Hidden Factory: Uncovering Manufacturing’s Invisible Waste
Manufacturing excellence demands more than visible process optimization. The hidden factory concept reveals operational inefficiencies that lurk beneath standard metrics and reporting systems.
These unseen problems drain resources, inflate costs, and compromise product quality while remaining undetected by traditional management approaches.
Modern manufacturing faces increasing pressure to eliminate waste and maximize efficiency. Yet many organizations struggle with invisible bottlenecks and quality issues that standard measurements fail to capture.
Understanding and addressing these hidden factories has become crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in today’s digital manufacturing environment.
Key Highlights
- Digital tools reveal invisible process waste
- AI-powered hidden factory detection methods
- Real-time monitoring prevents quality issues
- Industry 4.0 integration optimizes operations
What Is The Hidden Factory?
The hidden factory represents the sum of activities, delays, and inefficiencies that decrease production quality or efficiency without appearing in standard measurements.
These invisible operations typically consume 20-40% of manufacturing capacity through rework, unofficial procedures, and quality compromises that bypass normal tracking systems.
Quality expert Armand Feigenbaum first identified this concept in the 1970s when studying why actual production costs often exceeded theoretical calculations.
He discovered that traditional metrics failed to capture numerous unofficial activities that drained resources and compromised efficiency.
Core Elements Of Hidden Factory Operations
Manufacturing operations generate hidden factories through three main mechanisms.
First, operators develop unofficial fixes for recurring problems, creating parallel processes that consume resources without documentation.
Second, quality issues trigger rework cycles that remain unreported in standard metrics. Third, process bottlenecks spawn temporary workarounds that become permanent fixtures of daily operations.
Modern Manufacturing Context
Today’s manufacturing environment makes hidden factories increasingly costly yet harder to detect.
Digital systems and automated processes can mask underlying inefficiencies through temporary fixes and workarounds.
Without proper detection methods, these issues compound over time and create significant operational drag.
Quality control professionals now face additional challenges as hidden factories adapt to modern production systems.
Automated processes may hide quality compromises within complex algorithms, while connected systems can propagate workarounds across multiple production lines.
Impact of Hidden Factory On Production Economics
Hidden factories generate substantial economic impact through:
- Production Capacity Loss: Unofficial procedures typically consume 1.5 to 2 times more resources than standard processes
- Quality Cost Inflation: Rework and compromises add 15-25% to true production costs
- Equipment Efficiency Reduction: Workarounds often stress machinery beyond design parameters
- Material Waste Generation: Unofficial fixes frequently require additional raw materials

Digital Detection Methods
Modern manufacturing technologies offer new ways to identify hidden factories.
Sensor networks can track actual vs. theoretical process times, while AI analytics detect unusual patterns in production data.
These tools help quality managers spot developing issues before they become embedded in daily operations.
Industry 4.0 capabilities now enable real-time monitoring of process variations that might indicate hidden factory activities.
Integration of production data across systems helps reveal unofficial workflows that traditional observation methods might miss.
This evolving technical capability marks a significant shift from traditional hidden factory detection approaches. Manufacturing managers can now implement data-driven strategies to identify and eliminate these efficiency drains systematically.
The hidden factory concept remains central to modern manufacturing improvement efforts.
Understanding its formation mechanisms and implementing effective detection methods helps manufacturing leaders maintain operational excellence in increasingly complex production environments.
Unlock the Power of Hidden Factory Detection
The Hidden Factory In Six Sigma: A Strategic Approach
Six Sigma methodology provides powerful tools for uncovering and eliminating hidden factory issues in manufacturing operations.
This data-driven approach helps organizations identify root causes of inefficiencies while implementing lasting solutions that prevent waste from recurring.
DMAIC Framework For Hidden Factory Elimination
The DMAIC framework offers a structured path to address hidden factory challenges.
During the Define phase, teams identify specific areas where unofficial processes might exist. Measurement tools then capture data about these activities, while Analysis reveals root causes of inefficiencies.
Implementation teams use these insights to develop targeted improvements, followed by Control measures that prevent hidden factories from reforming.
This systematic approach ensures sustainable results rather than temporary fixes.
Key Six Sigma Tools For Detection
Value Stream Mapping reveals unofficial workflow paths and highlights areas where hidden factories might develop.
Process capability studies identify variations that could indicate unauthorized procedure modifications. Statistical process control charts detect subtle shifts in production patterns that often signal hidden factory formation.
