Essential Lean Manufacturing Tools: A Comprehensive Guide
Manufacturing companies that implement lean tools see an average 25-30% reduction in operating costs within the first year.
Yet, many businesses struggle to identify and correctly apply these powerful efficiency-boosting techniques.
Lean manufacturing tools transform how companies operate – from the shop floor to the executive suite.
Key Highlights
- How to select the right tools for your specific challenges
- Step-by-step implementation instructions with real examples
- Common pitfalls to avoid and troubleshooting tips
- Ways to measure and track your success
- Latest digital innovations in lean manufacturing
What is Lean Manufacturing?
Lean manufacturing is derived from Toyota’s production system in the 1950s.
From a small Japanese automaker into the world’s leading automaker, Toyota used these methods to cut waste and supercharge quality.
To stay competitive these proven techniques/methodologies are being used by organization across industries.

Think of lean tools as your efficiency toolkit. Each tool tackles specific challenges in your production process.
Some tools, like 5S, organize workspaces to save time and reduce errors. Others, like Kanban, create smooth workflow systems that prevent bottlenecks and excess inventory.
The core principles behind these tools focus on:
- Eliminating waste in all forms
- Creating consistent, repeatable processes
- Building quality into every step
- Respecting and engaging workers
- Driving continuous improvement
Modern manufacturers face new challenges – from global competition to rapid technological change. Industry 4.0 technologies now enhance traditional lean tools.
Smart sensors track production metrics in real-time. AI systems predict maintenance needs before breakdowns occur.
Cloud platforms connect teams across locations for better collaboration.
Leading companies like Boeing, Nike, and Intel adapt lean tools for today’s needs. Boeing cut production time for the 737 aircraft by 50% using lean methods.
Nike’s lean initiatives reduced labor costs by 20% and boosted on-time delivery to 95%.
But the basic principle remains: identify and eliminate anything that doesn’t add value for your customer. Whether you run a small machine shop or a global enterprise, these time-tested tools can transform how you operate.
The Foundation: 3M Framework
Japanese manufacturers built lean tools around three fundamental concepts: Muda, Mura, and Muri. These “3Ms” help teams spot and fix problems that drain productivity and profits.
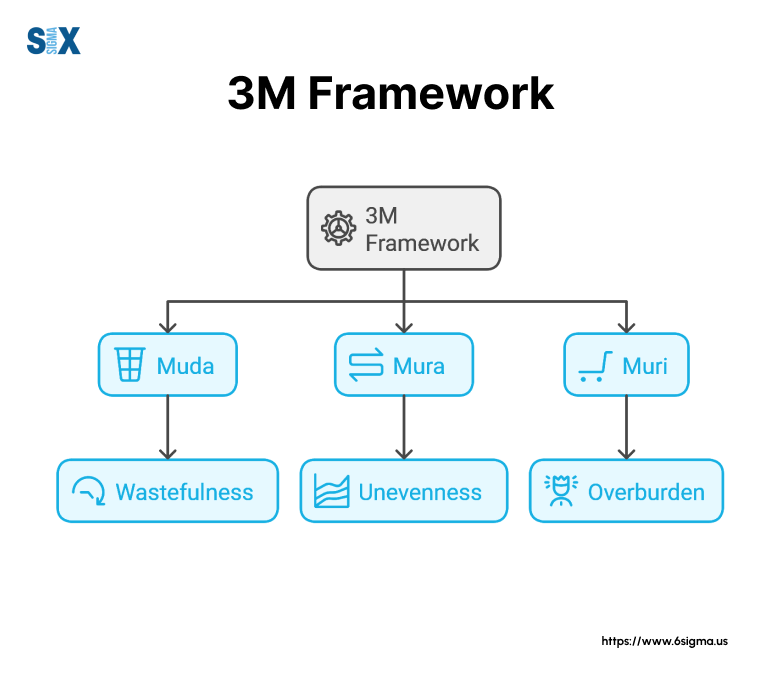
Muda (Waste)
Muda targets eight types of waste that eat into your bottom line:
- Transportation – Moving materials more than needed
- Inventory – Storing excess raw materials or finished goods
- Motion – Unnecessary movement of people or equipment
- Waiting – Idle time between process steps
- Overproduction – Making more than customers need
- Over-processing – Adding features customers won’t pay for
- Defects – Quality problems requiring rework
- Unused talent – Not tapping employee ideas and skills
Ford Motor Company cut assembly time 25% by reducing transportation waste between workstations. Their teams mapped material flows and reorganized layouts to minimize movement.
Mura (Unevenness)
Mura shows up as peaks and valleys in your workflow. One day your team scrambles to fill orders, the next they sit idle. This inconsistency creates stress and waste.
