Project Management Techniques. Managing Project Cost Management
Project cost management is very important for finishing projects on time and budget. It includes many steps from first estimating costs to finally reporting on costs and analyzing them.
Managing project costs well is key for companies to lower financial risks, make more money, and stay competitive.
The main goal of cost management is correctly predicting and controlling costs like labor, materials, equipment, and services throughout the project timeline.
Key Highlights
- Managing project costs is very important for completing projects successfully and using resources well.
- It involves estimating, planning, controlling, and tracking costs throughout the project timeline.
- Good cost management helps companies finish projects within budget, lower risks, and increase profits.
- Key parts of cost management include estimating costs, creating a budget, monitoring costs, predicting future costs, and comparing planned costs to actual costs.
- Tools and techniques are used to follow expenses, find differences from the plan, and make changes when needed.
- Best practices like setting a cost baseline, evaluating risks, and setting performance goals support good cost management.
- Challenges can come up from incorrect initial estimates, changing needs, limited resources, and outside factors that affect budgets.
- Keeping close control of project spending is important to deliver projects on schedule and on budget.
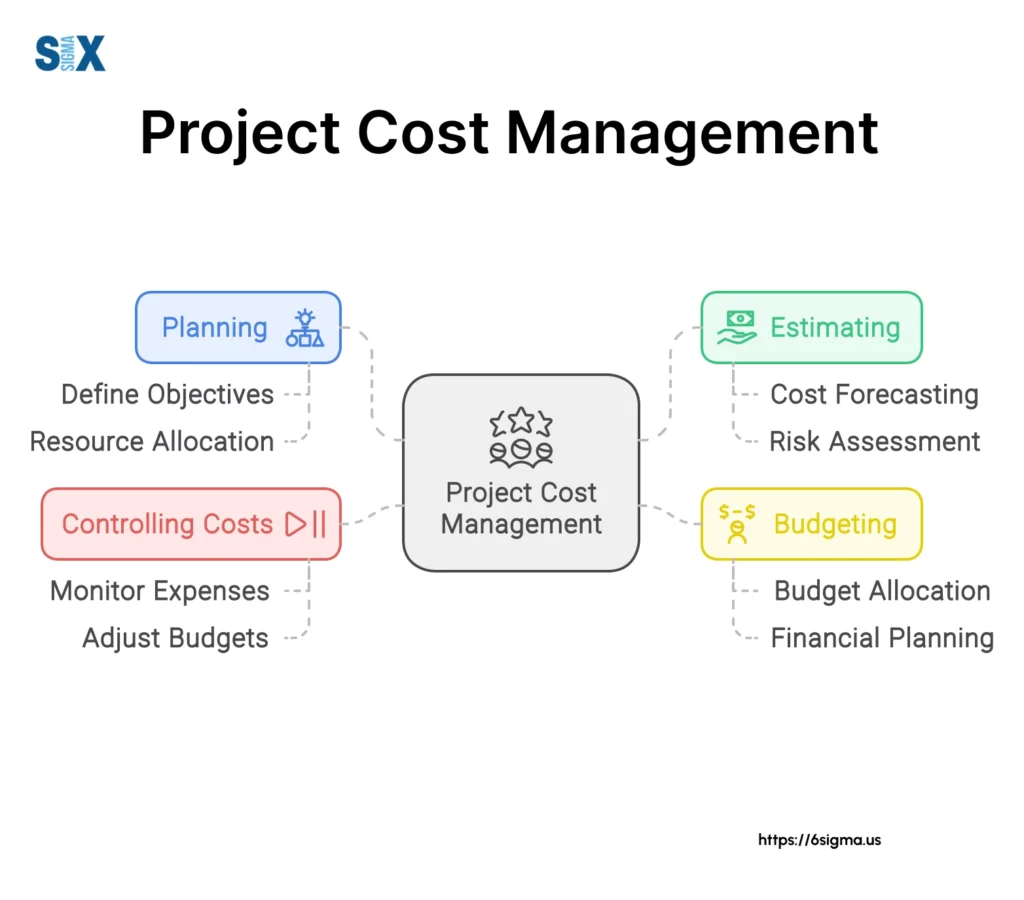
What is Project Cost Management?
Managing project costs is a very important part of successfully planning and carrying out any project. It involves estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs to finish the project within the approved budget.
Good cost management makes sure projects are completed within the planned financial limits and gets the most value from the money invested in the project.
