Process Optimization: Revolutionizing Business Efficiency
Modern businesses face mounting pressure to deliver superior results while managing costs and resources efficiently.
Process optimization stands as the cornerstone of operational excellence, enabling organizations to streamline their workflows and maximize output.
The following sections will guide you through:
- Essential process optimization methodologies and their applications
- Step-by-step implementation strategies
- Advanced tools and technologies
- Industry-specific optimization approaches
- Success measurement and continuous improvement techniques
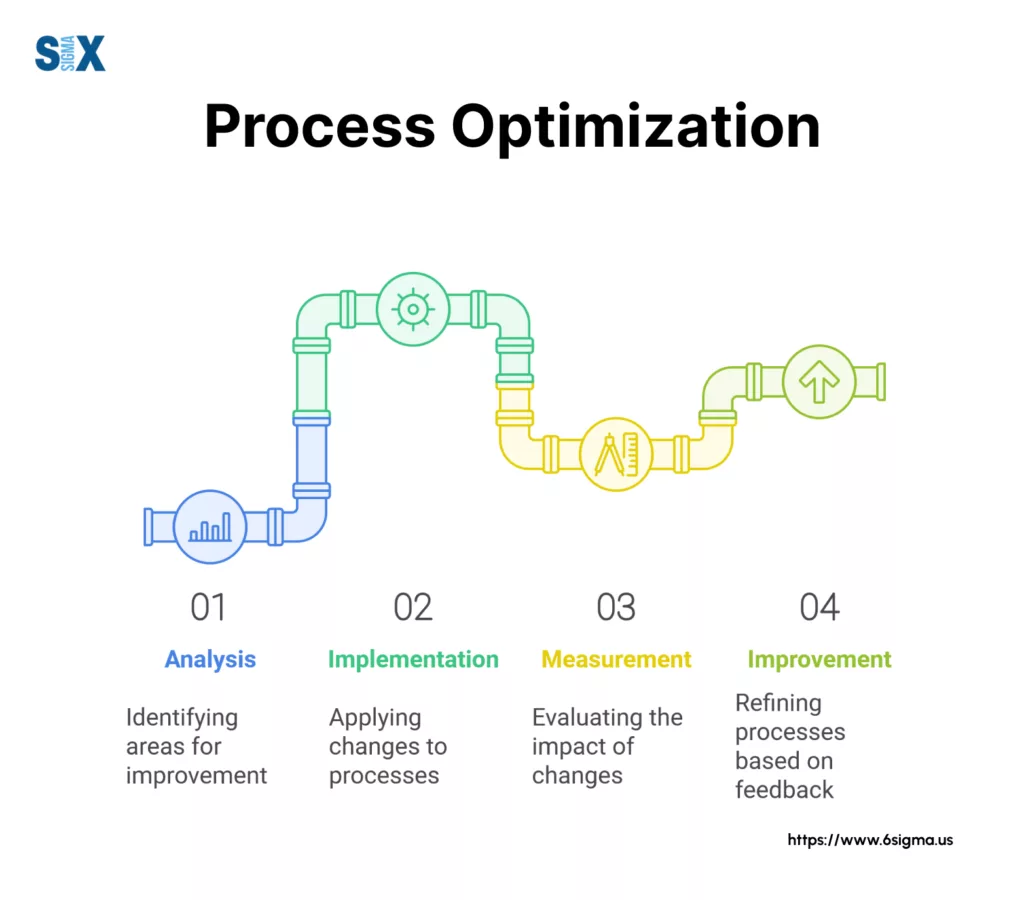
What is Process Optimization?
Process optimization refers to the systematic refinement of business operations to achieve maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
This method involves analyzing, redesigning, and enhancing existing workflows to reduce waste, cut costs, and boost productivity.
Business process optimization has become crucial for organizations aiming to maintain their competitive edge.
Master process mapping and optimization with our certified training program.
Process Optimization vs Process Improvement
While often used interchangeably, process optimization and process improvement serve different purposes.
Process improvement focuses on making incremental changes to existing workflows, whereas process optimization involves a more radical transformation of operations.
This distinction matters because optimization often requires fundamental changes to how work gets done, not just minor adjustments to current procedures.
