 Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Unit I
Unit I
Introduction to Statistical
Introduction to Statistical
Design of Experiments
Design of Experiments
|
 2
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
To determine if there is a better way to do
To determine if there is a better way to do
something
something
An experiment is performed under controlled
An experiment is performed under controlled
conditions to determine an unknown effect
conditions to determine an unknown effect
Statistical Design of Experiments (DOE) is a
Statistical Design of Experiments (DOE) is a
method of controlling one or more input
method of controlling one or more input
variables at two or more levels to determine if
variables at two or more levels to determine if
and how one or more output variables change
and how one or more output variables change
Why Experiment?
Why Experiment?
|
 3
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Optimize Process/Product
Optimize Process/Product
Performance
Performance
Minimize Variability/Robust Design
Minimize Variability/Robust Design
Identify Factors that effect Process
Identify Factors that effect Process
Performance
Performance
Minimize Development Time!
Minimize Development Time!
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
|
 Example: Suppose you are
building a new house and
must landscape. How will
you grow the
Example: Suppose you are
Example: Suppose you are
building a new house and
building a new house and
must landscape. How will
must landscape. How will
you grow the
you grow the
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
•
Seed Types
•
•
Seed Types
Seed Types
•
Moisture
•
•
Moisture
Moisture
•
Fertilizer
•
•
Fertilizer
Fertilizer
•
Soil
•
•
Soil
Soil
4
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
|
 5
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Response Variable
Response Variable
The observed/measured result
The observed/measured result
“Output variable, dependent
“Output variable, dependent
variable”
variable”
Quality characteristic
Quality characteristic
Is the “what” to be improved
Is the “what” to be improved
through Experimentation.
through Experimentation.
From the Example: Thick, Green Grass
From the Example: Thick, Green Grass
Thick, Green Grass
is a Response
is a Response
Variable
Variable
|
|
6
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Main Effects
Main Effects
Independent Variable/Input Factor
Independent Variable/Input Factor
--
--
an
an
assignable cause which may affect the
assignable cause which may affect the
response variable and which is included
response variable and which is included
at different levels in the experiment.
at different levels in the experiment.
From example: the following Main Effects could affect thick,
From example: the following Main Effects could affect thick,
Green Grass
Green Grass
-
-
Type of grass seed
Type of grass seed
-
-
Type of soil
Type of soil
-
-
Amount of Fertilizer
Amount of Fertilizer
-
-
Amount of Water
Amount of Water
|
 7
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Main Effect Descriptors
Main Effect Descriptors
Qualitative
Qualitative
--
--
category and/or order,
category and/or order,
alphanumeric
alphanumeric
Type of soil: Clay, Top Soil
Type of soil: Clay, Top Soil
Quantitative
Quantitative
--
--
numeric
numeric
Amount of water: 20 minutes of water
Amount of water: 20 minutes of water
per day; 60 minutes of water per day
per day; 60 minutes of water per day
|
 8
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Main Effect Levels
Main Effect Levels
Level
Level
--
--
a given setting or amount of an Main Effect
a given setting or amount of an Main Effect
–
–
Set a Main Effect at two or more levels to determine if a
Set a Main Effect at two or more levels to determine if a
Response Variable improves at a given level
Response Variable improves at a given level
From the grass example:
From the grass example:
Type of Grass Seed
Type of Grass Seed
-
-
Level 1 = Red Fescue
Level 1 = Red Fescue
-
-
Level 2 = Perennial
Level 2 = Perennial
Rye
Rye
Amount of Fertilizer
Amount of Fertilizer
-
-
Level 1 = 2 bags per
Level 1 = 2 bags per
week
week
-
-
Level 2 = 1 bag per week
Level 2 = 1 bag per week
|
|
9
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
A characteristic of the Design of
A characteristic of the Design of
Experiments method is the ability to
Experiments method is the ability to
test a combination of Main Effects at
test a combination of Main Effects at
different levels. Therefore, Design of
different levels. Therefore, Design of
Experiments allows the experimenter
Experiments allows the experimenter
to see how many Main Effects
to see how many Main Effects
affecting a product or process
affecting a product or process
interrelate.
interrelate.
