ADKAR Model: The Guide to Successful Change Management
Change management often fails when organizations focus solely on processes while overlooking the human element.
The ADKAR model tackles this challenge by providing a structured approach to guide individuals through organizational changes.
Developed by Prosci founder Jeff Hiatt in 1998, the ADKAR model has become a leading framework for managing change in businesses worldwide.
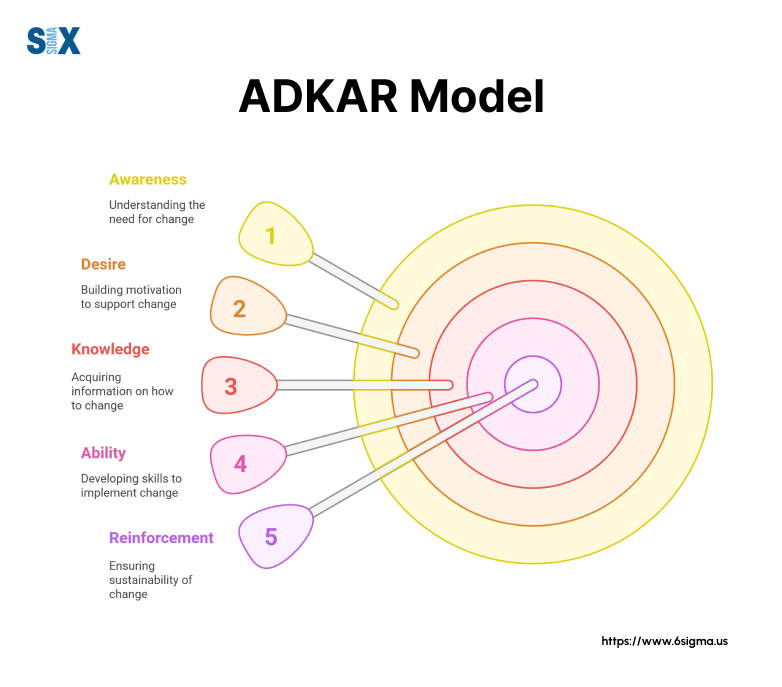
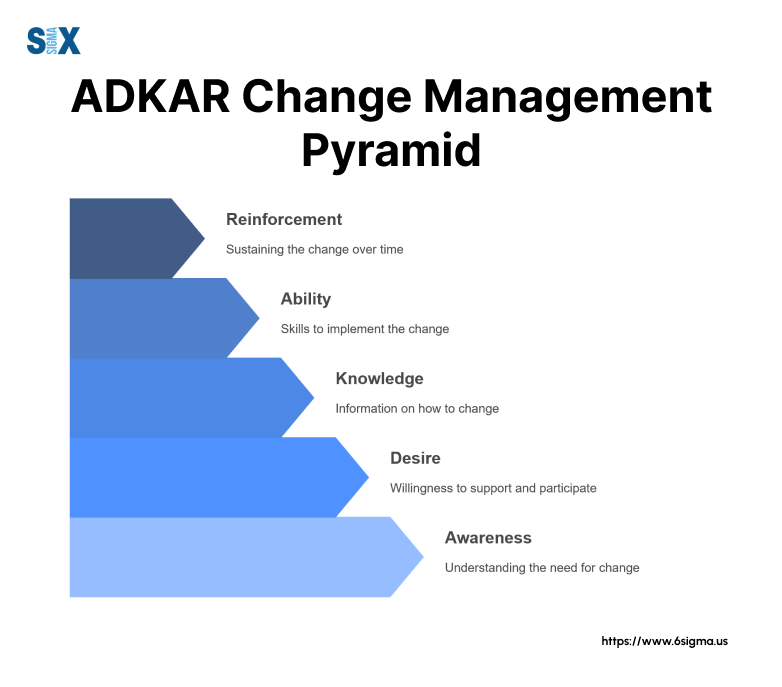
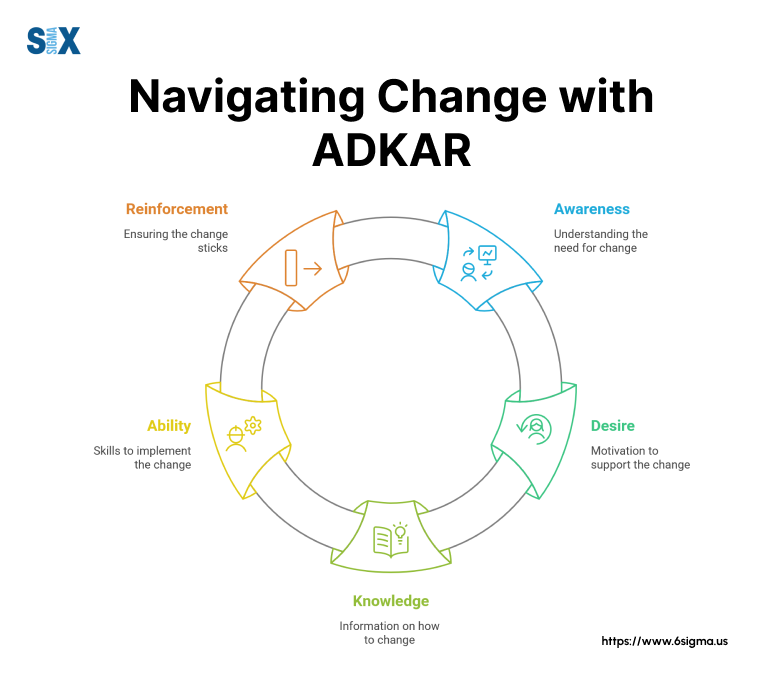
This goal-oriented methodology breaks down change into five key components: Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement.
Think of ADKAR as your GPS for navigating change – it shows you exactly where you are, where you need to go, and the steps to get there.
Key Highlights
- Master each stage of ADKAR model
- Implement change management with real examples
- Integrate ADKAR with modern business tools
- Apply ADKAR across different business contexts
What is ADKAR Model?
The ADKAR model stands as a results-driven framework that guides organizations through change by focusing on individual transitions.