Root cause analysis techniques like the 5 Whys and Ishikawa diagrams help teams understand why operators create workarounds.
This understanding proves crucial for developing effective countermeasures that address underlying issues rather than symptoms.
Quality Control Integration with Hidden Factory
Quality control systems play a vital role in hidden factory prevention. Six Sigma methods help quality teams:
- Monitor process variations that might indicate unofficial procedures
- Track rework patterns that could reveal hidden quality issues
- Measure true first-pass yield versus reported metrics
- Document actual process times compared to standards
Data-Driven Decision Making
Six Sigma’s emphasis on data-driven decisions helps organizations avoid common pitfalls in hidden factory elimination.
Rather than relying on assumptions, teams gather concrete evidence about:
- Actual vs. reported process times
- True quality costs including unofficial rework
- Resource consumption patterns
- Equipment efficiency metrics
This quantitative approach enables manufacturing leaders to prioritize improvement efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Implementation Strategy Development
Successful hidden factory elimination requires careful strategy development.
Six Sigma tools help teams:
- Create detailed implementation roadmaps
- Set realistic improvement targets
- Establish meaningful metrics
- Design sustainable control measures
Organizations using this structured approach typically achieve better results than those relying on ad-hoc improvement efforts.
The integration of Six Sigma methodology with hidden factory elimination efforts provides manufacturing organizations with proven tools for achieving lasting improvements.
This systematic approach helps quality professionals and process improvement specialists deliver measurable results while preventing future hidden factory formation.
Master Advanced Hidden Factory Elimination Techniques and Become a Hidden Factory Detection Expert
Hidden Factory Examples Across Industries
Hidden factories manifest differently across various industries, yet their impact on efficiency and quality remains consistently significant.
Manufacturing organizations frequently encounter these issues, while service sectors face unique challenges in identifying and eliminating hidden waste.
Manufacturing Sector Hidden Factories
Automotive manufacturing plants often discover hidden factories in their paint shops, where operators develop unofficial touch-up procedures to meet quality standards.
These undocumented processes consume additional materials and labor while masking underlying quality issues in the primary coating process.
Electronics manufacturers frequently encounter hidden factories in testing procedures.
Technicians create unofficial pre-testing steps to improve pass rates, effectively hiding systematic quality problems that should be addressed at their source.
These extra steps add significant time and cost to the production process.
Process Industry Examples
Chemical processing plants reveal hidden factories through equipment cleaning procedures.
Operators typically develop unofficial maintenance routines to prevent quality issues, creating parallel workflows that consume resources without appearing in standard metrics.
Food and beverage producers often find hidden factories in their changeover procedures.
Line workers implement unofficial cleaning steps between product runs, extending changeover times while masking equipment design issues that should be addressed systematically.
Service Industry Applications
Financial services organizations encounter hidden factories in their document processing operations.
Staff members create unofficial verification steps to prevent errors, adding significant processing time without addressing the root causes of documentation issues.
Healthcare providers discover hidden factories in patient scheduling systems.
Administrative staff develop workarounds for appointment booking, creating unofficial procedures that consume time while hiding underlying system inefficiencies.
Digital Transformation Cases of Hidden Factory
Software development teams face hidden factories in their testing procedures. Developers implement unofficial debug cycles that consume resources while masking systematic code quality issues.
E-commerce operations reveal hidden factories in their order fulfillment processes. Warehouse staff create unofficial inventory checks to prevent errors, adding steps that hide underlying system integration problems.
Modern Detection Methods
Advanced analytics now enable organizations to detect hidden factories through:
- Real-time process monitoring systems that track actual vs. planned activities
- Pattern recognition algorithms that identify unofficial procedures
- Resource consumption analysis that reveals hidden operations
- Time study data that exposes unofficial process steps
These digital tools help quality professionals spot developing issues before they become embedded in standard operations.
Manufacturing managers can implement preventive measures based on early warning signals from these systems.
Implementation Success Stories
A major automotive supplier eliminated hidden factories in their assembly operations through systematic analysis of process data.
The resulting efficiency improvements reduced operating costs by 15% while improving quality metrics.
A pharmaceutical manufacturer identified hidden factories in their packaging operations using advanced monitoring systems.
Addressing these issues decreased changeover times by 30% and reduced material waste significantly.
These examples demonstrate how modern detection methods and systematic improvement approaches help organizations across industries identify and eliminate hidden factories effectively.