The main goal of cost management is to keep costs reasonably on target while achieving the project goals.
It helps project managers make informed decisions about assigning resources, dealing with risks, and adjusting the budget throughout the project timeline.
Not paying attention to costs properly can lead to costs going over budget, delays, changing needs, and even project failure.
Cost management has several key steps:
- Estimating how much money different tasks will require
- Dividing the total estimated budget among the work
- Managing things that affect the planned budget
- Tracking and reporting on costs to predict if costs will go over budget
Integrating principles from Lean fundamentals, which focus on eliminating waste and streamlining processes, can further enhance cost management effectiveness throughout the project lifecycle.
These steps are all connected and guide project teams in making good financial choices from start to finish. Doing cost management well increases the ability to predict costs, ensures money is used as planned, and helps with important decisions.
As projects get more complex, comprehensive cost management becomes very important for organizations to get the most from their money, lower risks, and finish projects successfully within the given limits.
Cost Estimation Techniques
Accurate cost estimation is critical for effective project cost management. and professionals with a six sigma green belt certification can apply statistical tools like parametric estimating to improve the precision of cost forecasts. Several techniques can be employed to estimate project costs:
Top-Down Estimating
This technique starts with an overall project budget allocation or cost estimate, which is then broken down into smaller components. Top-down estimating is useful for getting a high-level estimate early in the project planning phase.
Bottom-Up Estimating
The bottom-up approach involves estimating individual work packages or activities, and then rolling up these estimates to calculate the total project cost. This method tends to be more accurate but also more time-consuming.
Analogous Estimating
This technique uses actual costs from previously completed, similar projects as the basis for estimating the new project’s costs. It can work well when historical information is available.
Parametric Estimating
Parametric models leverage statistical data and historical project information to calculate cost estimates for the new project. This quantitative method can increase estimation accuracy.
Three-Point Estimating
This technique looks at three cost estimates for each work package – pessimistic, optimistic, and most likely. It helps account for uncertainty and risk in cost projections.
When using parametric or three-point estimating, teams trained in root cause analysis can identify underlying inefficiencies in historical data, improving accuracy.
Vendor Bid Analysis for Project Cost Management
When hiring vendors or contractors, their bid proposals and price quotes provide valuable data points for estimating associated costs.
Reserve Analysis for Project Cost Management
This identifies anticipated risks and calculates additional cost reserves to cover potential contingencies that may arise over the project timeline.
Project Cost Budgeting
Establishing a comprehensive project budget is a critical component of effective cost management. The budget outlines approved costs for the entire project lifecycle and serves as the benchmark for cost monitoring and control.
Cost Baseline
The cost baseline forms the foundation of the project budget. It is a time-phased budget that maps out the anticipated expenditures over the project timeline.
Developing an accurate cost baseline requires a detailed estimation of costs for labor, materials, equipment, and any other resources required.
Techniques like parametric estimation, analogous estimation, and bottom-up estimation can aid in calculating reliable cost estimates.
Budget Components for Project Cost Management
The project budget should account for all potential cost categories and elements, including:
- Labor costs (salary, benefits, overtime)
- Materials and supplies
- Equipment costs (rental, purchase, maintenance)
- Contracted services
- Travel and Transportation
- Facilities and overhead
- Risk reserves for contingencies
Establishing a well-structured Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) can help ensure no cost element is overlooked during budgeting.
Budget Approvals
Once compiled, the project budget typically goes through an approval process with key stakeholders like sponsors, financial controllers, and executives.
Having an agreed-upon approved budget provides the official cost performance measurement baseline.
Budget Updates for Project Cost Management
Project budgets are not static – they require regular updates and revisions as actual costs become known. This ensures the budget remains a relevant forecasting tool.
Formal budget change processes should be implemented to analyze and approve budget updates.
Cost Control and Monitoring for Project Cost Management
Once the project cost baseline and budget are established, it’s critical to actively control and monitor costs throughout the project lifecycle.
Cost control involves managing factors that can cause changes to the approved cost baseline. Cost monitoring tracks cost performance by comparing actual expenditures against the budget.
Cost Control Techniques
- Change Control Process – Implement a formal process to review, evaluate, and approve or reject proposed changes that could impact costs.
- Earned Value Management (EVM) – Use earned value metrics like cost variance (CV) and cost performance index (CPI) to measure cost efficiency.
- Resource Smoothing – Reallocate resources across activities to better optimize utilization and costs.
