Contingency Planning: Safeguarding Your Business Against the Unexpected
Numerous uncertainties can disrupt business operations. May be it natural disasters to various cybersecurity threats, they all need an effective contingency plan.
What Makes Contingency Planning Essential?
Today a single disruption can trigger a chain reaction of problems.
Organizations must prepare for unexpected challenges as recent events like the global pandemic, supply chain disruptions, and increasing cyber threats have increased.
Through contingency plan the foundation of business operations is maintained during difficult times.
Key Highlight
- Risk Assessment and Strategy Development
- Implementation and Team Responsibilities
- Testing and Plan Maintenance
- Resource Management and Communication
What is Contingency Planning?
A structured approach that organizations use to prepare for potential emergencies, disruptions, or unexpected events is called as Contingency planning.
This strategic process involves identifying possible risks and developing specific action plans to address them effectively when they occur.
Breaking Down The Definition
Organizations use contingency planning to create backup strategies and alternative courses of action.
These plans outline exactly how a business will respond to various scenarios, from natural disasters to market shifts.
The goal is to minimize disruption and maintain essential operations during challenging times.
Think of contingency planning as your organization’s safety net – it catches you when unexpected events threaten to derail normal operations.
A well-crafted plan includes specific steps, designated responsibilities, and resource allocation strategies to handle various scenarios.
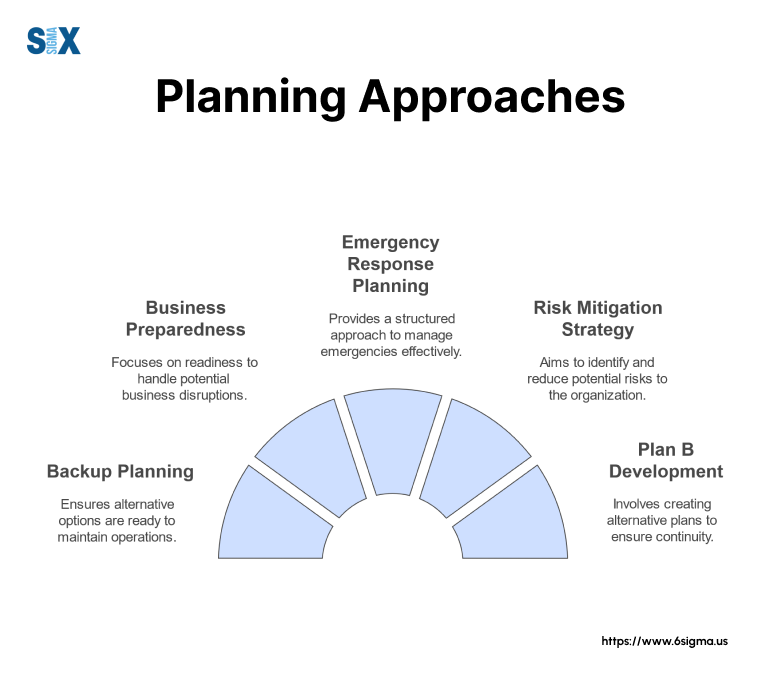
Different Names, Same Purpose
Many organizations refer to contingency planning by other names, including:
- Backup planning
- Business preparedness
- Emergency response planning
- Risk mitigation strategy
- Plan B development
While these terms might vary slightly in their specific focus, they all share the common goal of preparing organizations for unexpected challenges.
Setting Apart From Other Planning Types
Contingency planning differs from other risk management approaches in several key ways:
Mitigation Planning focuses on reducing the likelihood or impact of specific risks before they occur. For example, installing fire sprinklers to prevent fire damage.
Business Continuity Planning addresses how to maintain operations during any disruption, regardless of the cause. This planning type takes a broader view of organizational resilience.
Crisis Management Planning deals with immediate responses to emergencies as they happen, often focusing on communication and damage control.
The Role of Contingency Planning
Unlike these other approaches, contingency planning creates specific response strategies for identified risks.
