Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): The Ultimate Guide to Optimizing Production
With all the digital technologies changing traditional production processes the manufacturing industry continues to grow.
Bridging the gap between enterprise planning and shop floor operations, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) is at the forefront of this.
To make data-driven decisions that increases efficiency and quality, these systems monitor, control, and optimize production activities in real-time.
Key Highlights
- Production Control and Optimization Methods
- Real-time Data Collection and Analysis
- Quality Management Integration Techniques
- Enterprise System Integration Strategies
What is Manufacturing Execution Systems?
Manufacturing Execution Systems transform production processes through several key functions.
These systems track and document the conversion of raw materials into finished products, providing real-time data throughout the manufacturing cycle.
The software monitors equipment performance, manages work orders, and ensures quality control standards are met consistently.
Production scheduling stands as a primary function, allowing managers to optimize resource allocation and minimize downtime.
The system analyzes current operations and adjusts schedules based on real-time conditions, helping maintain efficient production flow while meeting delivery deadlines.
Quality management functions ensure products meet specified standards through automated checks and documentation.
This reduces defects and waste while maintaining consistent product quality across production runs.
How Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) Works in Modern Manufacturing
Manufacturing Execution Systems operate by collecting data from multiple sources on the production floor.
Connected sensors and equipment provide continuous updates about operational status, while operators input additional information through user interfaces.
This creates a detailed picture of the entire manufacturing process.
The system processes this information to:
- Monitor production progress in real-time
- Track material usage and inventory levels
- Manage work orders and scheduling
- Document quality control measures
- Generate performance reports
Essential Components of Manufacturing Execution Systems
The architecture of Manufacturing Execution Systems consists of several interconnected modules that work together to optimize production:
Production Management Module: Controls work orders, tracks progress, and manages production scheduling.
Quality Control Module: Monitors product quality, manages testing procedures, and maintains quality documentation.
Resource Management Module: Tracks equipment status, manages maintenance schedules, and monitors resource utilization.
Data Collection Module: Gathers information from equipment sensors, operator inputs, and other sources.
Reporting Module: Generates analysis reports, tracks KPIs, and provides insights for decision-making.
Strategic Benefits of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) Implementation
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) deliver significant advantages that directly impact operational efficiency and bottom-line results:
Improved Production Efficiency: Real-time monitoring and automated scheduling reduce downtime and optimize resource usage.
Enhanced Quality Control: Automated quality checks and documentation ensure consistent product quality while reducing waste.
Better Decision Making: Access to real-time data enables managers to make informed decisions quickly.
Reduced Operational Costs: Optimized resource allocation and reduced waste lead to significant cost savings.
Regulatory Compliance: Automated documentation and traceability features help meet industry regulations.
These benefits make Manufacturing Execution Systems essential tools for modern manufacturers looking to maintain competitive advantages in their markets.
The system’s ability to integrate with other business solutions creates a connected manufacturing environment that supports continuous improvement and growth.
Future-Ready Manufacturing Operations
As manufacturing technologies evolve, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) continue to adapt and incorporate new capabilities.
Integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning enables predictive maintenance and more sophisticated optimization algorithms.
Cloud connectivity provides greater flexibility and accessibility, while mobile interfaces allow managers to monitor and control operations from anywhere.
Master the fundamentals of Lean Six Sigma and process control with Green Belt training
- Optimize your manufacturing operations.
- Hands-on learning with examples
Learn essential statistical tools and process analysis techniques for MES implementation.
MES vs. ERP: Making Sense of Manufacturing Software Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems manage business operations across departments, from finance and human resources to supply chain and customer relationships.
These systems focus on high-level business planning, resource allocation, and strategic decision-making. ERP platforms coordinate various business functions to create a unified flow of information throughout the organization.
Key Distinctions Between MES and ERP
Manufacturing Execution Systems and ERP systems serve different yet complementary roles in manufacturing operations.
While ERP handles broad business processes, Manufacturing Execution Systems focus specifically on shop floor operations and production control.
Time Scope:
- ERP: Long-term planning and strategic decisions
- MES: Real-time monitoring and immediate production control
Data Management:
- ERP: Business-level data aggregation and analysis
- MES: Shop floor data collection and production metrics
Operational Focus:
- ERP: Business process management and resource planning
- MES: Production execution and quality control
Creating Synergy Between Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and ERP
Manufacturing Execution Systems work alongside ERP systems to create a seamless flow of information between shop floor operations and business management. This integration enables:
Production Planning: ERP systems generate production orders based on business requirements, while Manufacturing Execution Systems translate these orders into detailed production schedules.