Treatment Combination
Treatment Combination
|
|
10
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
--
--
The
The
combination of Main Effects and
combination of Main Effects and
levels for each experimental trial
levels for each experimental trial
in a fractional or full factorial
in a fractional or full factorial
Design of Experiment.
Design of Experiment.
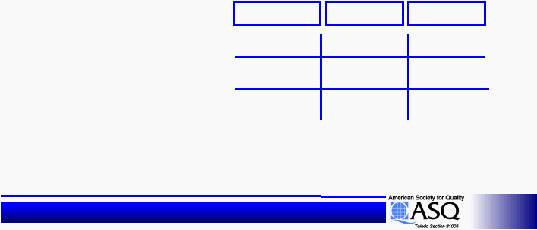
Treatment Combination
Treatment Combination
|
 11
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Treatment Combination
Treatment Combination
Possible
Possible
Treatment
Treatment
Combination:
Combination:
Main Effect
Main Effect
Level 1
Level 1
Level 2
Level 2
Grass Seed
Grass Seed
Soil Type
Soil Type
Amount of
Amount of
Water
Water
Red Fescue
Red Fescue
Clay
Clay
20
20
Min/Day
Min/DayMin/Day
Per. Rye
Per. Rye
Top Soil
Top SoilTop Soil
60
60
Min/Day
Min/Day
Red Fescue,
Red Fescue,
Top Soil and
Top Soil and
20 minutes
20 minutes
water
water
Red Fescue
Red Fescue
20
20
Min/Day
Top Soil
|
 12
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Repeated Trial (Replication)
Repeated Trial (Replication)
Repeat a treatment combination 2 or
Repeat a treatment combination 2 or
more times.
more times.
A repeated trial is done to estimate
A repeated trial is done to estimate
the pure trial-to-trial estimate of
the pure trial-to-trial estimate of
error, so that the lack of fit may be
error, so that the lack of fit may be
judged.
judged.
|
  13
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
is Useful in Agriculture
is Useful in Agriculture
Agricultural Fields were
Agricultural Fields were
ideal for testing more
ideal for testing more
than one treatment
than one treatment
combination since land
combination since land
can be sectioned.
can be sectioned.
|
  14
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
is Useful in Agriculture
is Useful in Agriculture
Historically,
Historically,
DOE was used
DOE was used
in Agriculture as
in Agriculture as
well as
well as
Academia.
Academia.
|
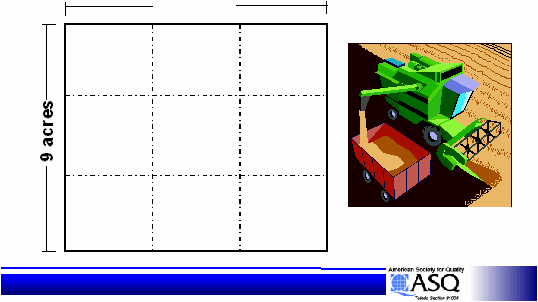 15
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
is Useful in Agriculture
is Useful in Agriculture
9 acres
9 acres
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
#1
#1
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
# 2
# 2
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
# 3
# 3
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
# 4
# 4
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
# 5
# 5
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
# 6
# 6
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
# 7
# 7
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
# 8
# 8
Treatment
Treatment
Combination
Combination
# 9
# 9
|
  16
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Treatment
Treatment
combination
combination
results would
results would
be compared
be compared
for each section
for each section
of land to
of land to
determine the
determine the
best.
best.
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
is Useful in Agriculture
is Useful in Agriculture
|
  17
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
R. A. Fisher
R. A. Fisher
approach to
approach to
Design of
Design of
Experiments.
Experiments.
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
is Useful in Agriculture
is Useful in Agriculture
|
  18
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
For Example:
For Example:
A
A
corn farmer
corn farmer
desires to
desires to
increase corn
increase corn
yield. The
yield. The
farmer has
farmer has
sectioned his
sectioned his
land into 1 acre
land into 1 acre
plots ...
plots ...
