The Top 15 Process Improvement Tools: Boost Your Business Efficiency
Process improvement tools help businesses identify problems, streamline operations, and boost efficiency.
Each tool serves a specific purpose in making your operations better. From mapping out workflows to solving complex problems, these tools give you practical ways to enhance how your business runs.
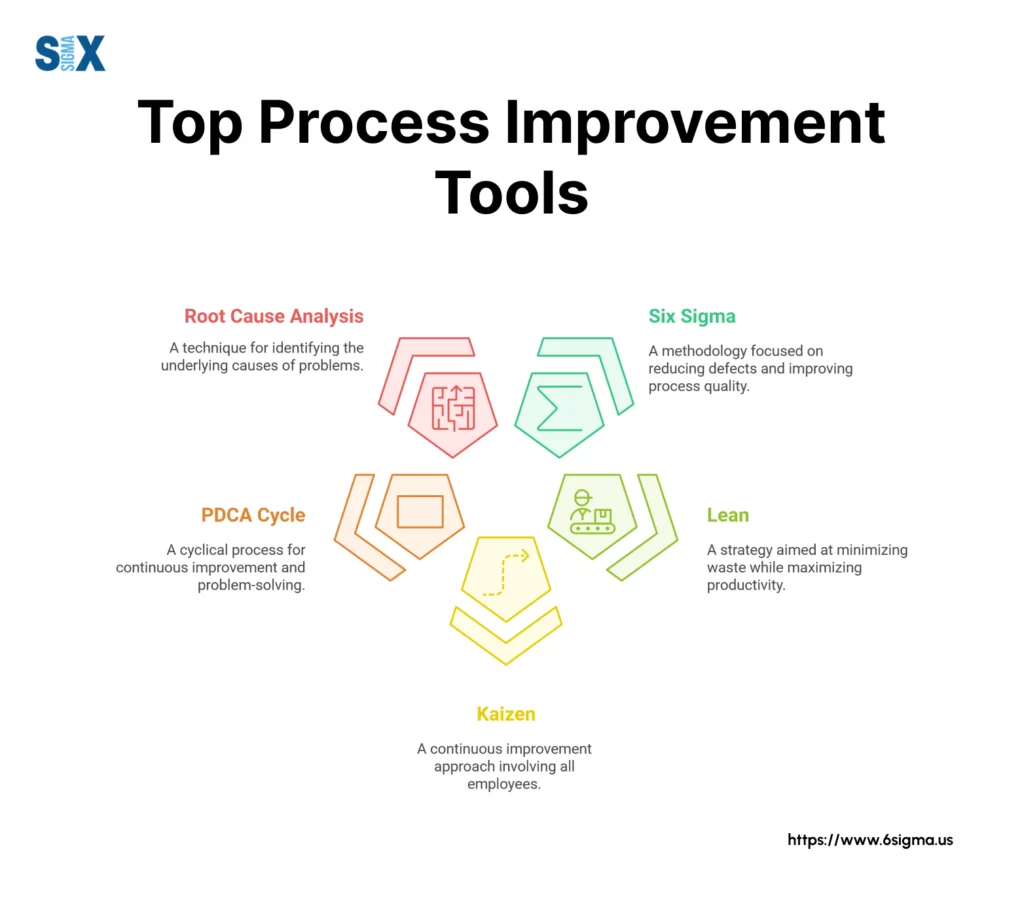
What You’ll Learn in This Guide
- Detailed explanations of each tool
- Real examples of how businesses use these tools
- Step-by-step guides for implementation
- Tips to avoid common pitfalls
- Ways to measure success
What Is Process Improvement?
Process improvement means making your business operations work better. It’s like fine-tuning an engine – you identify what’s slowing things down, fix the issues, and keep your business running smoothly.
Every business, from small startups to large corporations, can benefit from improving their processes.
Six Sigma certification focuses on mastering systematic methodologies where you can identify inefficiencies and driving measurable improvements.
Examples of Process Improvement
Let’s look at how process improvement works in practice:
- A restaurant cuts food prep time by reorganizing their kitchen layout
- An insurance company reduces claim processing from 5 days to 2 days
- A manufacturing plant decreases defects by 40% through better quality checks
Why Process Improvement Tools Matter
Process improvement tools give you a structured way to solve business problems.