Resource Management: ERP handles resource allocation at the business level, and MES optimizes these resources during actual production.
Quality Control: MES monitors and controls product quality in real-time, feeding this data back to ERP for broader quality management initiatives.
Integration Benefits and Operational Impact
The collaboration between Manufacturing Execution Systems and ERP creates significant operational advantages:
Real-time Decision Support: Combined data from both systems enables better-informed decisions at all levels.
Improved Accuracy: Automated data exchange reduces manual entry errors and improves information reliability.
Enhanced Visibility: Managers gain clear insights into both production operations and business performance.
| Aspect | MES | ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Production Control | Business Management |
| Timeframe | Real-time | Strategic Planning |
| Data Type | Shop Floor Metrics | Business Analytics |
| Primary Users | Production Teams | Management Teams |
| Key Functions | Process Control | Resource Planning |
Successful integration of Manufacturing Execution Systems with ERP requires careful planning and implementation.
Key considerations include:
- Data Synchronization: Ensuring consistent information flow between systems
- Interface Design: Creating user-friendly access points for different user groups
- Security Protocols: Maintaining data security across integrated systems
- Performance Monitoring: Tracking system performance and optimization opportunities
This integration creates a robust foundation for digital manufacturing operations, enabling organizations to maintain competitive advantages through improved efficiency and decision-making capabilities.
The combined power of Manufacturing Execution Systems and ERP supports both operational excellence and strategic business goals.
Implementing Manufacturing Execution Systems: A Strategic Approach
Essential Implementation Steps
The successful deployment of Manufacturing Execution Systems requires careful planning and execution. The implementation process typically spans several phases:
Assessment Phase (1-2 months):
- Evaluate current manufacturing processes
- Define specific requirements and goals
- Select appropriate MES solution
- Establish project team and responsibilities
Design Phase (2-3 months):
Manufacturing Execution Systems must align with existing workflows while introducing improvements. This phase involves mapping processes, defining integration points, and creating detailed implementation specifications.
Development Phase (3-4 months):
System configuration begins with database setup, interface development, and initial testing. This phase requires close collaboration between IT teams and manufacturing specialists to ensure proper system setup.
Testing Phase (1-2 months):
Rigorous testing validates system functionality, data accuracy, and integration capabilities. This includes pilot runs in controlled environments before full deployment.
Common Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Technical Integration Issues:
Many manufacturers struggle with connecting Manufacturing Execution Systems to legacy equipment. Solution: Implement middleware solutions and gradual integration approaches to bridge technological gaps.
User Adoption:
Staff resistance often hampers implementation success. Solution: Develop structured training programs and involve key users early in the implementation process.
Data Management:
Converting and migrating existing data presents significant challenges. Solution: Establish clear data standards and implement systematic data cleaning procedures.
Overcome MES implementation challenges with advanced statistical analysis and process control techniques.
Implementation Timeline and Key Milestones
A typical Manufacturing Execution Systems implementation spans 8-12 months:
- Months 1-2: Requirements gathering and system selection
- Months 3-4: System design and process mapping
- Months 5-7: Configuration and development
- Months 8-9: Testing and validation
- Months 10-12: Training and rollout
Cost Analysis and ROI Expectations of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
Initial Investment Components:
- Software licensing fees range from $100,000 to $500,000
- Hardware upgrades: $50,000 – $200,000
- Implementation services: $150,000 – $400,000
- Training costs: $20,000 – $50,000
ROI Calculations Should Consider:
Production Efficiency Gains:
- Reduced downtime (15-30% improvement)
- Increased throughput (10-20% improvement)
- Lower inventory costs (20-30% reduction)
Quality Improvements:
- Reduced defect rates (25-40% reduction)
- Lower scrap costs (15-25% reduction)
- Decreased rework requirements (20-35% reduction)
Ensuring Implementation Success
Critical success factors for Manufacturing Execution Systems implementation include:
Executive Support:
Secure ongoing commitment from leadership teams to maintain implementation momentum and resource allocation.
Clear Communication:
Establish regular updates and feedback channels between implementation teams and stakeholders.
Phased Approach:
Roll out functionality in manageable phases to minimize disruption and allow for adjustments.
Performance Monitoring:
Track implementation progress against established KPIs and adjust strategies as needed.