Created by Jeff Hiatt in 1998, this methodology emerged from research involving over 1000 organizations undergoing significant changes.
Origins And Development
Hiatt founded Prosci, a change management research firm, and developed the ADKAR model after observing why some changes succeeded while others failed.
His research revealed that successful change happened when organizations focused on individual transitions rather than just system-wide implementations.
The name ADKAR represents five essential elements:
- Awareness of why change is needed
- Desire to support the change
- Knowledge of how to change
- Ability to demonstrate new skills
- Reinforcement to maintain the change
Core Purpose Of The ADKAR Model
The ADKAR model serves as a practical roadmap for change management professionals and business leaders.
Unlike traditional change models that focus mainly on processes, ADKAR zeros in on people—the true drivers of successful change.
This model helps organizations:
- Identify barriers to change early
- Guide employees through transitions
- Measure progress effectively
- Create targeted action plans
- Build sustainable transformations
How The ADKAR Model Works
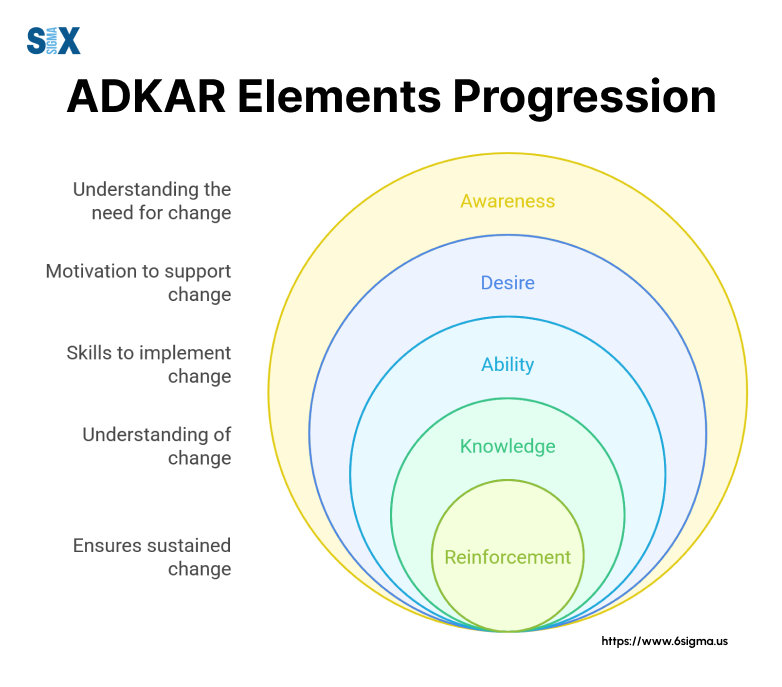
The model operates sequentially, meaning each element builds upon the previous one.