Quality professionals can apply these lessons to develop targeted solutions for their specific operational challenges.
Become a Six Sigma Hidden Factory Elimination Specialist
Identifying Hidden Factories: Modern Tools And Techniques
Digital transformation has revolutionized how organizations detect and eliminate hidden factories.
Modern detection tools leverage advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time monitoring to spot inefficiencies that traditional methods often miss.
Digital Detection Systems
Smart sensors now monitor production processes continuously, generating data streams that reveal unofficial procedures and workarounds.
These systems track key parameters like process times, resource consumption, and quality metrics to identify patterns that suggest hidden factory activities.
Process monitoring software analyzes these data streams in real-time, alerting managers when activities deviate from standard procedures.
This immediate feedback enables quick intervention before unofficial processes become embedded in daily operations.
Machine Learning Applications
Machine learning algorithms excel at identifying subtle patterns that indicate hidden factory formation. These systems learn from historical data to recognize early warning signs of developing inefficiencies.
Neural networks analyze multiple data streams simultaneously, detecting correlations that human observers might miss.
Pattern recognition software helps quality teams spot emerging trends in process data. These tools flag unusual variations in cycle times, resource usage, or quality metrics that often signal hidden factory activities.
Industry 4.0 Integration Tools
Connected manufacturing systems provide unprecedented visibility into production processes. IoT devices monitor equipment performance, material flow, and operator activities, creating detailed digital records of actual vs. planned operations.
Manufacturing execution systems (MES) integrate data from multiple sources, enabling thorough analysis of process efficiency.
These platforms help identify gaps between documented procedures and actual practices where hidden factories often develop.
Advanced Analytics Platforms
Modern analytics tools transform raw process data into actionable insights. These platforms offer:
- Real-time performance tracking
- Predictive maintenance alerts
- Quality trend analysis
- Resource utilization monitoring
Visual analytics make complex data patterns easily understandable, helping teams identify potential hidden factory issues quickly.
Implementation Technologies of Hidden Factory
Digital work instructions guide operators through standard procedures while recording actual process times. These systems help identify when unofficial steps get added to normal workflows.
Automated tracking systems monitor material movement and resource consumption, revealing hidden inefficiencies in production processes. These tools provide objective data about actual vs. reported process performance.
Data Integration Systems
Modern detection platforms integrate data from multiple sources:
- Production equipment sensors
- Quality control systems
- Inventory management platforms
- Time tracking systems
This integrated approach provides a complete picture of operational performance, making hidden factories harder to conceal.
Monitoring And Control Features of Hidden Factory
Advanced monitoring systems offer continuous oversight of critical processes.
Real-time alerts notify managers when activities deviate from standard procedures, enabling prompt intervention.
Historical trend analysis helps identify patterns that might indicate developing hidden factory issues.
Control systems maintain detailed audit trails of process modifications, helping teams track when and why changes occur.
This documentation proves valuable for preventing unofficial procedures from becoming standard practice.
These modern tools and techniques provide manufacturing organizations with powerful capabilities for identifying and eliminating hidden factories.
Quality professionals can leverage these technologies to maintain process efficiency and prevent waste from accumulating in their operations.
Calculating The Impact Of Hidden Factory
Measuring the financial impact of hidden factories requires systematic analysis of both direct and indirect costs.
Organizations must examine multiple cost categories to understand the true scale of efficiency losses and quality impacts.
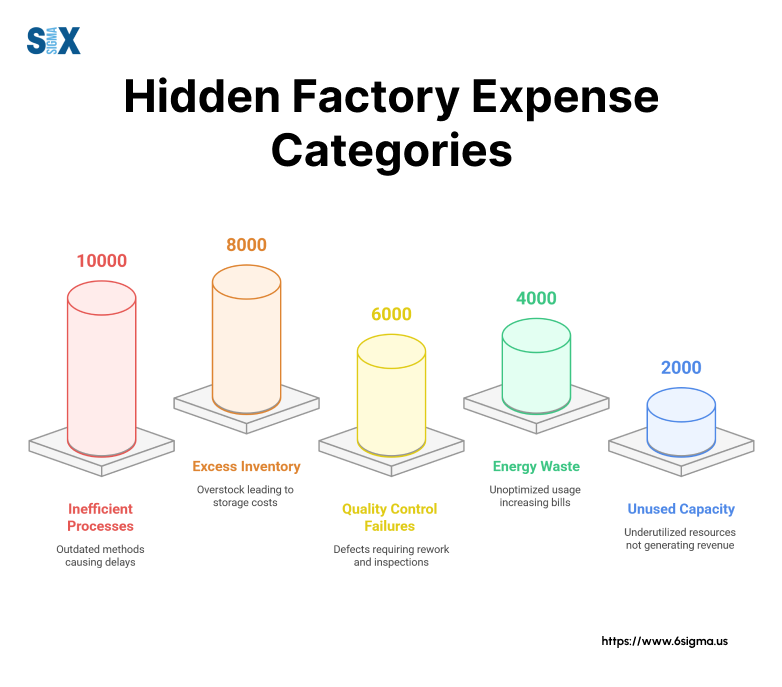
Direct Cost Analysis
Hidden factories generate significant direct costs through excess labor, materials, and equipment usage. Labor costs increase when operators perform unofficial rework or additional quality checks.