Post-Implementation Considerations of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
After deploying Manufacturing Execution Systems, organizations should focus on:
System Optimization:
Regular performance reviews and adjustments ensure optimal system operation.
User Support:
Ongoing training and support help maintain high adoption rates and system effectiveness.
Continuous Improvement:
Regular updates and feature enhancements keep the system aligned with evolving business needs.
ROI Tracking:
Monitor actual returns against projected benefits to validate investment value.
The successful implementation of Manufacturing Execution Systems requires careful planning, clear communication, and sustained commitment.
Organizations that follow these guidelines while remaining flexible to address challenges will achieve better results and faster returns on their investment.
Choosing the Right Manufacturing Execution Systems for Your Business
Selecting the right Manufacturing Execution Systems requires careful evaluation of several critical factors. The chosen system must align with current manufacturing processes while supporting future growth objectives.
Scalability needs deserve primary consideration, as the system should accommodate production volume increases and additional facility integration.
The software architecture must support both current operations and potential expansion plans.
Industry-specific requirements play a vital role in system selection. Different sectors, such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, or food and beverage, demand specific functionalities and compliance features.
The selected system should offer specialized modules that address these unique needs.
Technical compatibility with existing infrastructure determines implementation success.
The system should integrate smoothly with current equipment, databases, and enterprise software while requiring minimal customization.
Evaluation Process Framework
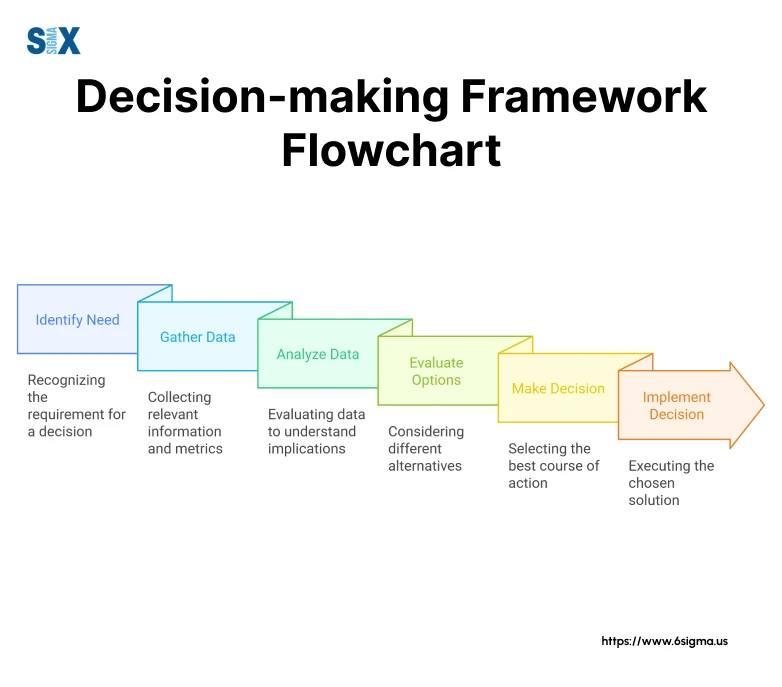
The evaluation process follows structured steps to ensure thorough assessment:
Requirements Analysis:
- Define specific operational needs
- Document current process workflows
- Identify integration requirements
- List compliance requirements
Vendor Assessment:
- Review vendor track records
- Evaluate implementation expertise
- Check customer references
- Assess support capabilities
Technical Evaluation:
- Test system functionality
- Verify integration capabilities
- Assess customization options
- Review security features
Implementation Best Practices
Successful implementation of Manufacturing Execution Systems relies on proven methodologies and careful planning.
Start with a pilot program in one production area before expanding to full deployment. This approach allows for testing and refinement of implementation procedures.
Create detailed documentation of current processes and desired improvements.
This documentation serves as a reference point for system configuration and helps identify areas requiring special attention during implementation.
Establish clear communication channels between all stakeholders.
Regular updates and feedback sessions ensure alignment between technical teams, operations staff, and management throughout the implementation process.