For example, before employees can learn new skills (Knowledge), they must first understand why the change is necessary (Awareness) and want to participate in it (Desire).
Organizations apply ADKAR across various scenarios:
- Technology implementations
- Process improvements
- Cultural transformations
- Organizational restructuring
- Policy changes
Key Components In Action
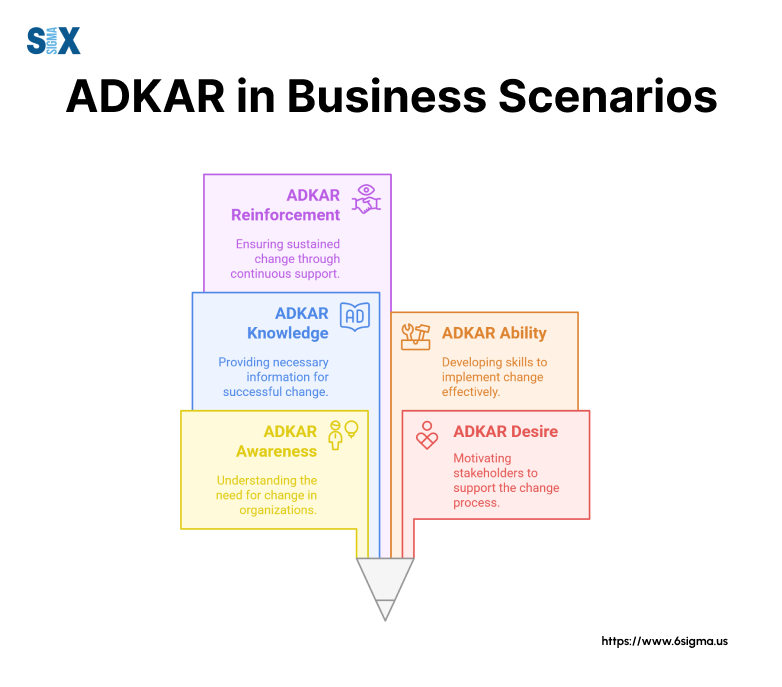
Each ADKAR component plays a specific role in change success. The Awareness phase involves clear communication about change necessity.
Desire focuses on motivation and benefits. Knowledge covers training and education. Ability ensures practical application. Reinforcement maintains long-term adoption.
Modern applications of the ADKAR model have evolved to address:
- Remote workforce transitions
- Digital transformation projects
- Agile methodology adoption
- Global team alignment
- AI integration initiatives
The model’s flexibility makes it particularly valuable for today’s rapidly changing business environment. Whether implementing new software or restructuring entire departments, ADKAR provides a clear framework for managing individual transitions that drive organizational success.
This structured approach to change management helps organizations avoid common pitfalls while ensuring sustainable transformations.
By focusing on individual readiness and progression through each stage, the ADKAR model increases the likelihood of successful change implementation.