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
is Useful in Agriculture
is Useful in Agriculture
|
 19
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Corn Yield Improvement
Corn Yield Improvement
How can corn
How can corn
yield be
yield be
improved?
improved?
|
 20
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Corn Yield Improvement
Corn Yield Improvement
What are the
What are the
Main Effects
Main Effects
which might help
which might help
to increase corn
to increase corn
yield?
yield?
|
 21
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Corn Yield Improvement
Corn Yield Improvement
How many levels
How many levels
per Main Effect?
per Main Effect?
|
 22
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Corn Yield Improvement
Corn Yield Improvement
At what levels
At what levels
should each
should each
Main Effect be
Main Effect be
tested?
tested?
|
 23
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Corn Yield Improvement
Corn Yield Improvement
Level 1
Level 1
Level 2
Level 2
Type of Seed
Type of Seed
Seed Population
Seed Population
Distance between
Distance between
corn plants
corn plants
A
A
2 seeds per
2 seeds per
Natural
Natural
B
B
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
12 inches
12 inches
Type of fertilizer
Type of fertilizer
A
A
B
B
Type of soil
Type of soil
6 inches
6 inches
Top soil
Top soil
Amount of water
Amount of water
Clay
Clay
Irrigation
Irrigation
Main Effects
Main Effects
|
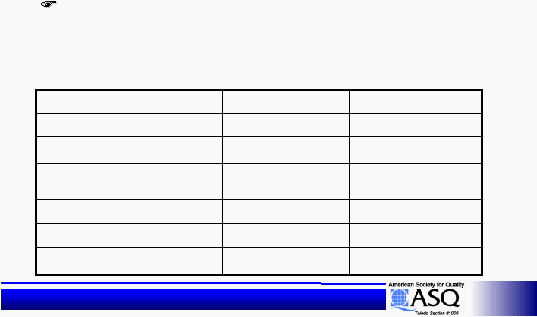 24
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Level 1
Level 1
Level 2
Level 2
Type of Seed
Type of Seed
Seed Population
Seed Population
Distance between corn
Distance between corn
plants
plants
A
A
2 seeds per
2 seeds per
Natural
Natural
B
BB
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
12 inches
12 inches
Type of fertilizer
Type of fertilizer
A
AA
B
B
Type of soil
Type of soil
6 inches
6 inches
Top soil
Top soil
Amount of water
Amount of water
Clay
Clay
Irrigation
Irrigation
Main Effects
Main Effects
Natural
Natural
BB
12 inches
12 inches
B
B
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
Top soil
Top soil
A
A
A
6 inches
6 inches
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
Top soil
Top soil
Irrigation
Irrigation
2 seeds per
2 seeds per
Clay
Clay
B
12 inches
12 inches
A
A
Irrigation
Irrigation
Seed Type A, 5 seeds per, 6 inches
Seed Type A, 5 seeds per, 6 inches
between plants, fertilizer A, top soil,
between plants, fertilizer A, top soil,
irrigation
irrigation
|
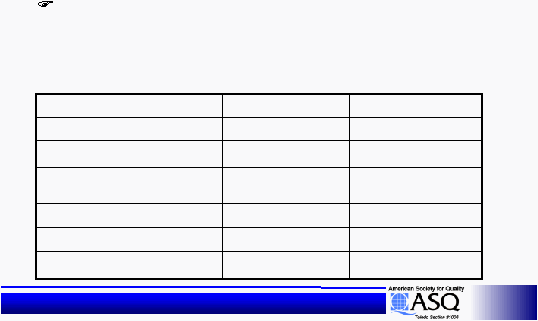 25
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Seed Type B, 5 seeds per, 12 inches
Seed Type B, 5 seeds per, 12 inches
between plants, fertilizer B, top soil,
between plants, fertilizer B, top soil,
natural water amount
natural water amount
Level 1
Level 1
Level 2
Level 2
Type of Seed
Type of Seed
Seed Population
Seed Population
Distance between corn
Distance between corn
plants
plants
A
A
2 seeds per
2 seeds per
Natural
Natural
B
BB
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
12 inches
12 inches
Type of fertilizer
Type of fertilizer
A
AA
B
B
Type of soil
Type of soil
6 inches
6 inches
Top soil