Material waste occurs through unauthorized process modifications and repeated quality failures.
Equipment costs rise due to unofficial maintenance procedures and unplanned downtime.
These direct expenses often amount to 15-25% of total production costs, yet remain buried in standard accounting reports.
Quality Cost Calculations
The Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) provides a framework for measuring hidden factory impacts. Prevention costs increase when teams implement unofficial quality checks.
Appraisal costs rise through redundant inspections and testing procedures. Internal failure costs multiply through rework and scrap.
External failure costs grow when quality issues reach customers despite hidden factory activities. These combined quality costs typically represent 20-30% of sales revenue in organizations with significant hidden factory issues.
Performance Metric Impact of Hidden Factory
Hidden factories affect key performance indicators across operations:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) decreases by 10-15%
- First Pass Yield drops 20-25% below theoretical capacity
- Process Cycle Time extends 30-40% beyond standard
- Labor Productivity falls 15-20% below target
ROI Calculation Methods
Return on Investment calculations for hidden factory elimination must consider:
- Implementation costs for detection systems
- Training expenses for proper procedures
- Equipment modifications to prevent workarounds
- Productivity gains from elimination efforts
Standard ROI formulas require adjustment to capture full benefits, including quality improvements and capacity gains.
Resource Utilization Analysis
Hidden factories impact resource utilization through:
- Excess inventory holding costs
- Additional storage space requirements
- Increased utility consumption
- Extended equipment runtime
These resource drains often amount to 10-15% of operating costs while remaining hidden in departmental budgets.
Long-Term Financial Effects of Hidden Factory
Hidden factories generate ongoing financial impacts through:
- Reduced manufacturing capacity
- Increased maintenance requirements
- Higher training costs
- Lost market opportunities
Organizations must consider these long-term effects when calculating total impact and prioritizing improvement efforts.
Measurement Systems
Modern measurement systems help organizations track hidden factory costs through:
- Real-time cost tracking
- Automated resource monitoring
- Quality cost analysis
- Performance metric correlation
These systems provide accurate data for ROI calculations and improvement prioritization.
Understanding the full financial impact of hidden factories helps manufacturing leaders justify investment in detection and elimination efforts.
Quality professionals can use these calculations to build strong business cases for improvement projects while tracking actual returns on elimination efforts.
Digital Transformation And The Future Of Hidden Factory Detection
Digital technologies are revolutionizing how organizations detect and eliminate hidden factories.
Advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and connected systems provide unprecedented visibility into manufacturing operations, enabling early detection of developing inefficiencies.
AI-Powered Detection Systems
Artificial intelligence transforms hidden factory detection through advanced pattern recognition and anomaly detection.
Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of production data to identify subtle indicators of unofficial processes.
These systems learn from historical patterns to predict where hidden factories might develop.
Neural networks process multiple data streams simultaneously, detecting correlations between process variables that traditional methods miss.
This capability helps quality teams spot developing issues before they become embedded in daily operations.
Remote Monitoring Solutions
Modern monitoring systems enable real-time oversight of manufacturing operations from anywhere.
Connected sensors track equipment performance, process parameters, and operator activities continuously. Cloud-based platforms make this data accessible to quality teams regardless of location.
Remote monitoring capabilities help organizations maintain consistent oversight across multiple facilities.
Quality professionals can compare performance metrics between plants, identifying best practices and potential hidden factory issues simultaneously.
