The Ultimate Guide to Quality Inspection in Manufacturing
Delivering consistent product quality is an absolute necessity – not an option.
A single defective item can severely tarnish a brand’s reputation and erode hard-earned customer trust.
This is where the vital significance of quality inspection comes into play – a meticulous process that acts as the gatekeeper for product excellence.
Key Highlights
- Understanding its fundamental principles
- Implementing cutting-edge inspection technologies
- Knowledge and tools necessary to elevate your quality control
- Various types of quality inspections
- Best practices, statistical sampling methods
- Practical tips
Mastering the Fundamentals: What is Quality Inspection?
Quality inspection refers to the process of examining, testing, measuring, and evaluating products or services against pre-defined standards and specifications.
This crucial undertaking ensures that what is being produced meets the required levels of quality, safety, and performance before reaching end-users.
While often used interchangeably, quality inspection is distinct from quality control and quality assurance.
Quality control encompasses the entire framework of activities and techniques aimed at preventing defects, whereas quality inspection focuses specifically on evaluating the final product or service against established criteria.
Quality assurance, on the other hand, refers to the overarching processes and systems that govern quality management within an organization, ensuring that products consistently meet customer requirements and industry standards.

The Evolution of Quality Inspection
The concept of quality inspection has its roots in the early 20th century when pioneering figures like Walter A. Shewhart and W. Edwards Deming introduced statistical quality control methods.
These groundbreaking approaches revolutionized manufacturing by transitioning from a reactive “inspect and sort” model to a proactive, data-driven system for identifying and addressing quality issues.
The Tangible Benefits of Quality Inspection
Implementing a comprehensive quality inspection program can yield numerous tangible benefits for manufacturers, including:
Cost savings: By identifying and addressing defects early, quality inspections help reduce the costs associated with rework, scrap, and product recalls, ultimately improving profitability.
Enhanced reputation: A track record of delivering high-quality products can significantly bolster a brand’s reputation, fostering customer loyalty and trust.
Improved efficiency: Quality inspections provide valuable data that can be used to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in the production process, enabling continuous improvement initiatives.
Regulatory compliance: Rigorous quality inspection protocols demonstrate a commitment to meeting industry standards and regulations, mitigating the risk of costly fines or legal actions.
Competitive advantage: By consistently delivering superior quality products, manufacturers can gain a competitive edge in their respective markets, potentially increasing market share and customer retention.
Ready to elevate your quality game? Our Yellow Belt course equips you with essential tools to implement robust quality inspection processes and drive product excellence.
The Quality Inspection Lifecycle: Types and Timing
Quality inspections are not a one-time event but rather an ongoing process that spans the entire product lifecycle.
Different types of inspections are conducted at various stages to ensure quality is maintained from the procurement of raw materials to the final delivery of finished goods.
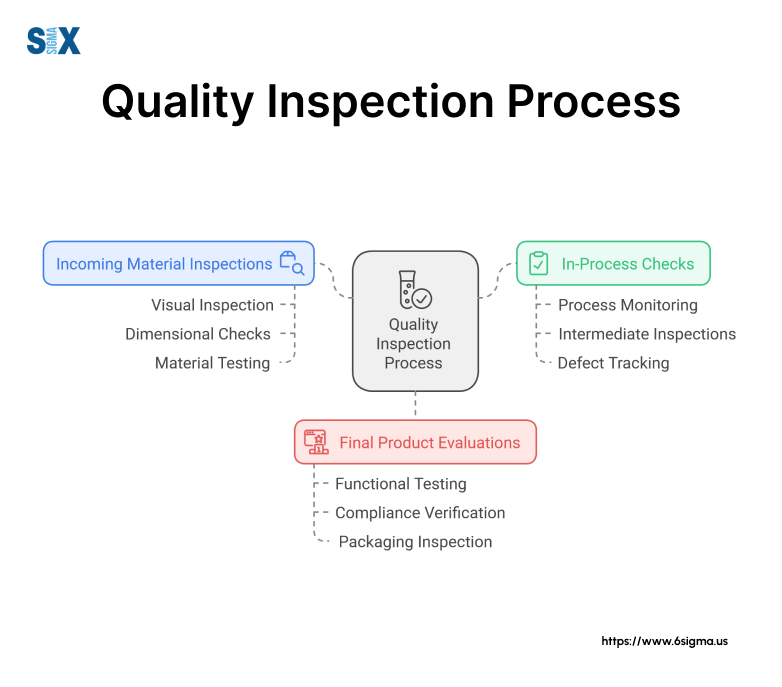
Pre-Production Inspection
Also known as incoming quality control (IQC), pre-production inspections are conducted before the manufacturing process begins.