It bridges the gap between prevention and response, ensuring organizations have clear directions when facing challenges.
For instance, a technology company might develop separate contingency plans for:
- Data center failures
- Supply chain disruptions
- Key personnel departures
- Cybersecurity breaches
Each plan would detail exact steps, responsibilities, and resources needed to address these specific scenarios.
Master the fundamentals of risk assessment and process control
With Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification. Learn how to identify, analyze, and mitigate operational risks.

Why Contingency Planning Matters
Recent global events have shown that businesses must prepare for unexpected disruptions.
Organizations that implement effective contingency planning gain significant advantages in managing crises and maintaining operations during challenging times.
Key Benefits of Strategic Planning
Proper contingency planning offers several measurable benefits to organizations. First, it reduces response time during emergencies by providing clear, pre-defined action steps.
When faced with a crisis, teams can immediately execute their planned responses rather than scrambling to develop solutions under pressure.
Financial protection stands out as another crucial benefit. Organizations with solid contingency plans typically experience lower recovery costs and shorter disruption periods.
These plans help preserve market share and maintain customer confidence during difficult times.
Employee confidence also increases when clear contingency plans exist. Staff members feel more secure knowing their organization has prepared for various scenarios, leading to better retention rates and higher productivity.
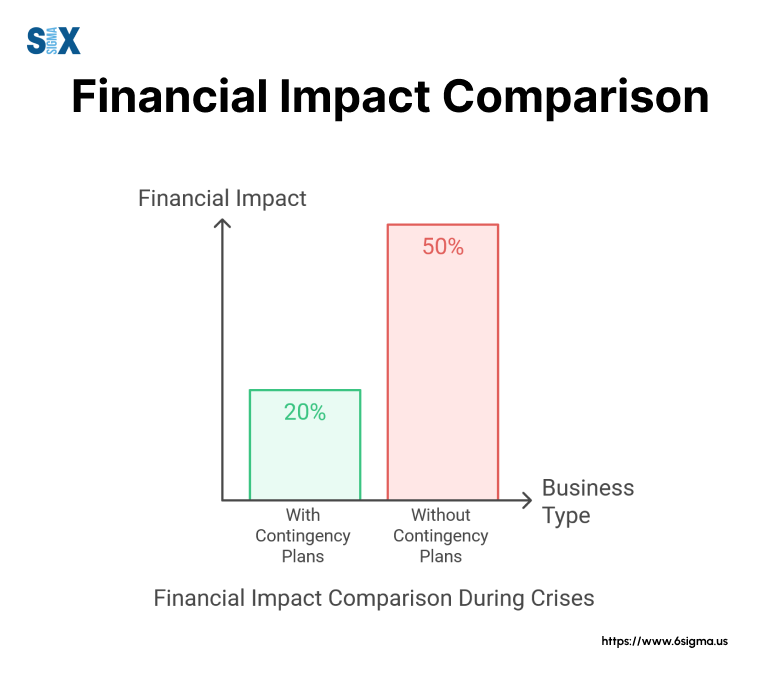
Risks of Operating Without A Contingency Plan
Organizations that skip contingency planning face several serious risks. Extended downtime during emergencies can lead to significant revenue losses and damaged customer relationships.
Without clear guidance, staff members might make costly mistakes during crisis response efforts.
Market share often suffers when businesses lack proper planning. Competitors with better preparation can step in to serve customers during disruptions, potentially leading to permanent customer loss.
Success Stories In Action
Several real-world examples demonstrate the value of contingency planning:
A major retailer maintained operations during widespread power outages by activating their backup power systems and alternative distribution networks.
Their advance planning helped them continue serving customers while competitors remained closed.
During the global pandemic, a manufacturing company quickly shifted to remote work operations thanks to their pre-established digital infrastructure and communication protocols.
This preparation allowed them to maintain productivity levels while ensuring employee safety.