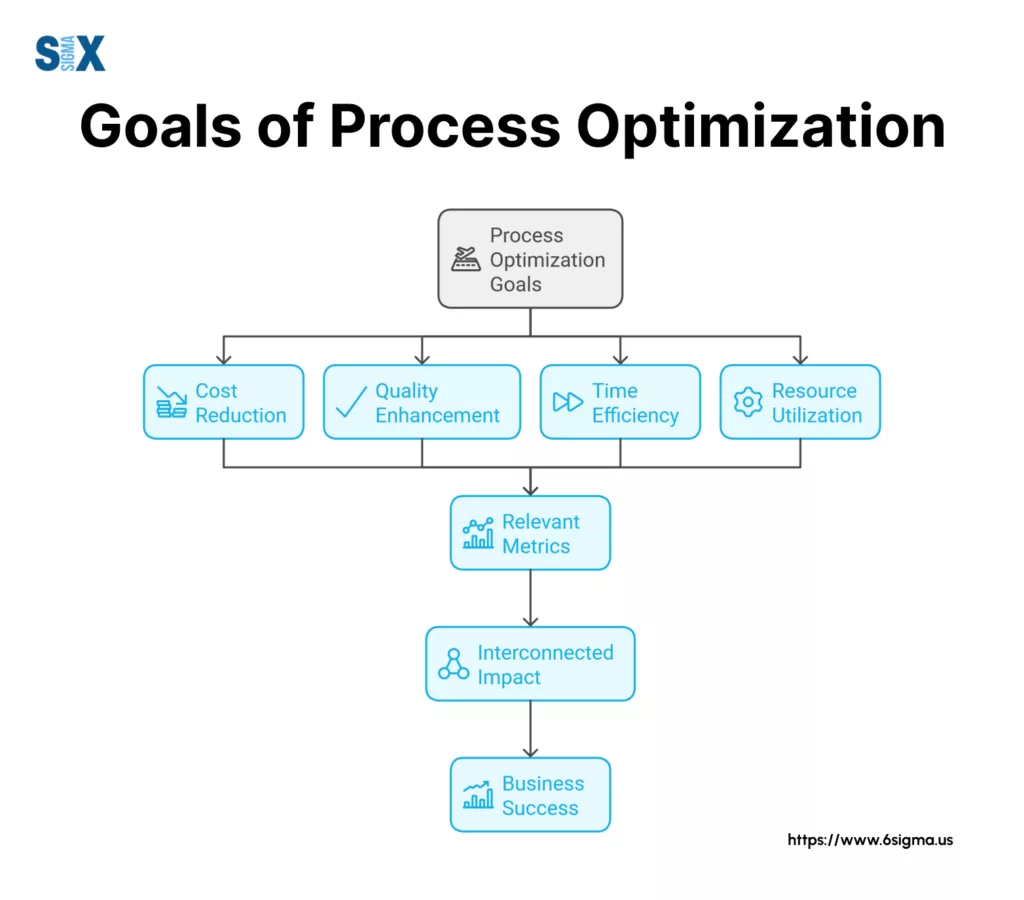
The Four Major Goals of Process Optimization
The primary objectives that drive process optimization efforts include:
- Cost Reduction: Organizations typically achieve 15-25% cost savings through optimized processes by eliminating redundant steps and reducing resource waste.
- Quality Enhancement: Optimized processes lead to fewer errors and more consistent outputs, resulting in higher customer satisfaction rates.
- Time Efficiency: Streamlined workflows can reduce process completion times by up to 50%, enabling faster response to market demands.
- Resource Utilization: Better allocation of human and material resources often yields productivity improvements of 20-30%.
Industry-Specific Impact of Process Optimization
Manufacturing: Process optimization in manufacturing operations typically results in reduced production cycles and improved product quality.
For example, automotive manufacturers have cut assembly time by 30% through optimized production processes.
Healthcare: Hospitals implementing process optimization have reduced patient wait times by up to 40% while improving care quality and staff utilization.
Financial Services: Banks and insurance companies use process optimization to accelerate transaction processing and improve customer service response times by 60%.
Retail: Retailers optimize their supply chain processes to reduce inventory costs by 20-25% while ensuring better product availability.
The Technology Factor in Modern Process Optimization
Today’s process optimization relies heavily on digital tools and advanced analytics.
Machine learning algorithms can now predict process bottlenecks before they occur, while AI-powered automation handles routine tasks with greater accuracy.
These technological advances have transformed how businesses approach process optimization, making it more precise and data-driven than ever before.
Benefits That Drive Business Success Through Process Optimization
Organizations implementing process optimization strategies witness substantial improvements across multiple business areas.
These benefits extend beyond simple efficiency gains, creating lasting value for businesses and their stakeholders.
Efficiency and Productivity Gains
Process optimization directly impacts operational efficiency by streamlining workflows and eliminating bottlenecks. Studies show that optimized processes reduce task completion time by 40-60% on average.
Teams spend less time on repetitive tasks and more time on strategic initiatives that drive business growth.
For example, manufacturing companies that optimize their production processes report productivity increases of up to 35% within the first year of implementation.
Strategic Cost Reduction and Resource Management
Business optimization processes generate significant cost savings through smarter resource allocation.
Organizations typically see a 25-30% reduction in operational costs after implementing optimized workflows. These savings come from:
- Reduced labor costs through automated task management
- Lower material waste by optimizing inventory processes
- Decreased error-related expenses
- Minimized redundancy in operations
Quality Enhancement and Customer Satisfaction with Process Optimization
When businesses optimize their processes, quality improvements naturally follow.
Organizations report a 50% reduction in errors and defects after implementing optimized workflows. This enhancement in quality leads to:
- Higher customer satisfaction scores (typically increasing by 30%)
- Reduced customer complaints (decreasing by up to 45%)
- Improved brand reputation
- Increased customer retention rates
Competitive Advantage Through Agility
Process optimization enables organizations to respond faster to market changes and customer demands. Companies with optimized processes can:
- Launch new products 40% faster than competitors
- Adjust production volumes within 24-48 hours
- Modify service offerings based on real-time customer feedback
- Scale operations without proportional cost increases
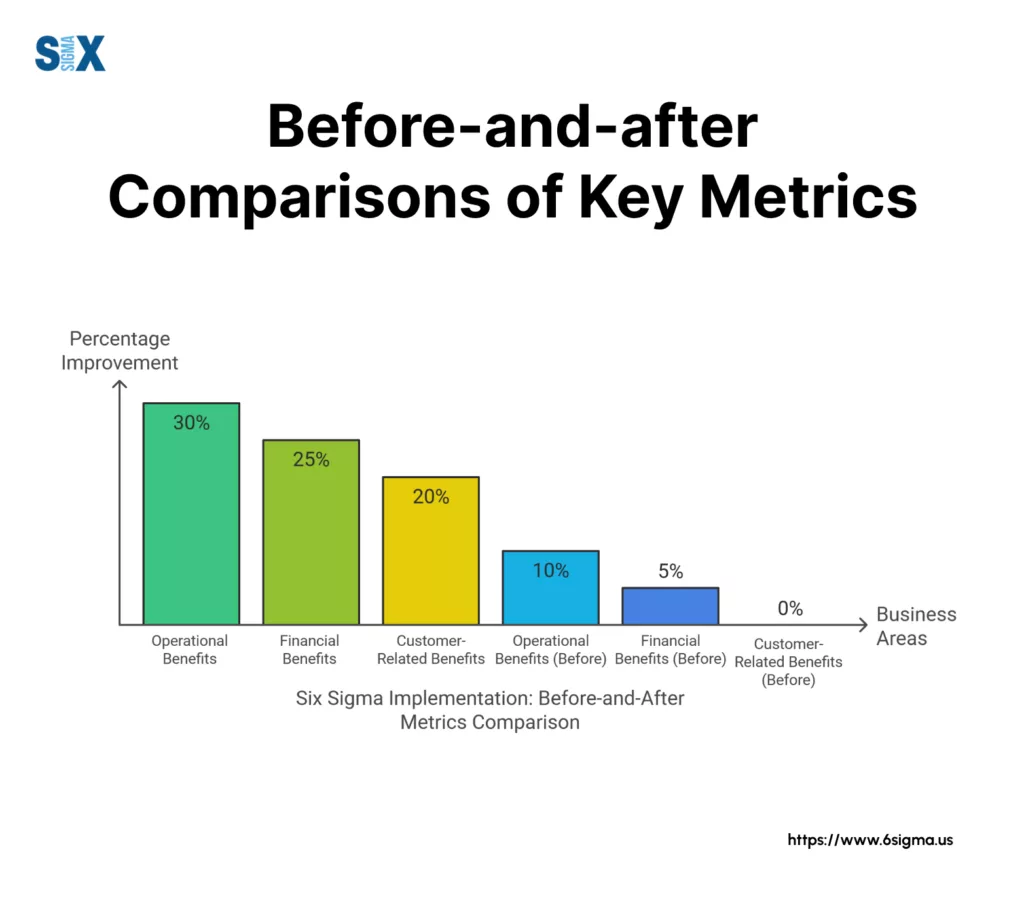
Measuring Success Through Key Metrics
The impact of business process optimization becomes clear through specific performance indicators:
Operational Metrics:
- Process cycle time reduction: 40-60%
- First-time-right rate improvement: 35-45%
- Resource utilization increase: 25-35%
Financial Metrics:
- Operating cost reduction: 25-30%
- Revenue per employee increase: 20-30%
- Return on investment: 150-200% within first year
Customer-Related Metrics:
- Customer satisfaction improvement: 30-40%
- Service delivery speed increase: 45-55%
- Customer retention rate growth: 15-25%
These measurable improvements demonstrate why organizations continue to prioritize process optimization initiatives.
As technology advances and market demands evolve, the benefits of optimized processes become increasingly crucial for maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring sustainable growth.
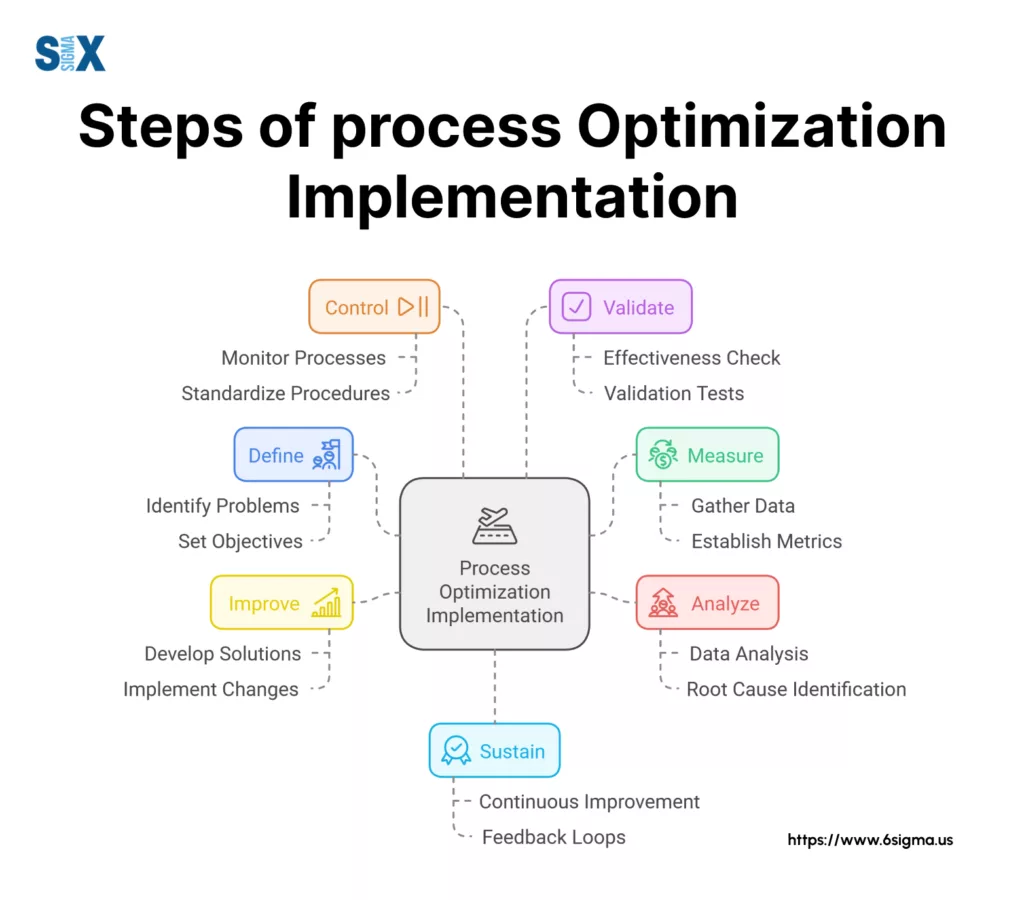
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide for Process Optimization
Successful process optimization requires a structured approach that ensures measurable results and sustainable improvements.
This guide outlines the essential steps organizations must follow to optimize their business processes effectively.
Identifying High-Impact Processes
The first step in process optimization involves selecting the right processes for improvement. Organizations should prioritize processes that:
- Generate significant costs or revenue
- Impact customer satisfaction directly
- Show frequent bottlenecks or delays
- Require substantial manual intervention
- Have high error rates or quality issues
For example, a manufacturing company might focus on production line processes that cause frequent delays, while a service organization could target customer onboarding procedures that generate numerous complaints.
Analyzing Current Process Performance
Before making changes, organizations must thoroughly document and analyze existing processes.
This analysis should include:
- Data Collection: Gather metrics on process duration, costs, error rates, and resource usage.
- Process Mapping: Create detailed flowcharts showing each step, decision point, and handoff.
- Bottleneck Identification: Locate points where work consistently slows down or stops.
- Resource Assessment: Evaluate how staff, technology, and materials are currently utilized.
Setting Clear Process Optimization Goals
Organizations must establish specific, measurable goals for their process optimization efforts. These goals should align with broader business objectives and might include:
- Reducing process cycle time by 30%
- Decreasing operational costs by 25%
- Improving quality metrics by 40%
- Increasing customer satisfaction scores by 35%
Designing Improved Process Flows
The redesign phase focuses on creating more efficient processes by:
- Eliminating unnecessary steps and approvals
- Automating manual tasks where possible
- Standardizing procedures across departments
- Implementing parallel processing for independent tasks
- Reducing handoffs between teams or systems
Managing Implementation Successfully with Process Optimization
Implementing optimized processes requires careful planning and execution:
Phase 1: Pilot Testing
- Select a small-scale environment for initial implementation
- Train relevant staff on new procedures
- Document early results and feedback
- Make necessary adjustments
Phase 2: Full Implementation
- Roll out changes systematically across the organization
- Provide comprehensive training and support
- Monitor adoption rates and compliance
- Address resistance to change promptly
Measuring and Monitoring Results
Regular monitoring ensures the optimized processes deliver expected benefits:
Key Performance Indicators:
- Process cycle times
- Error rates and quality metrics
- Resource utilization rates
- Cost per transaction
- Customer satisfaction scores
Ensuring Continuous Process Refinement
Process optimization doesn’t end with implementation. Organizations must establish mechanisms for ongoing improvement:
- Regular Performance Reviews: Conduct monthly or quarterly assessments of optimized processes.
- Feedback Loops: Create channels for employees and customers to suggest improvements.
- Technology Updates: Evaluate and implement new tools that could further enhance process efficiency.
- Market Alignment: Adjust processes as market conditions and customer needs evolve.
This methodical approach to process optimization helps organizations achieve sustainable improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
By following these steps and maintaining focus on continuous refinement, businesses can create robust processes that adapt to changing market demands and technological advances.
Leading Methodologies for Successful Process Optimization
Several proven methodologies drive successful process optimization initiatives.
Each approach offers unique benefits and can be adapted to specific organizational needs and goals.
Six Sigma: Data-Driven Excellence
Six Sigma methodology focuses on reducing process variations and defects through statistical analysis. Organizations implementing Six Sigma typically achieve a 99.99966% defect-free rate. This method follows the DMAIC framework:
- Define: Identify specific process problems and goals
- Measure: Collect relevant process data
- Analyze: Determine root causes of issues
- Improve: Implement solutions based on analysis
- Control: Monitor results and maintain improvements
Major corporations like General Electric have saved billions through Six Sigma implementation, reducing process defects by up to 92% in key operations.
Professionals looking to apply the the DMAIC framework effectively can benefit from our six sigma green belt certification program, which provides hands-on training in these techniques.
Lean: Eliminating Waste
Lean methodology targets waste reduction in business processes optimization. This approach identifies eight types of waste:
- Defects in products or services
- Overproduction of goods
- Waiting time between steps
- Non-utilized talent
- Transportation inefficiencies
- Inventory excess
- Motion waste
- Extra processing
Toyota’s implementation of Lean principles reduced production time by 50% while improving quality by 25%.
The methodology emphasizes creating value for customers while minimizing resource consumption.
Kaizen: Continuous Improvement Culture
Kaizen promotes ongoing, incremental improvements in process optimization.
This Japanese methodology involves all employees, from executives to front-line workers. Organizations using Kaizen report:
- 70% reduction in process-related problems
- 45% improvement in employee engagement
- 30% decrease in operational costs
- 25% increase in productivity
Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM integrates quality control into every aspect of business operations.
This methodology emphasizes:
- Customer-focused quality standards
- Process-centered decision making
- Integrated system approach
- Strategic quality planning
- Employee empowerment
Organizations implementing TQM report 40% fewer customer complaints and 35% higher customer satisfaction rates.
Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
BPR involves fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes. This methodology suits organizations needing dramatic performance improvements. Key aspects include:
- Clean-slate process redesign
- Technology-driven solutions
- Cross-functional coordination
- Customer-centric approach
- End-to-end process optimization
Companies implementing BPR have achieved:
- 65% reduction in process cycle times
- 75% decrease in process costs
- 80% improvement in quality metrics
Selecting the Right Methodology for Process Optimization
Organizations should consider several factors when choosing a process optimization methodology:
Business Goals:
- Quality improvement: Six Sigma or TQM
- Waste reduction: Lean
- Cultural transformation: Kaizen
- Radical change: BPR
Resource Availability:
- Training requirements
- Implementation timeframe
- Required investment
- Available expertise
Here’s a detailed comparison table for the five methodologies:
| Aspect | Six Sigma | Lean | Kaizen | Total Quality Management (TQM) | Business Process Reengineering (BPR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Reducing defects and variability to achieve near perfection (3.4 defects per million opportunities). | Eliminating waste to maximize value for customers. | Continuous small-scale improvements driven by employee involvement. | Organization-wide quality enhancement and customer satisfaction. | Radical redesign of business processes for dramatic improvement. |
| Key Tools | DMAIC, DMADV, Statistical Process Control (SPC), Fishbone Diagrams, Pareto Charts. | Value Stream Mapping, Kanban, 5S, Just-In-Time (JIT), Continuous Flow. | PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act), 5S, Gemba Walks, Suggestion Systems. | Quality Circles, ISO Standards, Benchmarking, Control Charts. | Process Flowcharts, IT-enabled Modeling, Workflow Analysis, Simulation Tools. |
| Implementation Time | Medium to long-term (months to years, depending on scope). | Medium to short-term (can be incremental and continuous). | Ongoing (integrated into daily operations). | Long-term (requires cultural shift and sustained focus). | Short to medium-term (depending on the scale of redesign). |
| Resource Requirements | High: Needs skilled personnel, training, and advanced statistical tools. | Moderate: Requires training and team involvement but fewer advanced tools. | Low: Relies on employee initiative and minor adjustments. | Moderate to High: Needs leadership commitment and organization-wide involvement. | High: Requires significant investment in technology and resources. |
| Typical Results | Drastic reduction in defects, cost savings, and improved customer satisfaction. | Streamlined operations, reduced lead times, and lower costs. | Incremental improvements in efficiency and morale. | Improved customer satisfaction, consistent quality, and better teamwork. | Quantum leaps in efficiency, cost reduction, and competitiveness. |
| Best Suited For | Processes with measurable data and where defects have high costs. | Repetitive processes with visible waste (e.g., manufacturing, logistics). | Organizations seeking ongoing small improvements and cultural engagement. | Organizations looking for broad quality and customer satisfaction improvements. | Companies needing major performance turnaround or competitive edge. |
| Success Examples | Motorola, General Electric, AlliedSignal. | Toyota Production System, Nike, Intel. | Toyota, Nestlé, and many small-medium enterprises. | Xerox, Johnson & Johnson, Ford Motor Company. | IBM, Ford (in the 1990s), Procter & Gamble. |
Six Sigma certification tiers (Six Sigma White Belt Certification to Six Sigma Master Black Certification Belt) offer progressive expertise for implementing these methodologies.
Organizations often combine methodologies for optimal results. Our Six Sigma certification programs integrate waste reduction with data-driven quality control, making them ideal for holistic process optimization.
Managing Change and Driving Adoption in Process Optimization
Successful process optimization depends heavily on effective change management and employee buy-in.
Organizations that excel in change management report 93% higher achievement of project objectives compared to those that neglect this crucial aspect.
Why Change Management Matters
Process optimization initiatives often fail not due to technical issues, but because of resistance to change.
Effective change management strategies increase adoption rates by 60% and reduce implementation time by 45%.
Building Effective Communication Channels
Clear communication forms the foundation of successful process optimization adoption. Organizations must establish multi-directional communication channels that:
- Share the vision and benefits of process changes
- Address concerns and questions promptly
- Provide regular updates on progress
- Celebrate early wins and successes
Regular town halls, team meetings, and digital platforms help maintain open dialogue throughout the optimization journey.
Companies that implement structured communication plans see 80% higher employee engagement in process changes.
Employee Training and Support Systems for Process Optimization
Organizations must invest in robust training, such as six sigma certification programs, to ensure smooth transitions during process optimization. Effective training approaches include:
- Role-specific training modules
- Hands-on practice sessions
- Mentoring programs
- Online learning resources
- Regular feedback sessions
Companies that allocate sufficient resources to training report faster adoption rates and fewer implementation issues.
Effective training programs include role-specific modules and hands-on practice. For instance, root cause analysis training helps teams address process inefficiencies at their source, reducing recurring issues by up to 40%.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Long-term success in process optimization requires creating an environment where improvement becomes second nature. Organizations can foster this culture by:
- Encouraging employee suggestions
- Recognizing and rewarding innovation
- Providing time for improvement activities
- Supporting experimentation
- Sharing success stories across teams
Organizations with strong improvement cultures see 50% higher employee participation in optimization initiatives and 35% better sustained results.
Measuring Change Management Success
Key metrics for tracking change management effectiveness include:
- Employee adoption rates
- Time to proficiency
- Resistance incidents
- Productivity during transition
- Employee satisfaction scores
Regular measurement helps organizations adjust their approach and provide additional support where needed.

Organizations must recognize that change management represents an investment in the success of their process optimization efforts.
By dedicating appropriate resources to managing change and supporting employees, businesses significantly increase their chances of achieving and sustaining desired improvements.
Moving Forward with Process Optimization
Process optimization stands as a crucial driver of business success in today’s competitive environment.
Organizations that implement structured optimization programs report higher operational efficiency and better customer satisfaction rates.
These improvements stem from systematic approaches to analyzing, redesigning, and enhancing business processes.
Key Takeaways for Business Success
The journey of process optimization requires careful planning, robust methodologies, and strong change management.
Organizations achieve the best results when they combine proven techniques like Six Sigma and Lean with modern technological solutions.
The Road Ahead
The future of process optimization lies in the integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation.
Industry 4.0 technologies will enable predictive optimization, allowing businesses to address inefficiencies before they impact operations.
Green process optimization will gain prominence as sustainability becomes a key business priority.
Organizations must act now to remain competitive. Start by assessing current processes, identifying improvement opportunities, and developing a structured optimization plan.
Remember that successful process optimization requires commitment, resources, and a willingness to embrace change.
The time to optimize is now. Begin your organization’s transformation journey with a clear vision, strong leadership support, and a focus on sustainable improvements.
The rewards of enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction await those who take action today.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