Their primary purpose is to assess the quality and conformity of raw materials, components, and parts received from suppliers.
During a pre-production inspection, quality inspectors examine items such as:
- Physical characteristics (dimensions, weight, color, etc.)
- Defects or damage sustained during transportation
- Compliance with specifications and documentation
- Proper labeling and packaging
By conducting thorough pre-production inspections, manufacturers can identify and address potential issues early, preventing defective materials from entering the production line and causing costly downstream problems.
In-Process Inspection
As the name suggests, in-process inspections occur during the active manufacturing stage.
These ongoing assessments aim to identify defects, non-conformities, or deviations from established standards as they occur, enabling immediate corrective actions.
Common in-process inspection activities include:
- Monitoring critical production parameters (temperature, pressure, etc.)
- Evaluating work-in-progress (WIP) products at specific checkpoints
- Conducting first article inspections (FAI) on initial production runs
- Verifying process capabilities and stability through statistical process control (SPC)
By maintaining a vigilant eye on the production process, manufacturers can prevent defective products from progressing further down the line, minimizing waste and rework.
Final Quality Inspection
Once production is complete, final inspections are conducted to ensure the finished product meets all specified requirements before being released for shipment or delivery. These comprehensive evaluations typically cover:
- Appearance and cosmetic attributes
- Dimensional accuracy and tolerances
- Functionality and performance testing
- Safety features and compliance
- Packaging and labeling integrity
Considering the time and resources invested in manufacturing, final inspections serve as a critical quality gate, safeguarding against defective products reaching customers and potentially causing reputational or financial harm to the business.
Statistical Sampling and Quality Control
While conducting 100% inspections may seem desirable, it is often impractical, costly, and time-consuming, particularly for high-volume production runs.
This is where statistical sampling techniques come into play, offering manufacturers a cost-effective and efficient approach to quality inspection.
Understanding Acceptable Quality Levels (AQL)
The Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) is a widely-used statistical measure that defines the maximum permissible number of defects or non-conformities in a sample size that can be considered acceptable.
AQL is typically expressed as a percentage or a ratio, such as 2.5 defects per 100 units.
Determining the appropriate AQL level is a critical decision that involves balancing various factors, including:
- Product complexity and criticality
- Customer requirements and expectations
- Industry standards and regulations
- Cost considerations and risk tolerance
Once the AQL is established, manufacturers can implement sampling plans that specify the sample size and acceptance/rejection criteria for a given lot or production run.
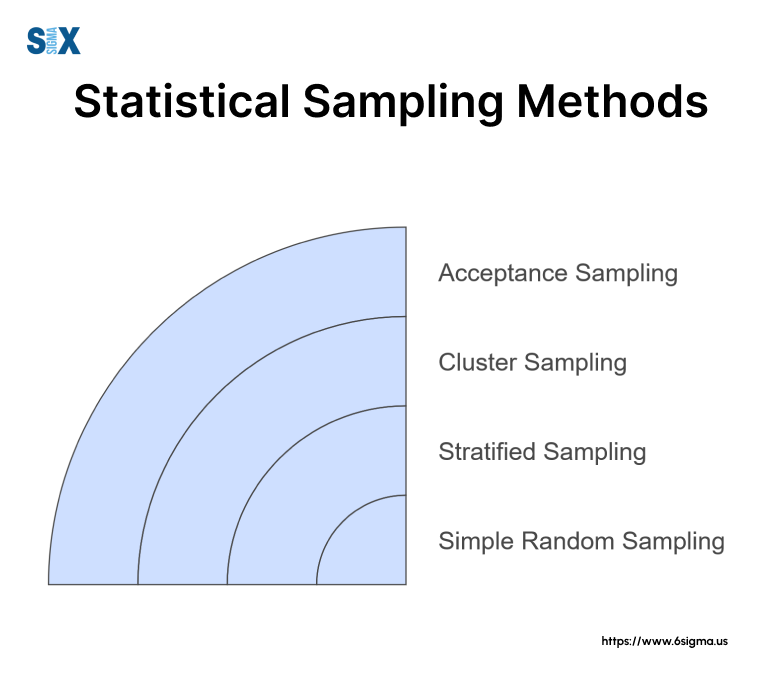
Sampling Techniques and Methods within Quality Inspection
Several statistical sampling methods are commonly employed in quality inspection processes, each with its own advantages and considerations. Some popular techniques include:
Simple random sampling: Each item in the lot has an equal chance of being selected for inspection, ensuring an unbiased representation.