A regional bank prevented significant data loss during a cybersecurity incident by immediately implementing their incident response plan.
Their quick action protected customer information and maintained trust in their services.
Long-Term Strategic Value of Contingency Planning
Beyond immediate crisis response, contingency planning provides lasting strategic advantages.
Organizations develop better risk awareness, stronger team coordination, and more resilient operations through the planning process. These improvements benefit daily operations, even when no crisis exists.
Regular plan updates and testing help organizations stay prepared for evolving threats while identifying areas for operational improvement.
This ongoing process creates a culture of readiness that strengthens the entire organization.
Types of Contingency Plans
Organizations need different types of contingency plans to address various risks and challenges.
Each type focuses on specific areas of vulnerability while working together to create a complete protection strategy.
Business Contingency Plans
Business contingency plans focus on maintaining critical operations during disruptions.
These plans typically address financial risks, supply chain interruptions, and staffing challenges.
For example, a retail business might create specific plans for:
- Sudden market changes
- Supply chain breakdowns
- Key supplier bankruptcies
- Leadership transitions
- Economic downturns
Environmental Contingency Plans
Natural disasters and environmental emergencies require specialized planning approaches.
These plans must account for both immediate response needs and long-term recovery strategies. Environmental contingency plans often include:
Weather-related emergencies like hurricanes, floods, or snowstorms require evacuation procedures and backup facility arrangements.
Chemical spills or hazardous material incidents need containment protocols and community safety measures. Fire emergencies demand clear evacuation routes and response procedures.
Technology Contingency Planning
Modern businesses rely heavily on technology, making tech-focused contingency plans essential.
These plans address various scenarios that could impact digital operations:
Data breaches require immediate response protocols to protect sensitive information. System failures need backup systems and data recovery procedures.
Power outages demand alternative power sources and manual operation procedures.
Industry-Specific Plans
Different industries face unique challenges requiring specialized contingency planning approaches:
Healthcare organizations need plans for medical emergencies, equipment failures, and patient surge scenarios.
Manufacturing companies must prepare for equipment breakdowns, material shortages, and quality control issues.
Financial institutions require plans for market volatility, regulatory changes, and fraud prevention.
Integrated Contingency Planning Approach
While each type of contingency plan serves specific purposes, they should work together as part of an integrated strategy.
Organizations need to consider how different types of emergencies might overlap and create compound challenges.
For example, a natural disaster might trigger both environmental and technology-related emergencies.
The contingency plan should address these interconnected risks through coordinated response strategies.
Customizing Plans For Your Organization
Organizations should evaluate their specific risks and requirements when determining which types of contingency plans to develop. Factors to consider include:
- Industry regulations and compliance requirements
- Geographic location and environmental risks
- Technology dependencies
- Supply chain complexity
- Customer service requirements
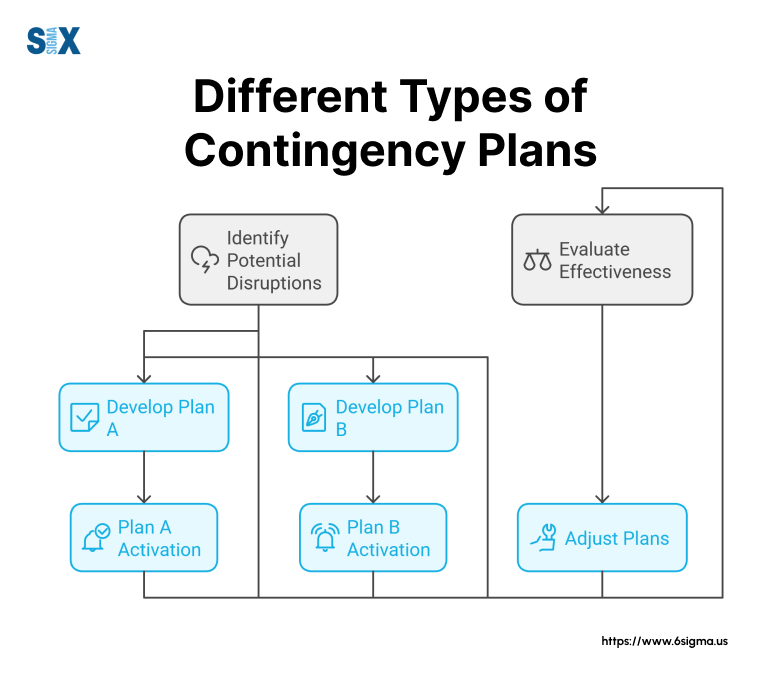
Regular Review and Updates
Each type of contingency plan requires regular review and updates to remain effective. New threats emerge, business operations change, and response capabilities evolve.