A metal fabricator struggled with rush orders causing overtime one week and layoffs the next. By implementing level scheduling tools, they smoothed production and cut labor costs 15%.
Muri (Overburden)
Muri happens when we push people or machines beyond reasonable limits. This leads to burnout, breakdowns, and quality problems.
Signs of Muri include:
- Excessive overtime
- High employee turnover
- Frequent equipment failures
- Safety incidents
- Quality issues
A food processor reduced Muri by cross-training workers and adding flexible automation. This cut overtime 40% while maintaining output.
The 3M Connection:
- Muda wastes resources
- Mura creates instability
- Muri burns out assets
- All three hurt productivity
Successful lean programs tackle all 3Ms together. Start by mapping your processes to spot these issues.
Then use targeted lean tools to fix root causes, not just symptoms.
Essential Lean Manufacturing Tools Categories
Lean tools fall into four main categories, each targeting specific improvement areas.
Let’s break down these categories and see how top manufacturers use them to boost performance.

Quality Improvement Tools
These tools catch and prevent defects before they reach customers. They build quality into your process instead of inspecting it afterward.
Key tools include:
- Six Sigma methods
- Error-proofing (Poka-Yoke)
- Quality circles
- Statistical process control
Example: A medical device maker cut defect rates 75% using Poka-Yoke fixtures that prevented incorrect assembly.
This saved $2M yearly in scrap and rework.
Process Flow Tools
Flow tools eliminate bottlenecks and keep work moving smoothly through your facility.
Popular options:
- Value Stream Mapping
- Kanban systems
- Quick changeover (SMED)
- Cell layouts
Success story: An auto parts supplier mapped their value stream and found 60% of production time was waste. New cell layouts and Kanban cards cut lead time from 23 days to 5.
Productivity Enhancement Tools
These tools boost output while using fewer resources.
They target efficiency at every step.
Must-have tools:
- 5S workplace organization
- Total Productive Maintenance
- Standard work
- Visual management
Employee Engagement Tools
Engagement tools tap into worker knowledge and creativity to drive improvements.
Key methods:
- Kaizen events
- Suggestion systems
- Skills matrices
- Team boards
Impact example: A furniture maker’s employee suggestion program generated 2,300 ideas in one year, saving $1.2M through process improvements.
| Tool Category | Primary Focus | Key Benefits | Best For |
| Quality | Defect prevention | Lower scrap/rework | High-precision work |
| Flow | Smooth operations | Reduced lead time | Complex processes |
| Productivity | Resource efficiency | Higher output | Labor-intensive work |
| Engagement | Worker innovation | Continuous improvement | All operations |
Choose tools based on your biggest pain points. Start small, master the basics, then add more as needed.
Remember – tools work best when used together as part of a complete lean system.
Take your lean skills to the next level with our Green Belt training
Top Lean Manufacturing Tools Explained
Let’s dive into the most effective lean manufacturing tools, with real examples of how companies use them to transform their operations.
Quality Management Tools
Six Sigma
This data-driven method targets defect reduction. GE saved $2 billion in their first year using Six Sigma to improve product quality.
Implementation steps:
- Define quality targets
- Measure current performance
- Analyze root causes
- Improve processes
- Control results
Poka-Yoke
These mistake-proofing devices prevent errors before they happen. A car parts maker installed sensors that stop machines if parts are loaded incorrectly, eliminating assembly errors.
Jidoka
This “automation with a human touch” lets machines detect problems and stop automatically. Toyota’s paint lines use Jidoka to spot defects instantly, saving thousands in rework costs.
Quality Circles
Small teams meet regularly to solve quality issues. A electronics manufacturer’s quality circles cut defect rates 40% in six months.
Process Optimization Tools
Value Stream Mapping
This visual tool tracks product flow from supplier to customer. A furniture maker mapped their process and found 65% of activities added no value. Their new streamlined process cut lead time 70%.
5S System
Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain – these steps organize work areas for maximum efficiency.
Case study: Metal fabricator’s 5S program results:
- 50% less motion waste
- 30% productivity gain
- 25% space savings
- 20% setup time reduction
Kanban
These visual signals control material flow. A food processor uses digital Kanban boards to manage inventory, cutting storage costs 35%.
Just-in-Time
JIT delivers materials only when needed. Dell’s JIT system reduced inventory costs $30M yearly.
Continuous Improvement Tools
Kaizen
This approach drives daily improvements through worker ideas. A tire maker collected 4,000 employee suggestions, saving $3M annually.
PDCA Cycle
Plan-Do-Check-Act guides improvement projects. An aerospace company uses PDCA to solve complex quality issues, raising first-pass yield 25%.