They’re like a mechanic’s toolkit – each tool helps fix specific issues in your operations. Some tools help you map out workflows, while others help identify and solve problems.
Key Benefits You’ll See
When you use process improvement tools correctly, you’ll notice:
- Faster delivery times
- Lower operational costs
- Fewer mistakes and defects
- Happier employees
- More satisfied customers
- Better profit margins
Common Challenges You Might Face
Improving processes isn’t always easy. Here are the challenges most businesses face:
Employee Resistance
People often resist change. The key is involving your team early and showing them how improvements make their jobs easier.
Resource Constraints
You might not have endless time or money. Start small – focus on one process at a time and build momentum through quick wins.
Lack of Clear Goals
Without specific goals, improvement efforts can lose direction. Set clear, measurable targets like “reduce processing time by 25%” or “cut errors by half”.
Maintaining Improvements
Many businesses struggle to keep improvements going. Regular monitoring and team check-ins help sustain the gains you make.
Getting Past These Challenges
Here’s what successful companies do:
- Start with small, manageable projects
- Measure results to show progress
- Celebrate wins with their teams
- Make improvement part of daily work
- Keep communication channels open
Remember, process improvement isn’t a one-time project – it’s an ongoing journey.
The most successful businesses make it part of their culture and keep looking for ways to get better.
Transform your business operations with our Yellow Belt training
Types of Process Improvement Tools
Let’s break down process improvement tools into four main categories. Think of these categories like different departments in a hardware store – each section has specific tools for different jobs.
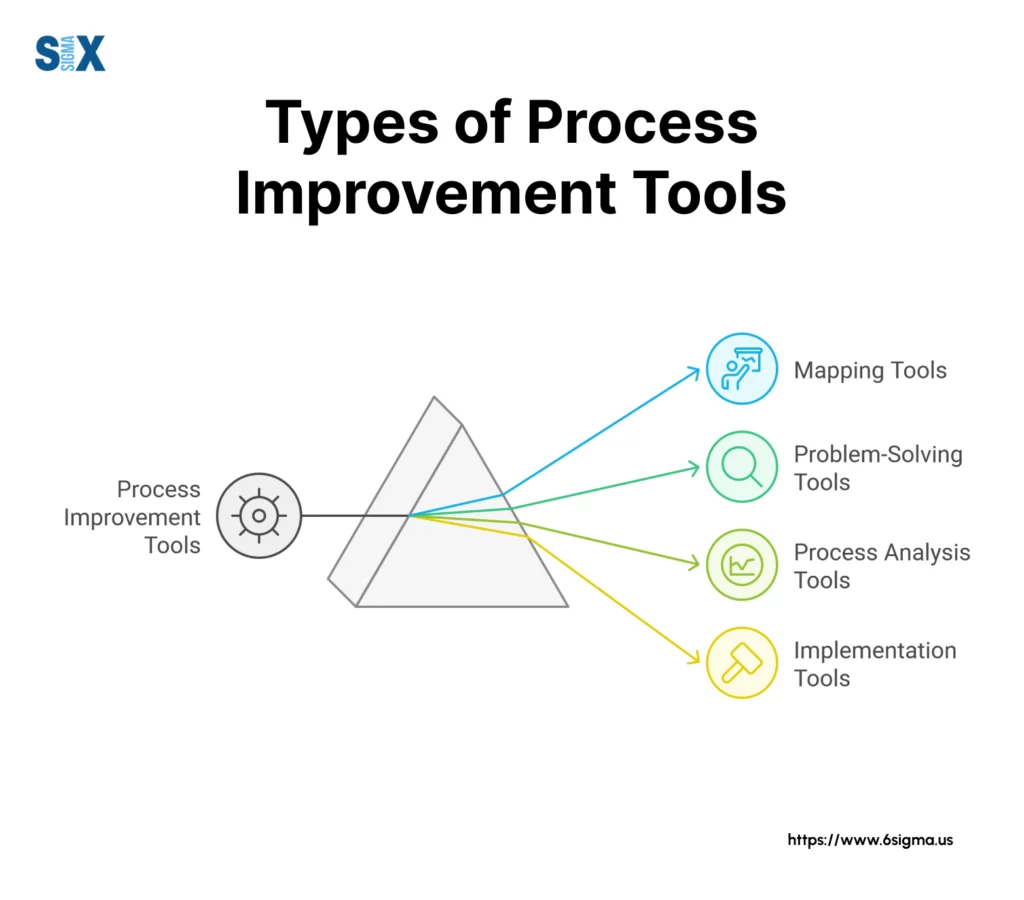
Mapping Tools: Visualize Your Processes
Mapping tools help you see how work flows through your business. They’re like creating a roadmap of your operations.