Organizations should schedule regular reviews to ensure their plans remain current and effective.
The Five Steps of Contingency Planning
Creating an effective contingency plan requires a structured approach.
Following these five essential steps helps organizations develop robust plans that address potential risks and maintain business operations during disruptions.
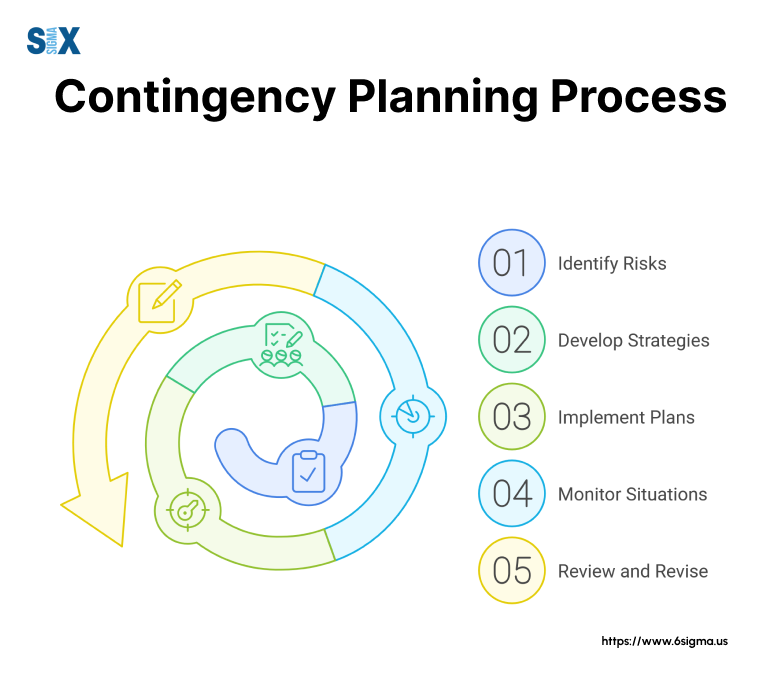
Step 1: Risk Assessment and Identification
The first step involves identifying potential threats to your organization. This process requires examining both internal and external risks that could disrupt operations.
Organizations should evaluate:
- Market conditions and economic factors
- Natural disaster possibilities
- Technology vulnerabilities
- Human resource challenges
- Operational weaknesses
Teams should prioritize risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. This prioritization helps focus resources on the most critical threats first.
Step 2: Impact Analysis
Once risks are identified, organizations must analyze how each threat could affect their operations.
This analysis should examine:
- Financial implications of different scenarios
- Operational disruption levels
- Customer service impacts
- Resource requirements for recovery
- Timeline estimates for different recovery phases
The impact analysis provides crucial data for determining resource allocation and recovery strategies in the next steps.
Step 3: Plan Development
Using information from the risk assessment and impact analysis, organizations can develop specific response plans.
Each plan should detail:
- Clear triggers for plan activation
- Specific response procedures
- Required resources and their locations
- Team member responsibilities
- Communication protocols
- Recovery timelines
Step 4: Testing and Training
Testing validates the effectiveness of contingency plans while training ensures team members can execute them properly.