Top soil
Amount of water
Amount of water
Clay
Clay
Irrigation
Irrigation
Main Effects
Main Effects
Natural
Natural
BB
12 inches
12 inches
B
B
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
Top soil
Top soil
A
A
A
6 inches
6 inches
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
Top soil
Top soil
Irrigation
Irrigation
2 seeds per
2 seeds per
Clay
Clay
B
12 inches
12 inches
A
A
Irrigation
Irrigation
|
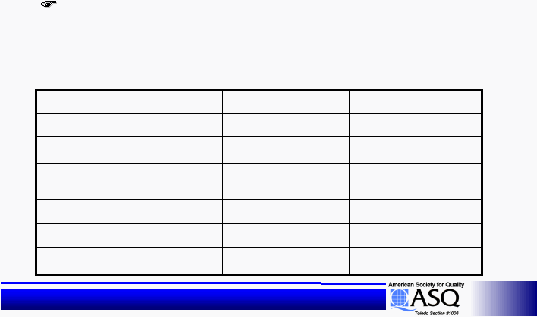 26
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Seed type B, 2 seeds per, 12 inches
Seed type B, 2 seeds per, 12 inches
between plants, fertilizer A, clay soil,
between plants, fertilizer A, clay soil,
irrigation, etc.
irrigation, etc.
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Level 1
Level 1
Level 2
Level 2
Type of Seed
Type of Seed
Seed Population
Seed Population
Distance between corn
Distance between corn
plants
plants
A
A
2 seeds per
2 seeds per
Natural
Natural
B
BB
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
12 inches
12 inches
Type of fertilizer
Type of fertilizer
A
AA
B
B
Type of soil
Type of soil
6 inches
6 inches
Top soil
Top soil
Amount of water
Amount of water
Clay
Clay
Irrigation
Irrigation
Main Effects
Main Effects
Natural
Natural
BB
12 inches
12 inches
B
B
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
Top soil
Top soil
A
A
A
6 inches
6 inches
5 seeds per
5 seeds per
Top soil
Top soil
Irrigation
Irrigation
2 seeds per
2 seeds per
Clay
Clay
B
12 inches
12 inches
A
A
Irrigation
Irrigation
|
  27
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Each of the
Each of the
sections of land will
sections of land will
receive a different
receive a different
treatment
treatment
combination.
combination.
|
  28
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
As the corn is
As the corn is
harvested, the
harvested, the
corn yield for each
corn yield for each
of the sections
of the sections
will be
will be
determined.
determined.
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Possible Treatment Combinations:
|
  29
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
The section
The section
(treatment
(treatment
combination)
combination)
which yields the
which yields the
most corn ....
most corn ....
Possible Treatment Combinations:
Possible Treatment Combinations:
|
|
30
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Applicable to:
Applicable to:
New Designs / New Processes
New Designs / New Processes
Existing Designs / Existing
Existing Designs / Existing
Processes
Processes
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
|
|
31
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Drivers of DOE
Drivers of DOE
Customer Led Quality
Customer Led Quality
Robust Designs / Processes
Robust Designs / Processes
Loss to Society
Loss to Society
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
|
|
32
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Foreign Competition
Foreign Competition
--
--
Success
Success
stories from Japan on how
stories from Japan on how
application of Statistical Methods
application of Statistical Methods
helped get the cost out and
helped get the cost out and
improve quality.
improve quality.