Popular mapping tools include:
- Value Stream Mapping: Shows how materials and information move through your business
- Process Flowcharts: Create step-by-step diagrams of your workflows
- SIPOC Diagrams: Map out suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs, and customers
When to use mapping tools:
- You need to understand complex workflows
- Teams aren’t clear about process steps
- You want to find bottlenecks in your operations
Problem-Solving Tools: Find and Fix Issues
These tools help you identify and solve specific problems in your processes.
Key problem-solving tools:
- 5 Whys Analysis: Dig deep to find root causes
- Fishbone Diagrams: Map out all possible causes of a problem
- Pareto Analysis: Focus on the vital few issues causing most problems
When to use problem-solving tools:
- Quality issues keep popping up
- You face recurring problems
- You need to prioritize which problems to tackle first
Process Analysis Tools: Measure and Improve
Analysis tools help you understand how well your processes work and where to improve them.
Popular analysis tools:
- Six Sigma: Reduce defects through data analysis
- Statistical Process Control: Monitor process performance
- Capability Analysis: Measure if processes meet requirements
When to use analysis tools:
- You need data to make decisions
- Quality standards aren’t being met
- You want to predict process performance
Organizations implementing Six Sigma often train teams through structured Six Sigma certification programs, which equip professionals with data-driven problem-solving frameworks like DMAIC.
Implementation Tools: Make Changes Stick
These tools help you put improvements in place and maintain them.
Key implementation tools:
- PDCA Cycle: Plan, Do, Check, Act for continuous improvement
- 5S: Organize workspaces for efficiency
- Kaizen Events: Make rapid improvements in specific areas
When to use implementation tools:
- You’re ready to make changes
- Teams need a structured way to improve
- You want to maintain gains over time
Choosing the Right Process Improvement Tools
Here’s a quick guide to picking the right tool:
- Start with mapping tools to understand your current process
- Use problem-solving tools to identify issues
- Apply analysis tools to measure and improve
- Use implementation tools to make changes and maintain them
How Process Improvement Tools Work Together
A manufacturing company I worked with used:
- Value Stream Mapping to visualize their production line
- 5 Whys to find the cause of delays
- Statistical Process Control to measure improvements
- PDCA to implement and maintain changes
Result: They cut production time by 40% and reduced defects by half.
Remember: You don’t need to use every tool. Pick the ones that fit your specific needs and start with the basics. As you get more comfortable, you can add more tools to your toolkit.
15 Most Effective Process Improvement Tools
Let’s explore the most powerful tools that can transform your business operations. I’ll share examples and practical tips for each tool based on my experience implementing them across different industries.
1. Six Sigma: Eliminate Defects and Variation
Six Sigma isn’t just a tool – it’s a complete methodology that helps you deliver near-perfect products and services.
The DMAIC Process
- Define: Identify the problem and goals
- Measure: Collect data about current performance
- Analyze: Find root causes of problems
- Improve: Implement and verify solutions
- Control: Maintain the improvements
Earning a Six Sigma Green Belt certification provides in-depth training on executing DMAIC, enabling practitioners to lead complex improvement projects.
Success Story
A medical device manufacturer used Six Sigma to tackle their quality issues.
They:
- Reduced defects by 40%
- Cut rework costs by $300,000 annually
- Improved customer satisfaction scores by 25%
2. Lean Manufacturing: Remove Waste
Toyota pioneered Lean manufacturing, and it’s now used worldwide to eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
Key Lean Tools
- 5S: Organize workspaces
- Kanban: Manage workflow
- Just-in-Time: Reduce inventory
- Value Stream Mapping: Visualize processes
Toyota’s Success Story
Toyota’s Lean approach helped them:
- Reduce inventory costs by 75%
- Cut production time by 50%
- Improve quality while lowering costs
To start with introductory Lean Fundamentals course often cover core tools like 5S and Value Stream Mapping, providing a foundation for waste reduction.
3. PDCA Cycle: Simple But Powerful
The Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle gives you a structured way to solve problems and improve processes.
How PDCA Works
- Plan: Set goals and predict outcomes
- Do: Test your solution on a small scale
- Check: Measure the results
- Act: Implement or adjust based on results
Practical Example
A restaurant used PDCA to improve their service time:
- Plan: Target 20-minute service time
- Do: Tested new kitchen layout
- Check: Measured actual service times
- Act: Rolled out new layout to all shifts
- Result: Cut average service time from 30 to 18 minutes
4. 5 Whys Analysis: Get to The Root Cause
The 5 Whys helps you dig deep to find the real cause of problems. It’s simple but incredibly effective.
How to Use 5 Whys
Start with your problem and keep asking “why” until you find the root cause. Here’s a real example:
Problem: Late deliveries
- Why are deliveries late? → Trucks leave the warehouse late
- Why do trucks leave late? → Loading takes too long
- Why does loading take too long? → Can’t find the right products
- Why can’t products be found? → Poor warehouse organization
- Why is the warehouse poorly organized? → No standard storage system
5. Value Stream Mapping: See The Whole Picture
Value Stream Mapping shows you exactly how work flows through your business. It’s like getting a bird’s eye view of your operations.
Creating Your Map
- Draw current state: Show how things work now
- Identify waste: Look for bottlenecks and delays
- Design future state: Map out improvements
- Create action plan: List specific changes needed
Success Story
An auto parts supplier mapped their process and found:
- 3 unnecessary handoffs
- 2 days of inventory sitting idle
- 40% reduction in lead time after improvements
6. Fishbone Diagram: Break Down Complex Problems
Also called the Ishikawa diagram, this tool helps you see all possible causes of a problem.
Main Components
- People: Staff-related issues
- Process: Workflow problems
- Equipment: Machine or tool issues
- Materials: Supply chain concerns
- Environment: Workplace factors
- Management: Leadership decisions
Healthcare Example
A hospital used this to reduce patient wait times:
- Found 23 potential causes
- Identified 3 major issues to fix first
- Cut wait times by 45%
7. Pareto Analysis: Focus On What Matters Most
The 80/20 rule helps you focus on the vital few issues causing most problems.
How It Works
- List all problems
- Measure their impact
- Rank from highest to lowest
- Focus on top 20% causing 80% of issues
Customer Service Example
A call center found:
- 3 issues caused 80% of complaints
- Fixed these first
- Reduced complaints by 60%
8. Process Flowcharts: Map Your Way To Success
Flowcharts give you a clear picture of how work should flow.
Types of Flowcharts
- Basic: Simple step-by-step
- Detailed: Including decisions points
- Swim lane: Shows who does what
- Cross-functional: Maps complex processes
Sales Process Example
A software company mapped their sales process:
- Found 5 unnecessary steps
- Cut sales cycle by 30%
- Improved close rate by 25%
9. Kaizen: Small Changes, Big Results
Kaizen means ‘continuous improvement‘ – making small changes every day.
Key Principles
- Everyone involved
- Daily improvements
- Focus on small wins
- Eliminate waste
Success Story
A manufacturing plant used Kaizen to:
- Reduce setup time by 20%
- Cut defects by 30%
- Boost productivity by 25%
10. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Data-Driven Decisions
SPC helps you monitor and control processes using statistical data. It’s like having a dashboard for your operations.
Key Features
- Control charts
- Process capability studies
- Variation analysis
- Trend monitoring
Manufacturing Example
A food processor used SPC to:
- Reduce product weight variation by 50%
- Save $200,000 in material costs
- Improve product consistency
11. Gemba Walk: See It For Yourself
Gemba means “the real place” – where work actually happens.
How to Do It Right
- Go to the workplace
- Observe actual work
- Talk to employees
- Look for improvement opportunities
Retail Success Story
A store manager’s Gemba walks revealed:
- Inefficient storage layout
- Unnecessary walking distances
- After changes: 30% faster restocking
12. SIPOC Diagram: Map Your Process Chain
SIPOC helps you see how your process connects with suppliers and customers.
Components
- Suppliers: Who provides inputs?
- Inputs: What goes into the process?
- Process: What happens?
- Outputs: What’s produced?
- Customers: Who receives the output?
Service Industry Example
An insurance company used SIPOC to:
- Identify missing process steps
- Reduce claim processing time by 40%
- Improve customer satisfaction
13. Root Cause Analysis (RCA): Solve Problems Permanently
RCA helps you find and fix the true source of problems.
Key Steps
- Define the problem
- Collect data
- Identify causes
- Find root cause
- Implement solutions
IT Case Study
A tech company used RCA to:
- Solve recurring server crashes
- Prevent 90% of downtime
- Save $500,000 annually
Formal root cause analysis training teach structured techniques like the 5 Whys and Fishbone Diagrams to systematically address recurring issues.
14. Bench-marking: Learn From The Best
Compare your processes with industry leaders to find improvement opportunities.
Types of Benchmarking
- Internal: Compare between departments
- Competitive: Study competitors
- Industry: Look at similar businesses
- Best-in-class: Learn from top performers
Healthcare Example
A hospital bench-marked patient discharge:
- Found 40% faster processes elsewhere
- Adopted best practices
- Reduced discharge time by 35%
15. Theory of Constraints (TOC): Remove Bottlenecks
TOC helps you identify and fix what’s holding your process back.
Core Principles
- Find the constraint
- Exploit the constraint
- Subordinate everything else
- Elevate the constraint
- Repeat the process
Project Management Success
A construction company used TOC to:
- Identify critical path bottlenecks
- Reduce project delays by 60%
- Improve resource allocation
Choosing The Right Tool
Pick your tool based on your goal:
- Quality issues? Start with Six Sigma
- Efficiency problems? Try Lean
- Unknown issues? Use 5 Whys or RCA
- Complex processes? Begin with Value Stream Mapping
These tools work best when combined thoughtfully. Start with one, master it, then add others as needed.
How to Choose The Right Process Improvement Tool
Picking the right tool makes all the difference in your improvement efforts. Here’s how to make the best choice for your situation.
Key Factors to Consider when Selecting a Process Improvement Tool
Before selecting a tool, ask yourself:
- What problem are you trying to solve?
- How complex is your process?
- What resources do you have?
- How much time can you invest?
- What’s your team’s experience level?
Matching Tools to Business Problems
Quality Issues:
- Six Sigma for reducing defects
- SPC for monitoring quality
- Fishbone diagrams for finding causes
Efficiency Problems:
- Lean Manufacturing for removing waste
- Value Stream Mapping for process flow
- Theory of Constraints for bottlenecks
Unknown Problems:
- 5 Whys for root causes
- Gemba Walks for direct observation
- SIPOC for process overview
Drive game-changing improvements with our Black Belt training in advanced process optimization techniques
Making Process Improvements Stick
Start Small
- Pick one process
- Set clear goals
- Get quick wins
Build Your Team
- Train key people
- Assign clear roles
- Create accountability
Track Progress
- Measure results
- Document changes
- Share successes
Watch Out For These Pitfalls
- Trying too much too soon
- Not involving front-line staff
- Skipping the training step
- Forgetting to measure results
- Losing momentum after initial success
Keys to Long-Term Success
Make it routine
- Regular check-ins
- Monthly reviews
- Ongoing training
Celebrate wins
- Share success stories
- Recognize team efforts
- Build on momentum
Keep improving
- Set new goals
- Try new tools
- Learn from setbacks
Next Steps: Getting Started with your Process Improvement Tool
Ready to improve your processes? Here’s what to do:
- Pick your biggest pain point
- Choose one tool that fits
- Start small and measure results
- Build on your success
Process improvement isn’t a one-time project – it’s a journey. Start where you are, use what you have, and keep moving forward.
Your Action Plan
This week:
- Identify one process to improve
- Pick a suitable tool
- Get your team on board
Next month:
- Implement your first improvement
- Measure the results
- Share the success
Long term:
- Build your toolkit
- Train your team
- Create a culture of improvement
The most successful businesses make process improvement part of their DNA. You’ve got the tools – now it’s time to put them to work.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