This step includes:
- Regular simulation exercises
- Team training sessions
- Plan validation activities
- Performance measurements
- Feedback collection
Organizations should conduct different types of tests, from tabletop exercises to full-scale simulations, to ensure plans work as intended.
Step 5: Maintenance and Updates
Contingency plans require regular updates to remain effective. Organizations should establish a maintenance schedule that includes:
- Quarterly plan reviews
- Annual full-scale updates
- Post-incident assessments
- Regular contact list updates
- Resource verification checks
Changes in business operations, new threats, or lessons learned from incidents should trigger immediate plan updates.
Learn to implement and validate contingency plans using proven statistical methods and testing procedures.
Essential Components of a Contingency Plan
Every effective contingency plan contains specific elements that work together to ensure proper risk management and response.
These components form the foundation of a plan that can guide organizations through various emergencies and disruptions.
Risk Scenario Documentation
The first component involves detailed documentation of potential risk scenarios. Each scenario should outline:
- Specific trigger events that activate the plan
- Expected impact on operations
- Early warning signs and indicators
- Historical data from similar events
- Potential cascading effects
Organizations must regularly review and update these scenarios as new risks emerge and business conditions change.
Strategic Response Frameworks in Contingency Planning
Response strategies provide clear directions for handling each identified risk scenario. These strategies should detail:
- Immediate response actions
- Secondary response phases
- Recovery procedures
- Alternative operational methods
- Success criteria and endpoints
Team Roles and Responsibilities
Clear assignment of roles eliminates confusion during emergencies. This section must specify:
- Primary decision-makers and their authority levels
- Response team compositions
- Backup personnel assignments
- Escalation procedures
- External stakeholder involvement
Each role requires detailed descriptions of responsibilities and expectations during plan activation.
Communication Protocols in Contingency Planning
Effective communication proves crucial during emergencies. Communication protocols should establish:
- Internal notification procedures
- External stakeholder communications
- Media response guidelines
- Emergency contact lists
- Status reporting requirements
These protocols must account for various communication methods in case primary channels become unavailable.
Resource Management Guidelines
Resource allocation plans ensure teams have necessary tools and support during emergencies. This component covers:
- Financial resource access
- Equipment and supplies
- Personnel requirements
- External vendor support
- Alternative facility arrangements
Implementation Timelines
Clear timelines help teams track progress and maintain focus during response efforts.
Timeline components include:
- Response phase duration
- Key milestones and checkpoints
- Recovery time objectives
- Progress monitoring methods
- Plan deactivation criteria
Organizations should establish realistic time-frames while maintaining flexibility for unexpected developments.
Documentation Requirements of Contingency Planning
Proper documentation supports both current response efforts and future plan improvements. Required documentation includes:
- Incident logs and reports
- Decision records
- Resource usage tracking
- Cost documentation
- Lesson learned reports
These records provide valuable data for plan updates and compliance requirements.
Testing and Validation Procedures
Regular testing ensures all components work together effectively. Testing procedures should specify:
- Testing frequencies
- Exercise types and scope
- Performance metrics
- Feedback collection methods
- Update procedures
Organizations must document test results and use them to improve plan components.
Integration Guidelines
Components must work together seamlessly during emergencies. Integration guidelines ensure:
- Proper component coordination
- Cross-functional cooperation
- Resource sharing procedures
- Communication flow
- Decision-making alignment
Regular reviews help maintain effective integration between all plan components.
Creating an Effective Contingency Plan
Building a strong contingency plan requires careful attention to detail and systematic execution.
This process helps organizations prepare for potential disruptions while ensuring quick and effective responses when needed.