The 5 Stages Of The ADKAR Model
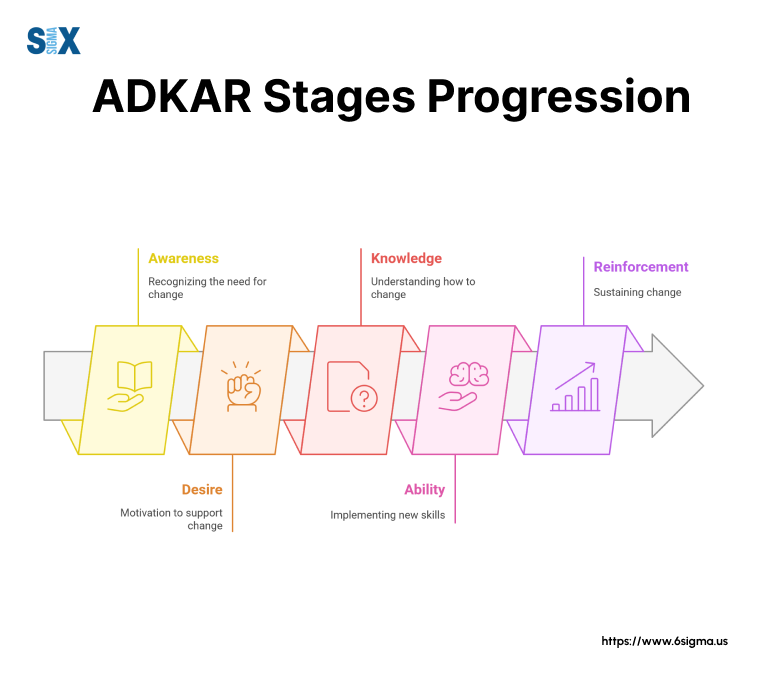
Stage 1: Awareness – Building The Foundation
Awareness marks the starting point of any successful change initiative.
Organizations must clearly communicate why change is necessary, focusing on business reasons, market demands, and potential risks of maintaining the status quo.
Implementation Strategy:
- Regular team meetings to discuss change impacts
- Data-driven presentations showing current challenges
- Clear messaging about future benefits
- Open forums for questions and concerns
Case Study: When Microsoft shifted to cloud services, they started with a six-month awareness campaign. This included regular updates, industry trend analysis, and competitor comparisons, resulting in 85% employee understanding of the change necessity.
Stage 2: Desire – Creating Change Champions
Desire transforms awareness into action. This stage focuses on motivating individuals to support and participate in the change.
Success depends on addressing personal concerns and highlighting individual benefits.
Building desire requires:
- Identifying and addressing resistance points
- Showcasing personal growth opportunities
- Creating early wins and success stories
- Engaging influential team members as change champions
Real Example: Adobe’s transition to subscription-based services succeeded by emphasizing how the change would provide stable income for employees and better career growth opportunities.
Stage 3: Knowledge – Equipping For Success
Knowledge provides the tools and information needed to implement change effectively. This stage involves structured training programs, resource allocation, and skill development initiatives.
Training Requirements:
- Role-specific technical training
- Process documentation
- Hands-on workshops
- Mentoring programs
Best Practice: Establish learning paths tailored to different roles and skill levels. Include both theoretical knowledge and practical application opportunities.
Learn the essential tools that drive successful organizational transformations with Minitab Essentials Online Training
Stage 4: Ability – Turning Knowledge Into Action with the ADKAR Model
Ability focuses on transforming knowledge into practical skills. This stage requires hands-on practice, coaching, and performance monitoring to ensure successful implementation.
Key Performance Indicators:
- Task completion rates
- Error reduction
- Productivity metrics
- Adoption rates
Support Systems:
- On-demand coaching
- Peer support networks
- Practice environments
- Regular feedback sessions
Stage 5: Reinforcement – Sustaining The Change
Reinforcement ensures long-term adoption of new behaviors and prevents reverting to old practices.
This stage requires consistent monitoring and celebration of success.
Sustainability Measures:
- Recognition programs
- Performance incentives
- Regular check-ins
- Success celebrations
Monitoring Tools:
- Usage analytics
- Performance dashboards
- Employee feedback surveys
- Progress reports
Each stage of the ADKAR model builds upon the previous one, creating a solid foundation for successful change implementation.
Organizations must ensure completion of each stage before moving to the next, as skipping stages often leads to change failure.
Success Factors Across All Stages:
- Clear communication channels
- Strong leadership support
- Regular progress assessment
- Flexible adaptation strategies
- Continuous feedback loops
The ADKAR model provides a structured approach to change management while remaining flexible enough to adapt to various organizational contexts.
Whether implementing new technology or restructuring teams, these five stages guide organizations through successful transformations.
Implementing The ADKAR Model: A Practical Guide
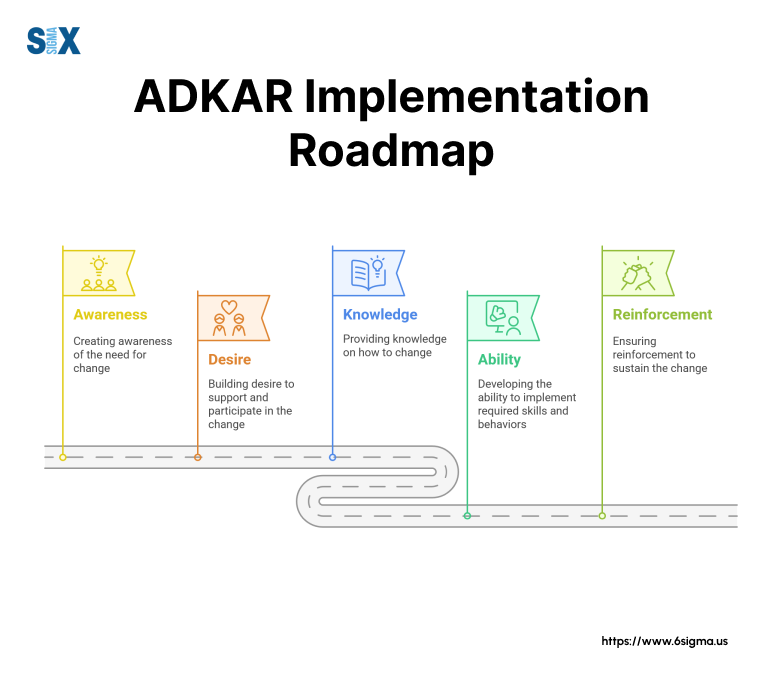
Successful implementation of the ADKAR model requires careful planning and systematic execution.
This guide breaks down each phase of implementation, providing practical steps for change management professionals and business leaders.
Pre-Implementation Assessment
Before launching any change initiative, organizations must evaluate their readiness and identify potential barriers.
This assessment phase helps determine the most effective approach for implementing the ADKAR model.
Key Assessment Areas:
- Current organizational culture
- Employee readiness for change
- Available resources and constraints
- Potential resistance points
- Technical infrastructure needs
Organizations should conduct stakeholder interviews, surveys, and focus groups to gather necessary data. This information shapes the implementation strategy and highlights areas requiring special attention.
Planning Your Change Strategy with the ADKAR Model
The planning phase transforms assessment insights into actionable steps.
This stage requires detailed documentation of goals, timelines, and resource allocation.
Strategic Elements:
- Change impact analysis
- Communication strategy development
- Training program design
- Resource allocation planning
- Risk mitigation strategies
Execution Framework
The execution phase brings plans to life through structured implementation.
This stage requires careful coordination between different organizational levels and departments.
Communication Rollout:
- Initial announcement meetings
- Regular update sessions
- Feedback collection channels
- Progress reporting methods
Training Implementation:
- Role-specific training modules
- Hands-on practice sessions
- Support documentation
- Mentorship programs
Monitoring Progress And Results with the ADKAR Model
Effective monitoring ensures the change initiative stays on track and allows for timely adjustments when needed.
Organizations should establish clear metrics and reporting mechanisms.
Key Performance Indicators:
- Adoption rates
- Employee engagement levels
- Productivity metrics
- Error reduction rates
- Cost savings
Tools for Tracking:
- Digital dashboards
- Progress reports
- Feedback surveys
- Performance analytics
Making Mid-Course Corrections
Regular evaluation allows organizations to identify and address implementation challenges quickly.