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
|
 33
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
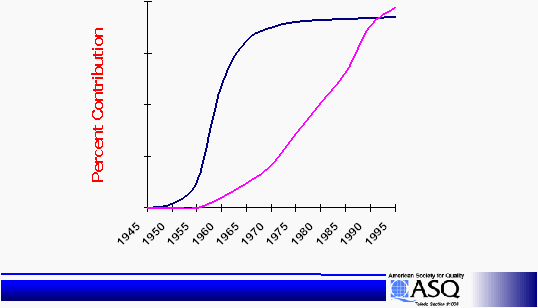
Japanese Quality Evolution
Japanese Quality Evolution
0
25
50
75
100
Quality
Quality
Due to Inspection
Due to Inspection
Quality Due to
Quality Due to
Process
Process
Control
Control
Quality Due to
Quality Due to
Design of
Design of
Experiments
Experiments
|
 34
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Design of Experiments -
Design of Experiments -
Steps
Steps
1.
Recognition of and Statement of the
Problem
2.
Selection of the response variable
3.
Choice of Factors and Levels
4.
Choice of experimental design
5.
Performing the experiment
6.
Data analysis
7.
Proof test of Optimal Treatment
Combination
8.
Conclusions and recommendations
9.
Write It Up !!
1.
Recognition of and Statement of the
Problem
2.
Selection of the response variable
3.
Choice of Factors and Levels
4.
Choice of experimental design
5.
Performing the experiment
6.
Data analysis
7.
Proof test of Optimal Treatment
Combination
8.
Conclusions and recommendations
9.
Write It Up !!
|
|
35
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Background:
Background:
CMEP is having a problem
CMEP is having a problem
with the variability of B-160 rotary fuel pump
with the variability of B-160 rotary fuel pump
timing. A designed experiment has been
timing. A designed experiment has been
used to determine what main effects affect
used to determine what main effects affect
fuel pump timing. During the brainstorming
fuel pump timing. During the brainstorming
session, many main effects are discussed,
session, many main effects are discussed,
and listed below are the 7 main effects
and listed below are the 7 main effects
thought to have the best possibility of
thought to have the best possibility of
affecting fuel pump timing.
affecting fuel pump timing.
Exercise 1 -
Exercise 1 -
Case Study
Case Study
|
|
36
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Objective:
Objective:
To determine which of
To determine which of
the selected Main Effects affect
the selected Main Effects affect
Fuel Pump Timing.
Fuel Pump Timing.
Exercise 1 -
Exercise 1 -
Case Study
Case Study
|
|
37
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Main Effect
Main Effect
A) Input air pressure
A) Input air pressure
B) Fuel pump mounting
B) Fuel pump mounting
C) TDC set point
C) TDC set point
D) Fuel pump mtg
D) Fuel pump mtg
nut
nut
torque seq.
torque seq.
E) Fuel pump gear torque
E) Fuel pump gear torque
F) Backlash tool
F) Backlash tool
G) Associate
G) Associate
Exercise 1 -
Exercise 1 -
Case Study
Case Study
LEVEL 1
LEVEL 1
100 psi
100 psi
Snug
Snug
0.75 deg.
0.75 deg.
Top first
Top first
Two step
Two step
METC
METC
Bob
Bob
LEVEL 2
LEVEL 2
80 psi
80 psi
Loose
Loose
0 deg.
0 deg.
Bottom first
Bottom first
One step
One step
Spring design
Spring design
Jim
Jim
|
|
38
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Background:
Background:
CMEP is having a problem
CMEP is having a problem
with the variability of B-160 rotary fuel pump
with the variability of B-160 rotary fuel pump
timing. A designed experiment has been
timing. A designed experiment has been
used to determine what main effects affect
used to determine what main effects affect
fuel pump timing. During the brainstorming
fuel pump timing. During the brainstorming
session, many main effects are discussed,
session, many main effects are discussed,
and listed below are the 7 main effects
and listed below are the 7 main effects
thought to have the best possibility of
thought to have the best possibility of
affecting fuel pump timing.
affecting fuel pump timing.
Exercise 1 -
Exercise 1 -
Case Study
Case Study
|
|
39
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
1.
1.
What is the response variable? What is
What is the response variable? What is
another name for the response variable?
another name for the response variable?
2.
2.
How many Main Effects are there?
How many Main Effects are there?
Identify 3 Main Effects.
Identify 3 Main Effects.
3.
3.
Identify the levels for the Main Effects
Identify the levels for the Main Effects
that you chose in question #2.
that you chose in question #2.