Cost and ROI Considerations for Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
Budget planning for Manufacturing Execution Systems should account for:
Initial Costs:
- Software licensing
- Hardware requirements
- Implementation services
- Staff training
Ongoing Expenses:
- Maintenance fees
- System updates
- Technical support
- Additional training
ROI Metrics:
- Production efficiency gains
- Quality improvement rates
- Reduced operational costs
- Increased throughput
Vendor Selection Criteria
The right vendor partnership proves crucial for successful implementation. Key evaluation criteria include:
Industry Experience:
- Previous implementations in similar industries
- Understanding of sector-specific requirements
- Proven success records
Support Infrastructure:
- Technical support availability
- Training programs
- Implementation assistance
- Regular system updates
Financial Stability:
- Company longevity
- Investment in product development
- Clear business roadmap
Future-Proofing Your Investment with Manufacturing Execution Systems
Manufacturing Execution Systems should accommodate future technological advances and business growth. Consider these aspects:
Integration Capabilities:
- APIs and connectivity options
- Support for emerging technologies
- Scalability features
Technology Roadmap:
- Regular feature updates
- Innovation focus
- Industry 4.0 readiness
Customization Options:
- Configuration flexibility
- Module addition capability
- Process adaptation tools
The selection process for Manufacturing Execution Systems requires balanced consideration of current needs and future requirements.
Organizations should prioritize solutions that offer robust functionality while maintaining flexibility for future growth and technological advancement.
Emerging Technologies Reshaping Manufacturing Execution Systems
Manufacturing Execution Systems now leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to transform production processes.
These technologies enable predictive maintenance by analyzing equipment performance data and identifying potential failures before they occur.
Smart scheduling algorithms optimize production sequences by considering multiple variables simultaneously, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
Machine learning algorithms continuously analyze production data to identify patterns and anomalies.
This capability allows Manufacturing Execution Systems to adjust process parameters automatically, maintaining optimal production conditions and product quality.
The system learns from historical data to make increasingly accurate predictions about maintenance needs, resource requirements, and production outcomes.
Blockchain Technology for Enhanced Traceability
Blockchain integration in Manufacturing Execution Systems creates immutable records of production processes, material sources, and quality certifications.
This technology ensures complete product genealogy and authentication throughout the supply chain. Manufacturing organizations benefit from enhanced transparency and improved compliance documentation.
The distributed ledger technology provides secure, verifiable records of:
- Material sourcing and authenticity
- Production process parameters
- Quality control results
- Shipping and handling conditions
- Regulatory compliance data
Augmented Reality Transforming User Interfaces
Augmented reality (AR) introduces new ways for operators to interact with Manufacturing Execution Systems.
AR interfaces overlay real-time production data onto physical equipment, enabling operators to access critical information without leaving their workstations.
This technology improves efficiency and reduces errors by providing contextual information exactly when and where it’s needed.
AR applications in manufacturing include:
- Maintenance guidance with visual instructions
- Real-time performance monitoring
- Quality inspection assistance
- Training and skill development
- Remote expert collaboration
The Future of Manufacturing Excellence
Manufacturing Execution Systems have evolved from basic production tracking tools to sophisticated platforms that drive manufacturing excellence.
The integration of emerging technologies continues to expand their capabilities, offering new opportunities for efficiency, quality, and innovation in manufacturing operations.
Modern manufacturers must recognize the strategic value of these systems in maintaining competitive advantages.
The combination of real-time monitoring, predictive capabilities, and advanced user interfaces creates powerful tools for optimizing production processes and driving business growth.
Taking Action for Manufacturing Innovation
Organizations considering Manufacturing Execution Systems implementation should:
Evaluate Current Needs:
Assess existing production processes and identify areas for improvement through automation and digital transformation.
Plan for Growth:
Select solutions that accommodate future technological advances and business expansion requirements.
Build Strong Foundations:
Invest in proper training and change management to ensure successful system adoption.
Moving Forward with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) Implementation
The path to manufacturing excellence through Manufacturing Execution Systems requires careful planning and strategic implementation.
Organizations should:
- Start with clear objectives and measurable goals
- Choose solutions that align with industry-specific requirements
- Implement systems gradually to ensure proper integration
- Monitor results and adjust strategies as needed
Success in modern manufacturing depends increasingly on digital transformation and the effective use of advanced technologies.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) provide the foundation for this transformation, enabling organizations to achieve higher levels of efficiency, quality, and competitiveness in global markets.
The future of manufacturing belongs to organizations that embrace these technological advances while maintaining focus on practical implementation and measurable results.
By implementing Manufacturing Execution Systems with emerging technologies, manufacturers position themselves for sustained success in an increasingly competitive global market.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