Gemba Walk
Leaders go to where work happens to spot issues. Daily walks helped a chemical plant cut downtime 45%.
A3 Problem Solving
This one-page format structures problem-solving. Teams use our downloadable A3 template to track improvements.
Workplace Organization Tools
Visual Management
Visual cues guide work and highlight problems. A distribution center’s visual boards cut picking errors 60%.
Before: Cluttered workstation, unclear status
After: Color-coded zones, digital displays showing real-time metrics
Standard Work
Documented best practices ensure consistency. A medical device maker’s standard work cut training time 50%.
Cellular Manufacturing
Grouped workstations improve flow. An electronics assembler’s cells reduced WIP 70%.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Operators maintain their own equipment. A paper mill’s TPM program cut breakdowns 80%.
Before: Monthly maintenance, frequent failures
After: Daily checks, predictive maintenance, 95% uptime
Success depends on choosing the right tools for your needs and using them consistently. Start with basic tools like 5S and visual management. Add more advanced tools as your team gains experience.
Lead transformative lean programs with our Black Belt training for advanced lean techniques strategies
Implementation Strategy
Rolling out lean manufacturing tools requires careful planning and execution. Let’s look at proven strategies that work in real manufacturing environments.
Assessment and Selection
Start by evaluating your current operations. Look for these warning signs:
- High inventory levels
- Long lead times
- Quality issues
- Excessive overtime
- Safety incidents
- Employee turnover
Match tools to your biggest problems. A food processor struggled with long changeover times. They focused on SMED (Single Minute Exchange of Die) first, cutting setup time 65%.
Priority Matrix for Tool Selection:
| Impact | Easy to Implement | Start Here |
| Impact | Hard to Implement | Plan Carefully |
| Low Impact | Easy to Implement | Quick Wins |
| Low Impact | Hard to Implement | Avoid Initially |
Implementation Roadmap
Follow this tested sequence:
- Train key team members (2-3 weeks)
- Start with 5S in one area (4-6 weeks)
- Add visual management (2-3 weeks)
- Implement standard work (4-6 weeks)
- Roll out additional tools (ongoing)
A metal stamping plant followed this approach. Their first area showed 40% productivity gains in 90 days. They then copied success to other departments.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Resistance to change
Solution: Show quick wins, involve workers in planning
Challenge: Lack of time
Solution: Start small, dedicate specific hours weekly
Challenge: Losing momentum
Solution: Track metrics, celebrate victories, adjust approach based on feedback
Week 1:
- Assess current state
- Pick pilot area
- Select initial tools
- Form implementation team
Week 2-4:
- Train team members
- Document baseline metrics
- Create action plan
- Begin 5S program
Successful implementation takes time and patience. Focus on building habits, not just using tools. Make changes stick by involving everyone and showing clear benefits.
Digital Integration of Lean Tools
Modern technology transforms traditional lean manufacturing tools, making them more powerful and easier to use.
Industry 4.0 Integration
Smart sensors now automate data collection for lean tools. A automotive supplier uses IoT devices to:
- Track machine performance real-time
- Alert maintenance before breakdowns
- Monitor work-in-progress inventory
- Adjust production pace automatically
Their smart factory cut downtime 45% and slashed inventory costs 30%.
AI and Machine Learning Applications
AI enhances lean tools by spotting patterns humans might miss. Examples include:
- Predictive maintenance scheduling
- Quality inspection automation
- Production flow optimization
- Demand forecasting
Digital Lean Tools
Paper-based tools go digital for better results:
- Digital Kanban boards
- Mobile 5S audits
- Cloud-based standard work documents
- Real-time visual management displays
Measuring Success
Key Performance Indicators
Track these vital metrics:
- On-time delivery
- First-pass yield
- Overall equipment effectiveness
- Labor productivity
- Inventory turns
ROI Calculation
Calculate returns using:
Cost savings + Revenue gains – Implementation costs = ROI
Example ROI breakdown:
- Tool investment: $50,000
- Training costs: $25,000
- Annual savings: $250,000
- First-year ROI: 233%
Continuous Monitoring
Set up daily/weekly/monthly reviews:
- Daily huddles check metrics
- Weekly team reviews address issues
- Monthly management reviews track progress
Conclusion
Lean manufacturing tools drive real results when properly selected and implemented.
Start small, focus on basics, and build on success. Digital technologies make these tools more powerful than ever.
Next steps:
- Assess your current operations
- Pick one area for improvement
- Choose appropriate tools
- Train your team
- Track results
Lean is a journey, not a destination. Keep learning, adjusting, and improving. Your effort will pay off in better quality, lower costs, and happier customers.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs








