The Guide to Project Success Criteria: Definition, Examples, and Best Practices
In the world of project management, success is not just about completion—it’s about meeting and exceeding expectations.
Modern project managers know that defining clear success criteria is crucial for delivering results that satisfy stakeholders and drive business value.
Key Highlights
- Set measurable goals that matter
- Track progress effectively
- Deliver consistent results
- Build stakeholder confidence
What is a Project Success Criteria?
Project success criteria serve as measurable benchmarks that determine whether a project has met its intended goals.
These criteria go beyond basic completion metrics, focusing on the actual value delivered to stakeholders and the organization.
Definition and Core Elements
Success criteria in project management establish clear, measurable standards that define project success. They act as a roadmap for project teams, guiding decisions and helping maintain focus on desired outcomes.
Rather than vague objectives, these criteria provide specific targets that teams can track and measure throughout the project lifecycle.
For example, a software development project might set success criteria such as “reduce system response time by 40%” or “achieve a user satisfaction rating of 4.5/5”.
These concrete metrics leave no room for interpretation and give teams clear targets to work toward.
How Success Criteria Differ From Project Objectives
Project objectives outline what needs to be done, while success criteria define how well it must be done.
Think of objectives as the destination and success criteria as the standards that determine if you arrived there successfully.
A project objective might state: “Launch a new customer service platform.” The corresponding success criteria would specify:
“Reduce average customer response time to under 2 minutes” and “Maintain a 98% uptime during peak hours.”
The Evolution of Modern Success Criteria
Project success criteria have transformed significantly over the past decade. Traditional metrics focused primarily on the iron triangle: time, cost, and scope. Today’s success criteria embrace broader considerations:
Stakeholder Satisfaction: Modern projects prioritize user experience and stakeholder engagement as key success indicators.
Business Value: Success criteria now link directly to organizational goals and measurable business outcomes.
Sustainability: Environmental impact and long-term viability factor into project success measurements.
Digital Integration: Success criteria increasingly include digital transformation metrics and technology adoption rates.
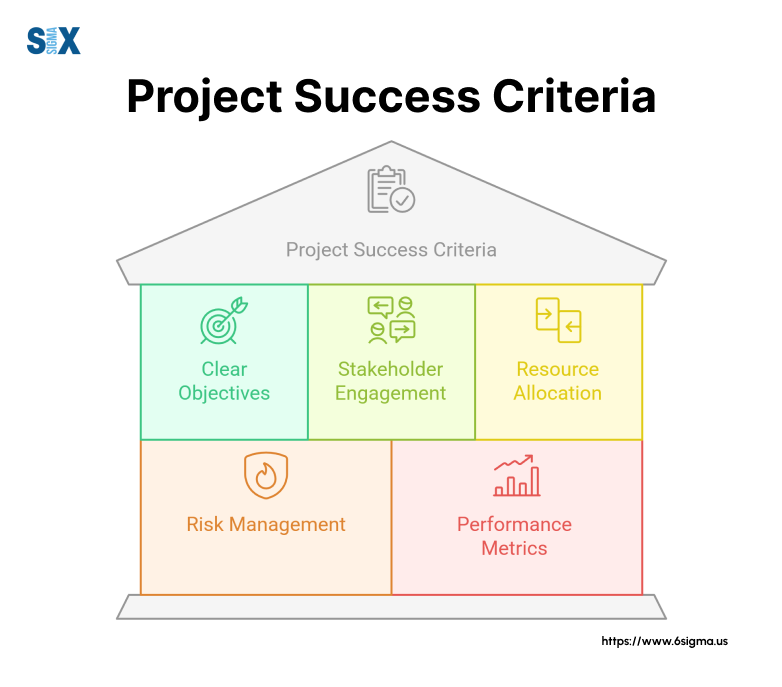
Setting The Foundation For Success
Effective project success criteria require input from all stakeholders. Project managers must facilitate discussions between team members, business leaders, and end users to define meaningful success metrics.
These conversations should address:
- Quality Standards: Specific requirements for deliverables and outcomes
- Performance Metrics: Measurable indicators of project effectiveness
- Resource Utilization: Efficient use of time, money, and personnel
- Risk Management: Acceptable levels of risk and mitigation strategies
Success criteria form the backbone of project evaluation and guide teams toward achieving meaningful results.
By establishing clear, measurable standards early in the project lifecycle, organizations can better track progress, make informed decisions, and deliver value to stakeholders.
Master the art of project selection and success criteria definition with our Define Phase training.
The 4 Characteristics of Project Success
Successful projects balance four essential characteristics that determine their overall effectiveness. These fundamental elements work together to create a framework for measuring and achieving project success.
Time Management and Deadlines
Time stands as a critical measure of project success. Meeting deadlines involves more than just hitting the final completion date.
Project managers must track multiple timelines:
- Milestone achievements
- Phase completions
- Resource allocation schedules
- Stakeholder review periods
Effective time management requires careful planning and regular monitoring of progress against established timelines. Teams need buffer periods for unexpected delays while maintaining steady progress toward project goals.
Cost Control and Budget Management
Budget management directly impacts project success. Projects must deliver value within approved financial parameters. Key cost considerations include:
- Resource expenses
- Equipment and materials
- External contractor fees
- Overhead costs
- Contingency funds
Modern project success metrics look beyond simple budget adherence to measure return on investment and long-term financial benefits. This approach helps justify project expenses and demonstrates business value.
Scope Definition and Control
Project scope outlines the boundaries and deliverables of the project. Clear scope definition prevents feature creep and ensures resources focus on essential elements. Successful scope management requires:
- Detailed documentation of requirements
- Change control procedures
- Regular scope reviews
- Stakeholder agreement on deliverables
When scope changes become necessary, teams must assess the impact on other success characteristics and adjust accordingly.
Quality Standards and Assurance
Quality measures determine whether project deliverables meet stakeholder expectations. Strong quality management includes:
- Defined quality standards
- Regular quality checks
- Testing procedures
- Performance metrics
- User acceptance criteria
Quality standards must align with project objectives while remaining achievable within time and budget constraints.
Regular quality assessments help identify issues early, allowing teams to maintain high standards throughout the project lifecycle.
Balancing The Four Characteristics
These four characteristics rarely carry equal weight in every project. Teams must prioritize based on project goals and stakeholder requirements. For example:
- A mission-critical software update might prioritize quality over cost
- A time-sensitive market launch could emphasize deadlines over scope
- A fixed-budget initiative would stress cost control over additional features
Success depends on finding the right balance among these characteristics while meeting stakeholder expectations and delivering business value.
Enhance your project success skills with our Yellow Belt certification program.
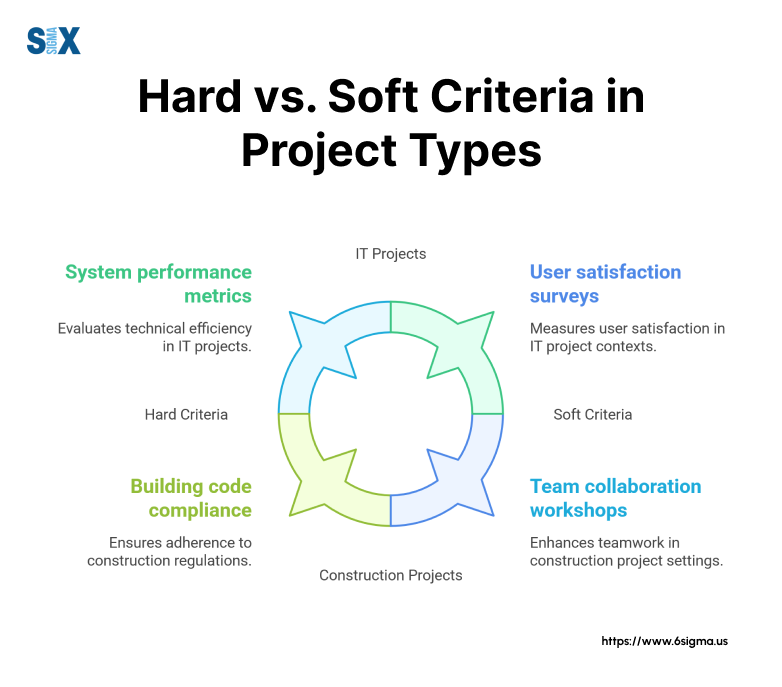
Types of Project Success Criteria
Project success criteria fall into two main categories: hard criteria and soft criteria.
Understanding both types helps project managers create balanced measurement frameworks that capture the full scope of project success.
Hard Criteria: Measuring Quantitative Success
Hard criteria provide measurable, numbers-based indicators of project success. These metrics leave little room for interpretation and offer clear evidence of project performance.
Financial metrics often form the backbone of hard criteria. Return on Investment (ROI), for example, might need to exceed 25% within the first year after project completion.
Similarly, cost savings targets might specify reducing operational expenses by $500,000 annually.
Time-based measurements represent another crucial hard criterion. Meeting project milestones, achieving specific completion dates, and reducing process times by predetermined percentages all fall into this category.
For instance, a manufacturing project might aim to reduce production time by 30% or decrease defect rates to less than 1%.
Soft Criteria: Evaluating Qualitative Outcomes
Soft criteria focus on less tangible but equally important aspects of project success. These measurements often relate to human factors and long-term business impacts.
Stakeholder satisfaction stands as a primary soft criterion. This might include employee engagement levels, customer feedback scores, or user adoption rates.
While these factors can be assigned numerical values through surveys or ratings, they fundamentally measure qualitative aspects of the project’s impact.
Team development and organizational learning represent other key soft criteria. Projects might aim to improve cross-departmental collaboration, enhance skill sets, or strengthen organizational capabilities in specific areas.
Balancing Hard and Soft Success Criteria
Modern projects require a balanced approach to success measurement. While hard criteria provide concrete evidence of project performance, soft criteria often determine long-term project value and sustainability.
For example, a software implementation project might meet all its technical specifications (hard criteria) but fail to gain user acceptance (soft criteria). Similarly, a reorganization project could achieve its cost-cutting targets while damaging team morale and productivity.
Successful project managers weigh both types of criteria when planning and executing projects. This balanced approach ensures projects deliver immediate results while building lasting value for the organization.
Adapting Success Criteria to Modern Challenges
Digital transformation and remote work environments have introduced new considerations for both hard and soft criteria. Projects now commonly include metrics for:
- Digital adoption rates
- Remote collaboration effectiveness
- Sustainability impacts
- Cybersecurity compliance
- Stakeholder engagement in virtual environments
How to Define Project Success Criteria
Defining project success criteria requires careful planning and collaboration with stakeholders. This process establishes clear benchmarks for project evaluation while ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
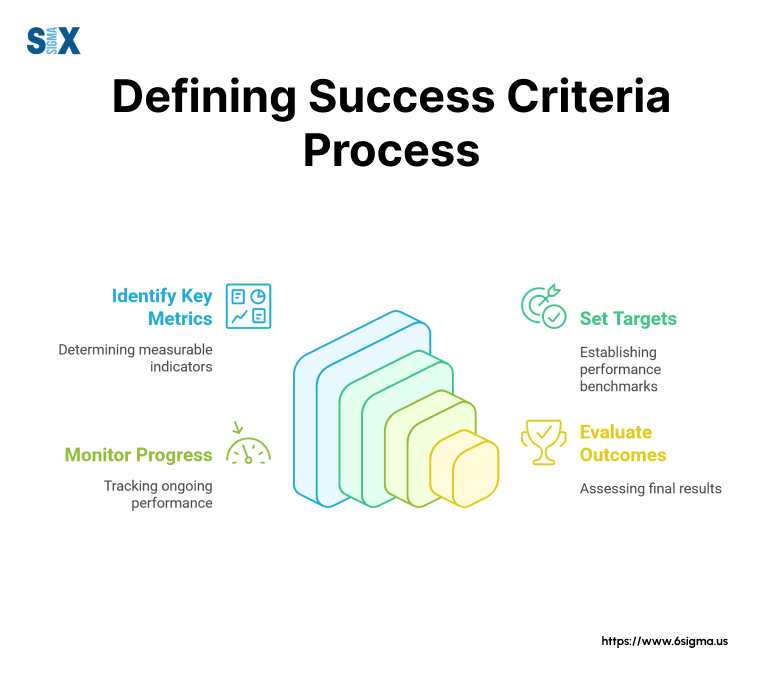
The Step-by-Step Process
Start with business objectives. Review organizational goals and strategic priorities to ensure project success criteria align with broader business aims.
This alignment helps justify project investments and demonstrate value to senior stakeholders.
Next, identify key stakeholders and their expectations. Different stakeholders often have varying perspectives on what constitutes success.
Document these viewpoints to create balanced success criteria that address multiple needs.
Then, draft initial success criteria based on gathered information. These drafts should include both quantitative and qualitative measures that reflect stakeholder priorities and business objectives.
Finally, refine and validate the criteria through stakeholder review sessions. These meetings help ensure the criteria are realistic, measurable, and aligned with project constraints.
Stakeholder and Team Member Involvement
Project managers must engage various stakeholders throughout the criteria definition process. Senior executives provide strategic direction and business context.
Team members offer practical insights into technical feasibility and resource requirements.
Regular workshops and feedback sessions help build consensus around success criteria.
These meetings should address potential conflicts between different stakeholder priorities and establish clear hierarchies for competing success measures.
Documentation from these sessions forms part of the project charter and helps maintain accountability throughout the project lifecycle.
Applying SMART Criteria
Success criteria must follow the SMART framework:
- Specific: Define exact requirements and outcomes
- Measurable: Include quantifiable metrics
- Achievable: Set realistic targets within project constraints
- Relevant: Align with business objectives
- Time-bound: Specify deadlines for achievement
For example, instead of “improve customer satisfaction,” a SMART criterion would state “achieve a customer satisfaction score of 4.5/5 within three months of launch.”
Documentation and Integration
Success criteria should appear in several key project documents:
- Project Charter: Lists high-level success criteria aligned with business objectives
- Requirements Document: Details specific metrics and measurements
- Project Management Plan: Outlines how criteria will be tracked and measured
- Status Reports: Updates progress toward meeting success criteria
These documents create a clear trail of accountability and provide reference points for project evaluation.
Modern Considerations in Success Criteria
Today’s project environments require additional success criteria considerations:
- Digital Transformation: Include metrics for technology adoption and digital capability development
- Remote Work: Address virtual collaboration effectiveness and distributed team performance
- Sustainability: Incorporate environmental impact and long-term viability measures
- Stakeholder Value: Balance multiple stakeholder needs across different organizational levels
Success Criteria Review and Adjustment
Success criteria should undergo regular review throughout the project lifecycle. Market changes, technological advances, or shifting business priorities might necessitate adjustments to maintain relevance.
These reviews ensure success criteria remain meaningful while allowing for necessary modifications as project conditions evolve.
Measuring and Tracking Project Success Criteria
Effective measurement and tracking of project success criteria ensures projects stay on course and deliver intended value.
This process requires systematic monitoring throughout the project lifecycle and appropriate tools to capture relevant data.
Essential Metrics and KPIs
Performance metrics fall into several key categories that align with project objectives.
Financial metrics track budget adherence, ROI, and cost variations. Schedule metrics monitor milestone completion, task progress, and timeline adherence.
Quality metrics assess deliverable standards, defect rates, and compliance levels.
Operational KPIs measure efficiency improvements, process changes, and resource utilization. These indicators help project managers identify trends and make data-driven decisions about project direction.
Tools and Technologies for Success Tracking
Modern project management platforms offer integrated tracking capabilities. Dashboard systems provide real-time visibility into project performance, while automated reporting tools generate regular updates on success criteria measurements.
Data analytics tools help process complex metrics and identify patterns. These systems can track multiple success criteria simultaneously, creating a holistic view of project performance across various dimensions.
Collaboration tools support distributed teams in monitoring and updating success criteria. These platforms ensure all team members access current information and contribute to progress tracking.
Measurement Frequency and Timing
Different success criteria require varying measurement frequencies. Daily monitoring suits operational metrics like task completion rates and resource utilization.