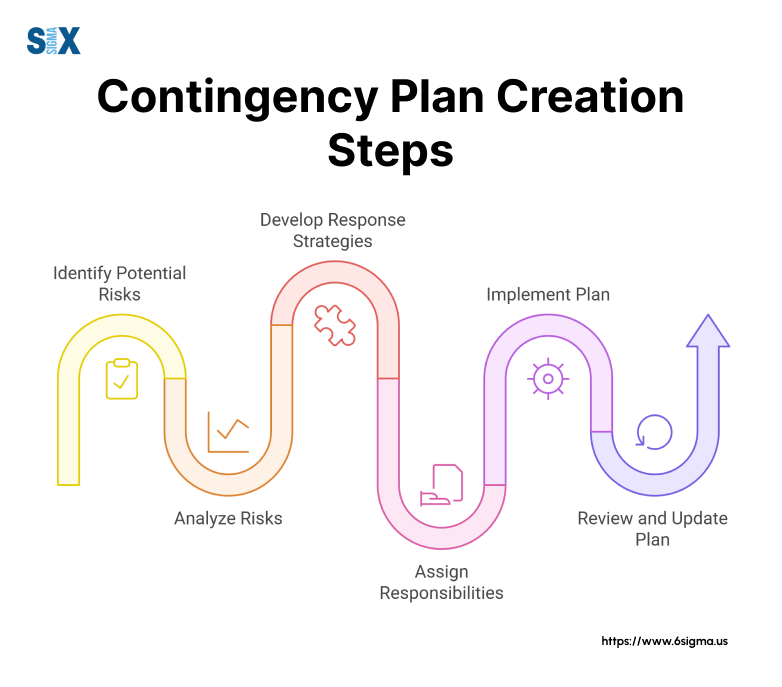
Identifying Risks and Threats
Start by examining potential risks that could impact your organization. Consider both internal and external factors such as:
- Market changes and economic shifts
- Natural disasters specific to your location
- Technology failures and cyber threats
- Supply chain disruptions
- Regulatory changes
Document each identified risk with specific details about potential triggers and warning signs.
Business Impact Assessment
Analyze how each identified risk could affect business operations. This assessment should evaluate:
- Financial implications of disruptions
- Operational impact levels
- Customer service interruptions
- Recovery time requirements
- Resource needs for each scenario
The results help prioritize risks and determine appropriate response levels for each situation.
Developing Strategic Responses in Contingency Planning
Create specific response strategies for each prioritized risk. These strategies must outline:
- Initial response procedures
- Step-by-step recovery actions
- Alternative operating procedures
- Success criteria
- Plan deactivation triggers
Assigning Team Responsibilities
Define clear roles and responsibilities for team members. This includes:
- Emergency response team structure
- Decision-making authority levels
- Backup personnel assignments
- External stakeholder roles
- Coordination procedures
Each role should have detailed descriptions and specific responsibilities during plan activation.
Establishing Communication Channels
Design communication protocols that ensure clear information flow during emergencies. Key elements include:
- Internal notification procedures
- Stakeholder communication guidelines
- Media response protocols
- Emergency contact lists
- Status reporting requirements
Consider multiple communication methods to ensure message delivery even if primary channels fail.
Resource Planning
Determine and allocate necessary resources for plan execution:
- Emergency funding access
- Equipment and supplies
- Personnel requirements
- External support needs
- Alternative facility arrangements
Document resource locations and access procedures for quick deployment during emergencies.
Testing and Refinement with Contingency Planning
Implement regular testing procedures to validate plan effectiveness:
- Schedule periodic drills
- Conduct tabletop exercises
- Test communication systems
- Evaluate team readiness
- Document test results
Use feedback from tests to improve and update the plan regularly.
Implementation Guidelines
Create clear guidelines for plan implementation that specify:
- Activation criteria
- Response phases
- Progress monitoring methods
- Documentation requirements
- Plan maintenance schedules
These guidelines ensure consistent execution across different scenarios and teams.
Monitoring and Updates with a Contingency Plan
Establish procedures for ongoing plan maintenance:
- Regular review schedules
- Update triggers
- Performance metrics
- Feedback collection
- Improvement processes
Keep the plan current by incorporating lessons learned and emerging risks.