- Cost Forecasting – Periodically re-forecast total costs at completion based on current performance.
Cost Monitoring Tools
- Cost Management Software – Utilize PM tools with cost tracking, reporting, and analytics capabilities.
- Cost Audits – Regularly audit cost accounts, transactions, and forecasts to verify accuracy.
- Progress Reports – Review recurring costs and progress reports from team members.
- Cost Databases – Maintain historical cost data from past projects to benchmark against.
Project Cost Management Tools and Strategies
Effective project cost management requires utilizing the right tools and strategies. Having the proper systems in place allows you to accurately track costs, identify issues proactively, and keep budgets under control.
Project Cost Management Software
Project management software with robust cost management capabilities is essential. Tools like Microsoft Project, Smartsheet, Wrike, and others provide features for resource planning, cost estimating, budget tracking, earned value analysis, and reporting. Cloud-based solutions make it easy for distributed teams to collaborate on cost data.
Earned Value Management (EVM)
EVM compares the planned costs against the actual costs expended to calculate cost and schedule variance metrics.
Earned value analysis highlights potential budget/timeline issues early so proactive adjustments can be made. Key EVM metrics include the Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI).
Cost Control Strategies
Proven cost control techniques include change control processes, contingency planning, enforcing an approval workflow for expenditures, and regular cost audits. Variance analysis identifies budget overruns quickly. Cost forecasting models extrapolate future costs based on current spending rates.
Risk Management
Identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential cost risks is crucial. Strategies include risk registers, decision trees, Monte Carlo simulations, and assigning contingency reserves. Proactive risk management prevents budget-busting surprises.
Agile Project Cost Management
For agile projects, cost management is integrated into each iteration cycle. Costs are tracked against the forecasted “budgeted cost of work scheduled” (BCWS). Cost burndown charts show actual versus planned expenditure trends.
Value Engineering for Project Cost Management
Value engineering analyzes project components and activities to optimize costs while still meeting requirements, and a training in the fundamentals of lean can enhance this process by teaching teams to eliminate waste and streamline project workflows. It focuses on eliminating unnecessary costs and finding more cost-effective alternatives.
Best Practices and Challenges for Project Cost Management
Implementing effective project cost management requires following some key best practices. One crucial best practice is to establish a comprehensive cost management plan early in the project lifecycle. This plan should define cost controls, reporting processes, roles, and responsibilities. It ensures cost management activities are well-coordinated from the start.
Another best practice is to utilize earned value management (EVM) and earned value analysis techniques like tracking planned value, earned value, and actual costs. EVM provides objective cost and schedule performance metrics that allow for accurate project cost forecasting.
Integrating cost data from all sources like contractor costs, material/equipment costs, and internal labor costs is also a best practice. This centralized cost repository enables complete cost visibility and control.
From a people perspective, ensuring there are clear cost management roles with proper training is vital, and a six sigma yellow belt certification provides foundational knowledge to team members, enabling them to contribute to cost estimation and control processes effectively.
Investing in robust cost management software tools is recommended as a best practice too. These solutions automate processes like cost tracking, analysis, and reporting for efficiency.
Despite following best practices, project teams can face some common cost management challenges. Inaccurate initial cost estimates can derail a project’s entire cost baseline, but a root cause analysis training can equip teams with the skills to identify underlying issues in estimation processes, ensuring more reliable cost projections.
The lack of integrated cost data across the organization is another major obstacle.
Undefined or inconsistent processes for activities like cost change control are problematic. Cost management efforts may lose credibility if reporting is delayed or metrics are questionable.
Shortage of trained cost management staff is a human resource challenge. Lack of leadership buy-in and enforcement of cost management processes can limit their effectiveness too.
Conclusion
Managing project costs effectively is very important for any project’s success. It involves careful planning, estimating, budgeting, monitoring, and controlling costs from start to finish.
It’s important to remember that cost management is an ongoing process that needs continuous attention and adjustments. Problems could come up as projects progress, requiring changes to cost predictions, budgets, and plans.
Investing in a program like Six Sigma certification or Lean Fundamentals ensures teams have the expertise to adapt cost management strategies proactively
Taking a proactive and flexible approach to cost management can help project teams get ahead of potential issues and make good decisions to keep costs under control.
Using the right tools and technologies can also hugely improve cost management. Software, analysis methods, and monitoring tools provide useful insights, automate processes, and make reporting easier for more efficient cost management.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






