer complaints.
Healthcare Industry: Leading healthcare organizations, such as Mayo Clinic and Cleveland Clinic, have implemented robust quality management systems to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance.
By investing in preventive measures, such as staff training, process standardization, and regular audits, these organizations have reduced the costs associated with non-conformance, such as medical errors, readmissions, and legal liabilities.
Aerospace Industry: Companies like Boeing and Airbus have strict quality control measures in place to meet stringent aerospace regulations.
They employ advanced quality tools, such as statistical process control (SPC) and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), to identify and mitigate potential non-conformances during the design and manufacturing stages, thereby reducing costly rework and delays.
Software Industry: Companies like Microsoft and Google have adopted agile methodologies and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) practices to ensure software quality and compliance with industry standards.
By automating testing and quality assurance processes, these companies can identify and address non-conformances early in the development cycle, minimizing the cost of fixing defects later.
ISO Certification: Many companies across various industries have adopted the ISO 9001 Quality Management System as a best practice for managing the cost of conformance.
By implementing standardized processes, documentation, and regular audits, organizations can improve quality, reduce non-conformances, and enhance customer satisfaction, ultimately leading to cost savings and increased profitability.
Conclusion and Future Trends
The cost of conformance is a critical aspect of quality management and operational excellence. By effectively managing and minimizing these costs, organizations can improve their bottom line, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
As we look to the future, several trends are likely to shape the landscape of cost of conformance management:
- Increased adoption of automation and digitalization: The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation, can streamline quality processes, reduce human errors, and drive cost efficiencies.
- Emphasis on data-driven decision-making: Organizations will increasingly rely on data analytics and business intelligence tools to gather, analyze, and interpret quality data, enabling them to make informed decisions and identify areas for cost optimization.
- Shift towards proactive quality management: Rather than reacting to non-conformances, companies will focus on proactive measures, such as preventive maintenance, risk management, and predictive analytics, to anticipate and mitigate potential issues before they occur, reducing the overall cost of conformance.
- Collaboration and knowledge sharing: As the importance of quality management grows, there will be a greater emphasis on collaboration and knowledge sharing among industry peers, suppliers, and customers, fostering best practices and accelerating the adoption of effective cost of conformance strategies.
- Integration of quality management with sustainability initiatives: Organizations will increasingly recognize the interconnectedness of quality, cost, and sustainability, leading to the development of integrated strategies that address all three aspects simultaneously.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