Weekly assessments work well for progress tracking and risk indicators. Monthly reviews typically cover financial metrics and broader performance indicators.
Key project phases often trigger specific measurements:
- Initiation Phase: Baseline measurements
- Planning Phase: Target setting and metric refinement
- Execution Phase: Regular progress monitoring
- Closing Phase: Final achievement assessment
Adapting Success Criteria Through Project Phases
Project success criteria must evolve as projects progress through their lifecycle. Early phases might emphasize planning and setup metrics, while later stages focus on delivery and quality measures.
Market changes, technological advances, or shifting business priorities might necessitate criteria adjustments. Regular review cycles help ensure success criteria remain relevant and achievable throughout the project lifecycle.
Reporting and Communication
Regular reporting keeps stakeholders informed about progress toward success criteria. Status reports should include:
- Current performance metrics
- Trend analysis
- Variance explanations
- Corrective actions
- Updated forecasts
Visual representations help communicate complex data effectively. Charts, graphs, and dashboards make it easier for stakeholders to understand project status and trending information.
Technology Integration and Automation
Modern tracking systems leverage automation to streamline data collection and analysis. Automated alerts notify teams when metrics fall outside acceptable ranges. Predictive analytics help forecast potential issues before they impact project success.
Digital transformation initiatives often introduce new tracking capabilities:
- Real-time performance monitoring
- Automated data collection
- Predictive trend analysis
- Integrated stakeholder communications
- Advanced visualization tools
Continuous Improvement Process
Regular evaluation of tracking methods ensures measurement systems remain effective. Teams should document lessons learned about success criteria measurement and use these insights to improve future project monitoring processes.
This feedback loop helps organizations refine their approach to defining and measuring project success criteria over time.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Project managers face several recurring challenges when implementing success criteria. Understanding these obstacles and their solutions helps teams maintain project momentum and achieve desired outcomes.
Stakeholder Misalignment Issues
Different stakeholders often have competing priorities and expectations for project success. Senior management might focus on financial returns, while end users prioritize functionality and ease of use. This misalignment can lead to confused project direction and conflicting success measures.
Solution: Implement structured stakeholder management processes. Regular alignment meetings help identify and resolve conflicting priorities early.
Document all stakeholder requirements and create a clear hierarchy of success criteria. This approach ensures everyone understands which metrics take precedence when conflicts arise.
Managing Unrealistic Expectations
Stakeholders sometimes demand outcomes that exceed project constraints or organizational capabilities. These unrealistic expectations often stem from market pressures or incomplete understanding of project limitations.
Solution: Base success criteria on solid data and proven capabilities. Present stakeholders with benchmark data from similar projects.
Create detailed feasibility analyses that clearly show the relationships between resources, time, and achievable outcomes.
This evidence-based approach helps set realistic success criteria that align with project constraints.
Handling Scope Changes
Project scope changes can invalidate originally defined success criteria. As requirements evolve, previously established metrics might no longer reflect project reality or business needs.
Solution: Establish a robust change management process that includes success criteria revision. When scope changes occur, automatically trigger a review of related success criteria. Document the impact of scope changes on success metrics and get stakeholder approval for revised criteria.
Addressing Metric Clarity Issues
Vague or poorly defined metrics create confusion and hamper project progress. Without clear measurements, teams struggle to track progress and demonstrate success.
Solution: Define specific, measurable indicators for each success criterion. Replace subjective statements with quantifiable metrics. For example, change “improve customer satisfaction” to “achieve a customer satisfaction score of 4.5/5 within three months of launch.”
Technology Integration Challenges
Modern projects often struggle with integrating new technologies into success criteria frameworks. Digital transformation initiatives can introduce complex measurement requirements that existing systems struggle to track.
Solution: Invest in appropriate measurement tools and platforms. Train teams on new tracking systems and ensure they understand how to collect and interpret data effectively.
Consider automated data collection and analysis tools to reduce manual effort and improve accuracy.
Remote Team Coordination
Distributed teams face unique challenges in monitoring and reporting on success criteria. Communication gaps and time zone differences can complicate progress tracking and stakeholder updates.