4.
4.
Are all the Main Effects in this
Are all the Main Effects in this
experiment Qualitative, Quantitative, or
experiment Qualitative, Quantitative, or
both? Identify examples of each.
both? Identify examples of each.
|
|
40
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
1.
1.
What is the response variable? What is
What is the response variable? What is
What is
another name for the response variable?
another name for the response variable?
Fuel Pump Timing
Fuel Pump Timing
Answer:
Answer:
Output Variable,
Output Variable,
Dependant Variable
Dependant Variable
|
|
41
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
2.
2.
How many Main Effects are there?
How many Main Effects are there?
Identify 3 Main Effects.
Identify 3 Main Effects.
Seven
Seven
Answer:
Answer:
Input Air Pressure,
Input Air Pressure,
Fuel Pump Mounting Unit
Fuel Pump Mounting Unit
TDC Set Point
TDC Set Point
Fuel Pump Mtg
Fuel Pump Mtg
Mtg
nut Torque Seq.
nut Torque Seq.
Fuel Pump Gear Torque
Fuel Pump Gear Torque
Backlash Tool
Backlash Tool
Associate
Associate
|
 42
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
3.
3.
Identify the levels for the Main Effects
Identify the levels for the Main Effects
that you chose in question #2.
that you chose in question #2.
Answer:
Answer:
Main Effect
Main Effect
LEVEL 1
LEVEL 1
LEVEL 2
LEVEL 2
A) Input air pressure
A) Input air pressure
100 psi
100 psi
psi
80 psi
80 psi
psi
B) Fuel pump mounting nut
B) Fuel pump mounting nut
Snug
Snug
Loose
Loose
C) TDC set point
C) TDC set point
0.75 deg. before
0.75 deg. before
TDC -
TDC -
-
top dead
top dead
ctr
ctr
(0 deg)
(0 deg)
D) Fuel pump mtg
D) Fuel pump mtg
mtg
nut torque seq.
nut torque seq.
Top first
Top first
Bottom first
Bottom first
E) Fuel pump gear torque
E) Fuel pump gear torque
Two step
Two step
One step
One step
F) Backlash tool
F) Backlash tool
METC
METC
Spring design
Spring design
G) Associate
G) Associate
Bob
Bob
Jim
Jim
|
|
43
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
Exercise 1 Cont’d.
4.
4.
Are all the Main Effects in this experiment
Are all the Main Effects in this experiment
Qualitative, Quantitative, or both?
Qualitative, Quantitative, or both?
Identify examples of each.
Identify examples of each.
Both !
Both !
Answer:
Answer:
Quantitative = A, C
Quantitative = A, C
Qualitative = B, D, E, F, G
Qualitative = B, D, E, F, G
|
 44
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Definitions -
Definitions -
Reference
Reference
|
 45
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Experiment
Experiment
-
-
An operation under controlled conditions
An operation under controlled conditions
(usually off line) to determine an unknown
(usually off line) to determine an unknown
response variable effect
response variable effect
Main Effect
Main Effect
-
-
The Variables which are manipulated or
The Variables which are manipulated or
controlled during the experiment.
controlled during the experiment.
Response Variable
Response Variable
-
-
The Variable that is observed
The Variable that is observed
or measured.
or measured.
Definitions -
Definitions -
Reference
Reference
|
 46
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
Levels
–
–
The values of the Main Effects in the experiment
The values of the Main Effects in the experiment
•
•
Example: 90 degrees = level 1 fuel temp.
Example: 90 degrees = level 1 fuel temp.
110 degrees = level 2 fuel temp.
110 degrees = level 2 fuel temp.
Effect
–
–
The change in the response variable caused by an
The change in the response variable caused by an
Main Effect moving from one level to another
Main Effect moving from one level to another
Treatment Combination
–
–
The specific combinations of levels of all the input
The specific combinations of levels of all the input
factors
factors
Definitions -
Definitions -
Reference
Reference
|
|
47
Statistical Design of Experiments
Statistical Design of Experiments
End
End
of
of
Unit One
Unit One
|