This might involve:
Adjustment Strategies:
- Modifying training approaches
- Enhancing communication methods
- Addressing resistance points
- Reallocating resources
- Updating timelines
Ensuring Long-Term Success with ADKAR Model
Sustainable implementation requires ongoing attention and support. Organizations should establish mechanisms for:
Sustainability Measures:
- Regular check-ins
- Refresher training
- Success celebrations
- Continuous improvement
- Knowledge sharing
The ADKAR model works best when organizations maintain flexibility while following the structured implementation approach.
This balance ensures the model can adapt to unique organizational needs while maintaining its effectiveness.
Implementation Tips:
- Start with small pilot groups
- Document lessons learned
- Share success stories
- Build internal expertise
- Create support networks
Remember that implementing the ADKAR model is not a one-time event but an ongoing process.
Organizations should regularly review and refine their implementation approach based on results and changing needs.
The success of ADKAR implementation often depends on:
- Leadership commitment
- Clear communication
- Adequate resources
- Employee engagement
- Consistent monitoring
By following this structured implementation guide while remaining adaptable to organizational needs, change management professionals can effectively lead their organizations through successful transformations using the ADKAR model.
ADKAR Model And Six Sigma
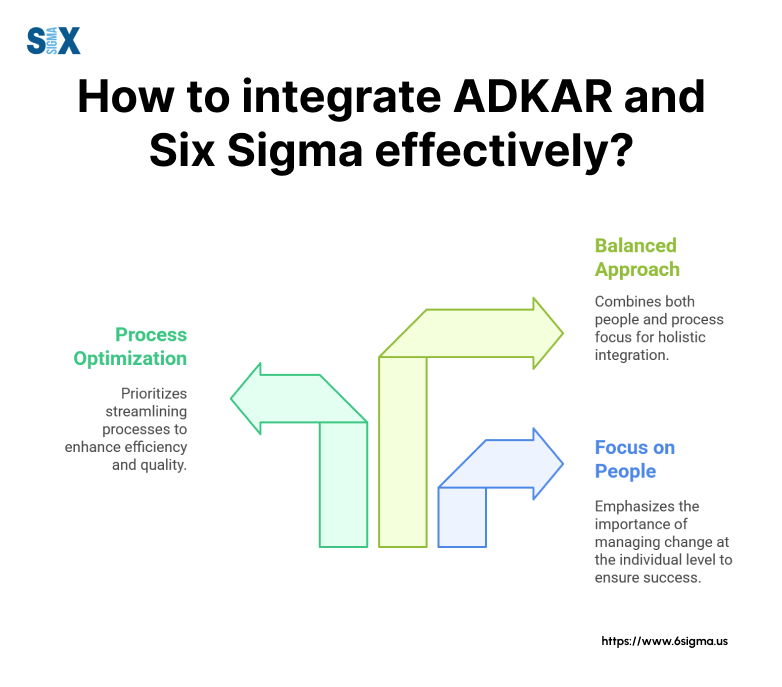
The ADKAR model works seamlessly with Six Sigma methodologies, creating a powerful approach that addresses both technical process improvements and human change management needs.
This integration helps organizations achieve better results in their transformation initiatives.
Aligning ADKAR With DMAIC
The DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) naturally complements the ADKAR model’s stages.
This alignment strengthens change initiatives by combining data-driven process improvement with effective people management.
Define Phase Integration:
- Awareness stage helps identify process challenges
- Stakeholder analysis supports change readiness
- Problem statements align with change objectives
Measure and Analyze Phases connect with Knowledge and Ability stages through:
- Data collection training
- Process mapping workshops
- Root cause analysis sessions
- Performance baseline establishment
Process Improvement Synergies
When organizations combine ADKAR with Six Sigma, they create stronger change initiatives.
The integration addresses both technical excellence and employee adoption, leading to sustainable improvements.