Solution: Implement centralized project management platforms that provide real-time visibility into success metrics. Establish clear reporting schedules that accommodate different time zones. Use automated alerts to keep all team members informed of significant metric changes or concerns.
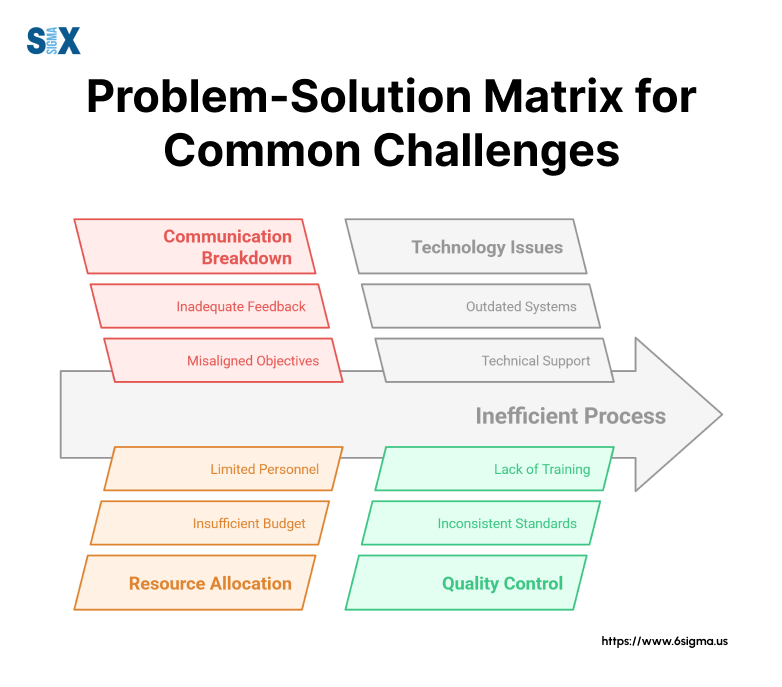
Prevention Strategies
Many common challenges can be prevented through proactive planning:
- Regular stakeholder engagement sessions maintain alignment
- Clear documentation prevents misunderstandings
- Robust change control processes protect project integrity
- Regular success criteria reviews ensure continued relevance
- Training programs build team capability
Lean Six Sigma in Project Selection Criteria
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that aims to improve the efficiency and quality of business processes. It combines the waste-reduction focus of Lean with the variability-reduction techniques of Six Sigma.
When applied to project management, Lean Six Sigma principles can significantly enhance the way success criteria are defined and measured.
By focusing on eliminating waste and reducing variability, projects can achieve higher quality outcomes, improved customer satisfaction, and more efficient use of resources—all key components of project success criteria.
Transform your project management approach with Lean Six Sigma principles.
Moving Forward With Project Success Criteria
The evolution from simple triple-constraint measurements to multi-dimensional success frameworks reflects the growing complexity of modern projects and stakeholder expectations.
Key Takeaways for Implementation
Success criteria must balance both hard and soft metrics to capture true project value.
Financial measures provide concrete performance indicators, while qualitative assessments gauge stakeholder satisfaction and long-term impact.
This dual approach ensures projects deliver immediate results while building lasting organizational value.
The Path to Continuous Improvement
Success criteria definition and measurement must evolve with changing business needs. Regular reviews help ensure criteria remain relevant and achievable throughout the project lifecycle.
Digital transformation continues to reshape project management practices.
Organizations must adapt their success criteria frameworks to incorporate new technologies, remote work considerations, and evolving stakeholder expectations.
Taking Action on Success Criteria
Project managers should begin implementing structured success criteria frameworks in their next projects. Start by engaging stakeholders early in the criteria definition process.
Document clear, measurable objectives that align with organizational goals. Establish regular review cycles to monitor progress and adjust criteria as needed.
The future of project success criteria lies in adaptability and integration.
As business environments continue to evolve, success frameworks must accommodate new ways of working, emerging technologies, and changing stakeholder priorities.
Organizations that master this balance will achieve consistently better project outcomes.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