Stratified sampling: The lot is divided into homogeneous subgroups (strata), and samples are drawn from each stratum, enabling targeted inspection of specific product characteristics or production batches.
Cluster sampling: The lot is divided into clusters or groups, and a random sample of clusters is selected for inspection, reducing the need to inspect individual items across the entire lot.
Acceptance sampling: Based on pre-determined acceptance criteria and AQL, a sample is inspected, and a decision is made whether to accept or reject the entire lot.
The choice of sampling method depends on factors such as product variability, production volumes, and the level of precision required in the inspection process.
Integrating Quality Inspection with Quality Control Systems
While quality inspections are crucial, they are most effective when integrated into a comprehensive quality control system.
By leveraging inspection data and insights, manufacturers can identify patterns, root causes of defects, and potential areas for process improvements.
For example, if a particular type of defect is consistently observed during in-process inspections, the data can be analyzed to pinpoint the underlying cause, such as a malfunctioning machine component or an operator error.
This information can then be fed back into the manufacturing process, enabling targeted corrective and preventive actions to be implemented.
Take your quality management skills to the next level. Learn to apply powerful statistical sampling techniques in our comprehensive Green Belt program.
Embracing Technology: The Future of Quality Inspection
As manufacturing becomes increasingly automated and data-driven, the realm of quality inspection is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by cutting-edge technologies that promise to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making capabilities.
Automated Inspection Systems
Traditional manual inspections, while effective, are susceptible to human error, fatigue, and subjective variability.
Automated inspection systems leverage advanced technologies such as machine vision, artificial intelligence (AI), and deep learning to automate the inspection process, offering unparalleled consistency and accuracy.
For example, AI-powered visual inspection systems can rapidly analyze high-resolution images or video footage of products, detecting even the most minute defects or deviations with precision that surpasses human capabilities.
Another application of automated inspection systems is in the realm of dimensional metrology, where laser scanners and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) can capture highly accurate 3D models of parts or assemblies, enabling precise comparisons against CAD specifications.
By automating inspection tasks, manufacturers can significantly reduce the time and resources required for quality control while simultaneously improving the reliability and reproducibility of inspection results.
Remote and Virtual Quality Inspections
The ability to conduct remote or virtual inspections is becoming an invaluable asset.
Leveraging technologies such as video conferencing, augmented reality (AR), and remote collaboration tools, quality inspectors can assess products, processes, and facilities without the need for physical on-site presence.
This capability not only reduces travel costs and carbon footprints but also enables timely inspections and audits, minimizing delays and disruptions to production schedules.
Moreover, virtual inspections can facilitate knowledge sharing and training by allowing experienced inspectors to guide and mentor personnel across multiple locations.
As remote inspection technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more advanced features, such as real-time data overlays, virtual walkthroughs, and seamless integration with quality management systems.
Data-Driven Quality Intelligence
Perhaps one of the most promising developments in the quality inspection realm is the rise of data-driven quality intelligence.
By harnessing the power of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) sensors, advanced analytics, and machine learning algorithms, manufacturers can unlock a wealth of insights from their inspection data.
For instance, predictive analytics models can be trained on historical inspection data to identify potential quality issues before they occur, enabling proactive interventions and minimizing the risk of defects.
Similarly, machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of inspection data to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and root causes that may have been overlooked through traditional methods.
Ready to become a quality inspection expert? Our Black Belt course prepares you to lead cutting-edge quality initiatives and drive strategic excellence through advanced technologies and data-driven approaches
Building a Robust Quality Inspection Program
Implementing an effective quality inspection program requires careful planning, execution, and a relentless commitment to continuous improvement.
From developing detailed inspection plans to fostering a culture of quality, this systematic approach ensures your organization can consistently deliver products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Developing an Inspection Plan
The foundation of any successful quality inspection initiative is a comprehensive inspection plan tailored to your organization’s specific products, processes, and quality requirements.
Developing such a plan involves:
Assessing product complexity and risk factors: Thoroughly evaluate the intricacies of your products, their intended applications, and the potential risks associated with quality defects. This assessment will guide the rigidity of your inspection criteria and acceptable quality levels.
Determining appropriate inspection types and frequencies: Based on your product assessment, establish when and where inspections should occur – from incoming material checks to in-process monitoring and final product evaluations.
Define optimal inspection frequencies based on factors like production volumes, past quality data, and risk profiles.
Establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability: Unambiguously define the roles of all personnel involved in the quality inspection process, from inspectors and quality managers to production staff and suppliers.
Establish chains of command, approval authorities, and mechanisms for escalating and addressing quality issues promptly.
By developing a comprehensive inspection plan upfront, you’ll foster consistency, ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations, and provide a robust framework for maintaining product quality across your operations.
Training and Certification for Inspectors
The effectiveness of any quality inspection program hinges on the skills and knowledge of its inspectors. Investing in comprehensive training and certification is paramount:
Importance of skilled and knowledgeable inspectors: Well-trained inspectors can accurately identify defects, understand the implications of non-conformances, and make informed decisions based on established criteria – reducing the risk of human error and subjective judgment calls.
Developing training programs and certification requirements: Implement robust training curricula covering product specifications, inspection methodologies, documentation practices, and the latest quality standards. Establish clear certification criteria and continuing education requirements to ensure inspectors’ knowledge remains up-to-date.
Staying current with evolving standards and technologies: The quality landscape is constantly evolving – your inspectors must stay ahead of the curve. Provide ongoing training on new regulations, emerging inspection technologies (such as AI-assisted vision systems), and industry best practices to maintain a competitive edge.
By prioritizing the development of a highly skilled and knowledgeable inspection workforce, you’ll enhance the accuracy, consistency, and effectiveness of your quality processes – ultimately improving product quality and customer satisfaction.
Continuous Improvement and Audits for Quality Inspection
A robust quality inspection program is never “set it and forget it” – it requires continuous evaluation, improvement, and a steadfast commitment to excellence:

Conducting regular program audits and assessments: Periodically audit your inspection processes, documentation, training programs, and overall system effectiveness. Identify areas for improvement and benchmark your performance against industry best practices and quality standards.
Identifying improvement opportunities and implementing corrective actions: Leverage insights from your audits, inspection data, customer feedback, and quality metrics to pinpoint vulnerabilities and opportunities for optimization. Implement corrective and preventive actions to address root causes of defects or inefficiencies systemically.
Fostering a culture of continuous improvement: Quality excellence is an ongoing journey, not a destination. Cultivate an organizational culture that embraces change, rewards innovation, and empowers staff at all levels to identify and drive improvements in your quality inspection practices continuously.
By committing to a cycle of constant evaluation, corrective action, and improvement, your quality inspection program will remain agile, adaptive, and capable of consistently delivering products that delight your customers while providing your organization with a sustainable competitive advantage.
Road Ahead
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the multifaceted world of quality inspection in manufacturing – from its fundamental principles and key processes to the cutting-edge technologies redefining this critical domain.
By mastering the art of quality inspections through statistical sampling techniques and leveraging emerging innovations like AI-powered automated inspection systems, manufacturers can unlock new frontiers of product excellence.
Woven throughout our in-depth examination was a common thread – the pivotal role that robust quality inspection programs play in safeguarding regulatory compliance, mitigating risks, elevating brand reputation, boosting profitability, and, most importantly, ensuring enduring customer satisfaction.
Quality inspection is more than just a box to check; it’s a fundamental pillar supporting the entire manufacturing ecosystem.
From the intricacies of statistical sampling and leveraging quality intelligence, to the future-forward applications of AI, automation, and virtual inspections – you now have a comprehensive roadmap for establishing quality inspection as a core competitive advantage for your organization.
The path to product excellence begins with a first step. Take yours today!
Unlock the power of quality inspection, and experience the tangible benefits of consistently delivering products that exceed customer expectations, ensure compliance, and propel your organization to new heights of success.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