Key Integration Points:
- Project scoping and stakeholder engagement
- Training program development
- Performance measurement systems
- Success validation methods
- Long-term sustainability plans
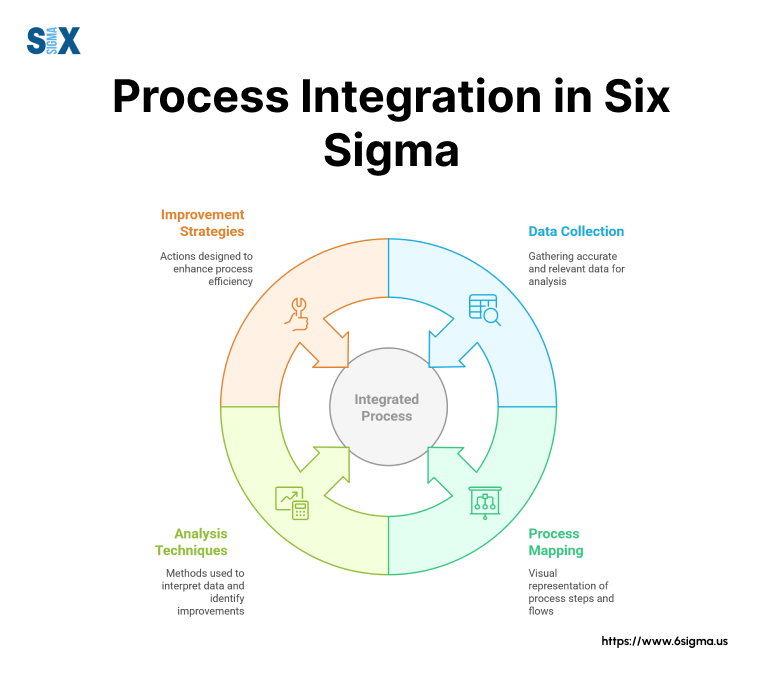
Real-World Application Examples
Manufacturing Sector Case Study:
A global automotive manufacturer used ADKAR alongside Six Sigma to improve production quality.
The integration resulted in:
- 40% defect reduction
- 85% employee engagement
- $2.3M annual savings
- Sustained process improvements
Healthcare Implementation:
A regional hospital network combined both methodologies to optimize patient care processes:
- Reduced wait times by 35%
- Improved staff adoption of new procedures
- Enhanced patient satisfaction scores
- Decreased process variations
Implementation Best Practices
Organizations implementing both methodologies should focus on:
Training Integration:
- Combined certification programs
- Cross-functional team development
- Shared terminology adoption
- Unified measurement systems
Leadership Alignment:
- Clear roles and responsibilities
- Consistent communication strategies
- Integrated project governance
- Unified success metrics
Measuring Combined Impact with ADKAR Model
Success measurement should include both technical and human factors:
Technical Metrics:
- Process capability improvements
- Defect reduction rates
- Cycle time optimization
- Cost savings
People Metrics:
- Change adoption rates
- Employee engagement levels
- Skill development progress
- Knowledge retention scores
The combination of ADKAR and Six Sigma creates a robust framework for managing organizational change.
This integrated approach ensures that process improvements succeed through proper change management support while maintaining technical excellence.
Success Factors:
- Strong leadership commitment
- Clear communication channels
- Integrated training programs
- Regular progress monitoring
- Continuous feedback loops
Organizations using this combined approach often report higher success rates in their improvement initiatives, demonstrating the value of addressing both technical and human aspects of change management.
By thoughtfully integrating these methodologies, organizations can create sustainable changes that deliver measurable business value while ensuring strong employee engagement and adoption.
Become a Change Management Powerhouse
Combine ADKAR methodology with proven Six Sigma techniques.