Predictive Analytics Applications
Predictive analytics tools forecast potential hidden factory formation based on current operational trends. These systems analyze:
- Process variation patterns
- Resource consumption trends
- Quality metric fluctuations
- Equipment performance data
Early warning capabilities enable proactive intervention before unofficial processes become established.
Integration of Hidden Factory With Industry 4.0
Smart manufacturing systems create digital twins of production processes, enabling detailed analysis of actual vs. planned operations.
These virtual models help identify gaps where hidden factories might develop. Connected equipment provides continuous feedback about process performance and potential deviations.
Future Detection Capabilities
Emerging technologies promise enhanced hidden factory detection through:
- Quantum computing analysis of complex process interactions
- Augmented reality visualization of process deviations
- Blockchain tracking of process modifications
- Advanced sensor networks for comprehensive monitoring
These innovations will provide quality teams with powerful new tools for maintaining process efficiency.
Data Integration Platforms
Modern platforms integrate data from multiple sources:
- Production equipment sensors
- Quality control systems
- Resource tracking tools
- Operator input devices
This consolidated view helps identify hidden factory activities that might otherwise go unnoticed across separate systems.
Implementation Considerations of Hidden Factory
Organizations implementing digital detection systems must address:
- Data security requirements
- System integration challenges
- Staff training needs
- Change management processes
Successful deployment requires careful planning and systematic execution to ensure effective adoption.
Future-Ready Solutions
Digital transformation enables scalable, adaptable hidden factory detection through:
- Cloud-based monitoring platforms
- Mobile access capabilities
- Automated reporting systems
- Continuous learning algorithms
These features help organizations stay ahead of evolving manufacturing challenges while maintaining operational excellence.
Digital transformation provides manufacturing organizations with powerful new capabilities for identifying and eliminating hidden factories.
Quality professionals must stay current with these evolving technologies to maintain effective oversight of their operations and prevent efficiency losses.
Implementation Roadmap And Best Practices
Successful hidden factory elimination requires systematic implementation following proven methodologies.
Organizations must develop clear plans, establish appropriate metrics, and maintain consistent execution to achieve lasting results.
Phase 1: Assessment And Planning
Initial assessment establishes current state conditions and identifies priority areas for improvement. Teams must document existing processes, gather baseline metrics, and map value streams to spot potential hidden factory locations. This phase typically requires 4-6 weeks of focused effort.
Stakeholder engagement proves crucial during planning.
Manufacturing managers, operators, and quality teams must align on improvement objectives and implementation approaches. Clear communication channels help ensure consistent execution across all levels.
Phase 2: Detection System Implementation
Installing appropriate detection systems marks the second major phase. Organizations should start with pilot areas to validate approaches before full deployment.
Modern monitoring tools require careful integration with existing systems while maintaining production schedules.
Quality teams must establish clear triggers for intervention when systems detect potential hidden factory activities.
Response protocols ensure consistent handling of identified issues while maintaining operational efficiency.
Common Implementation Pitfalls
Many organizations encounter similar challenges during implementation. Insufficient data collection systems often hamper effective detection efforts.
Resistance to process changes can delay improvement initiatives. Lack of clear success metrics makes progress difficult to track.
Poor communication between departments frequently allows hidden factories to persist. Organizations must address these common issues proactively through systematic planning and stakeholder engagement.
Success Metrics And KPIs
Effective implementation requires clear performance indicators:
- First Pass Yield improvement
- Process cycle time reduction
- Resource utilization gains
- Quality cost decreases
Regular metric reviews help teams track progress and adjust approaches based on actual results.
Sustainability Measures
Long-term success demands sustainable improvement approaches. Organizations must establish:
- Regular audit procedures
- Continuous training programs
- Performance review cycles
- Update mechanisms for standards
These measures help prevent hidden factories from reforming after initial elimination efforts.
Conclusion
Hidden factories represent significant operational challenges across manufacturing industries. Their impact on efficiency, quality, and costs demands systematic detection and elimination efforts.
Successful hidden factory elimination requires commitment to systematic implementation approaches. Organizations must leverage available technologies while maintaining focus on fundamental improvement principles.
The combination of proven methodologies with modern detection tools enables sustainable improvements in efficiency and quality. Organizations that master these approaches gain significant competitive advantages through reduced costs and improved operational performance.
Quality professionals must stay current with evolving detection technologies while maintaining systematic improvement approaches.
This balanced strategy helps organizations achieve and maintain optimal operational performance in increasingly competitive manufacturing environments.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