Develop the leadership skills to drive successful risk management and process improvement with Lean Six Sigma Champion – Leadership Program
Implementing and Maintaining Your Contingency Plan
Creating a contingency plan marks just the beginning of the preparation process.
Successful implementation and maintenance ensure the plan remains effective and ready for activation when needed.
Employee Training Programs
Effective employee training forms the foundation of successful contingency planning.
Regular training sessions help team members understand their roles and responsibilities during emergencies.
These sessions should cover plan activation procedures, response protocols, and communication guidelines.
Organizations must ensure all new employees receive proper training while existing staff participate in refresher courses.
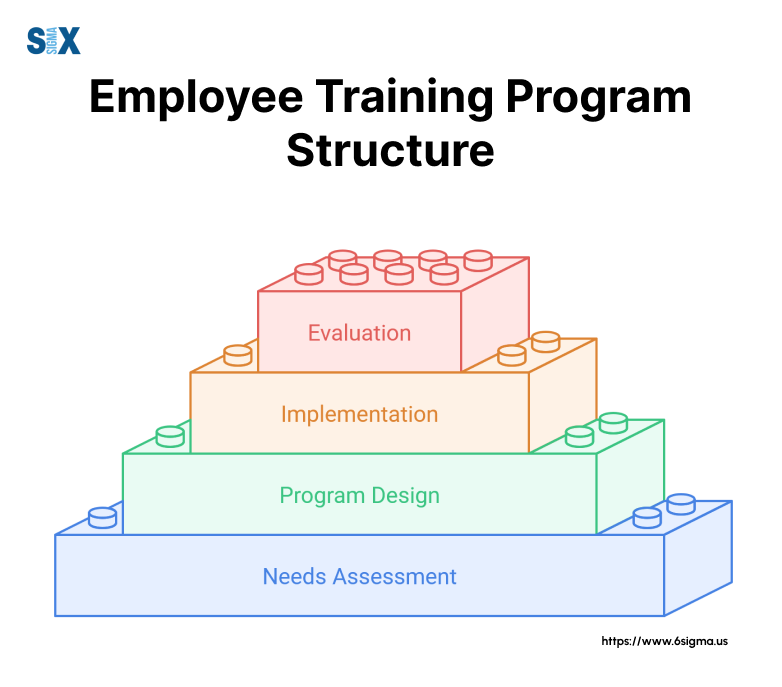
Testing Through Regular Simulations
Regular testing validates plan effectiveness and identifies potential improvements. Organizations should conduct various types of simulations throughout the year.
Tabletop exercises allow teams to discuss responses to theoretical scenarios. Full-scale simulations test actual response capabilities and resource deployment.
Each test provides valuable insights for plan refinement.
Adapting to Business Changes
Business environments evolve constantly, requiring regular plan updates. New technologies introduce different risks while changing market conditions create new challenges.
Organizations must review their contingency plans quarterly to ensure they address current threats. Updates should incorporate lessons learned from actual incidents and simulation exercises.
Conclusion
Contingency planning plays a vital role in modern business operations.
Organizations face increasing challenges from various sources, making proper preparation essential for long-term success.
The right contingency plan provides a roadmap for navigating unexpected events while maintaining critical operations.
Key Takeaways
Successful contingency planning requires ongoing commitment from all organizational levels.
Regular training ensures teams remain prepared for various scenarios.
Continuous testing and updates keep plans relevant and effective. Integration with overall business strategy helps maintain operational resilience.
Moving Forward
Organizations must prioritize contingency planning in today’s dynamic business environment. Start by assessing current preparedness levels and identifying areas for improvement.
Develop structured plans that address specific organizational needs. Implement regular training and testing programs to maintain readiness.
The time invested in contingency planning pays dividends through improved risk management and operational resilience.
Organizations that prioritize preparation position themselves for success regardless of future challenges. Take action today to strengthen your organization’s contingency planning capabilities.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