Benefits And Limitations Of The ADKAR Model
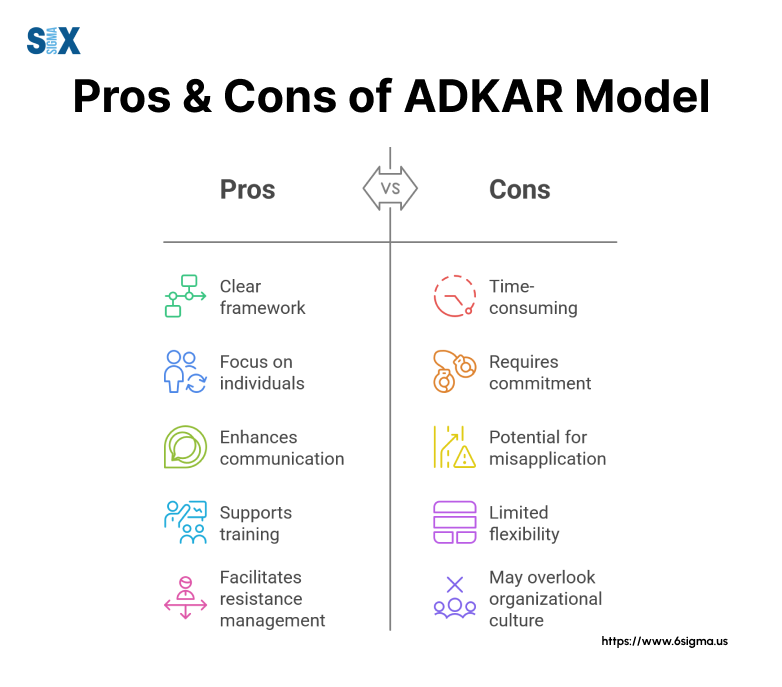
The ADKAR model offers significant advantages for organizations managing change while presenting certain challenges that require careful consideration.
Understanding these elements helps change management professionals and business leaders maximize the model’s effectiveness.
Key Advantages Of The ADKAR Model
The model’s structured approach delivers measurable benefits across various organizational contexts.
Many organizations report improved change success rates through systematic implementation.
Strategic Benefits:
- Clear goal-setting framework
- Measurable progress indicators
- Individual-focused approach
- Adaptable methodology
- Scalable implementation
Operational Advantages:
- Simplified change communication
- Reduced resistance to change
- Better resource allocation
- Enhanced stakeholder engagement
- Improved project outcomes
Potential Implementation Challenges of ADKAR Model
While powerful, the ADKAR model presents specific challenges that organizations must address for successful implementation.
Common Obstacles:
- Resource intensity requirements
- Time management constraints
- Cultural resistance issues
- Leadership alignment needs
- Measurement complexity
Critical Success Factors
Organizations successfully implementing the ADKAR model consistently demonstrate several key success factors:
Leadership Elements:
- Active executive sponsorship
- Clear vision communication
- Consistent support mechanisms
- Regular progress reviews
- Resource commitment
Team Factors:
- Skilled change managers
- Engaged stakeholders
- Proper training programs
- Regular feedback loops
- Strong support networks
Become a Change Leadership Expert with Leadership Champion Training for Six Sigma
Moving Forward With ADKAR
The ADKAR model continues to evolve, addressing modern business challenges while maintaining its core effectiveness.
Organizations can maximize their success by following these key takeaways:
Implementation Priorities:
- Start with thorough preparation
- Build strong awareness foundations
- Focus on individual transitions
- Maintain consistent communication
- Monitor and adjust regularly
Strategic Recommendations
Organizations planning to implement or improve their ADKAR methodology should:
Short-term Actions:
- Assess current change readiness
- Identify key stakeholders
- Develop communication plans
- Create training frameworks
- Establish measurement systems
Long-term Considerations:
- Build internal expertise
- Create support structures
- Develop feedback mechanisms
- Plan for sustainability
- Monitor industry trends
Final Thoughts
The ADKAR model provides a proven framework for managing organizational change. Its success depends on careful planning, dedicated execution, and consistent monitoring.
Organizations that understand both its strengths and limitations can better prepare for successful implementation.
Key Success Elements:
- Clear leadership commitment
- Strong communication strategy
- Adequate resource allocation
- Regular progress monitoring
- Continuous improvement focus
Moving forward, organizations should focus on:
- Building internal capabilities
- Developing support systems
- Creating measurement frameworks
- Maintaining flexibility
- Ensuring sustainability
The ADKAR model remains a valuable tool for managing change today.
By understanding its benefits and limitations, organizations can better prepare for successful implementation and sustainable results.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






