DMAIC in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care with Lean Six Sigma
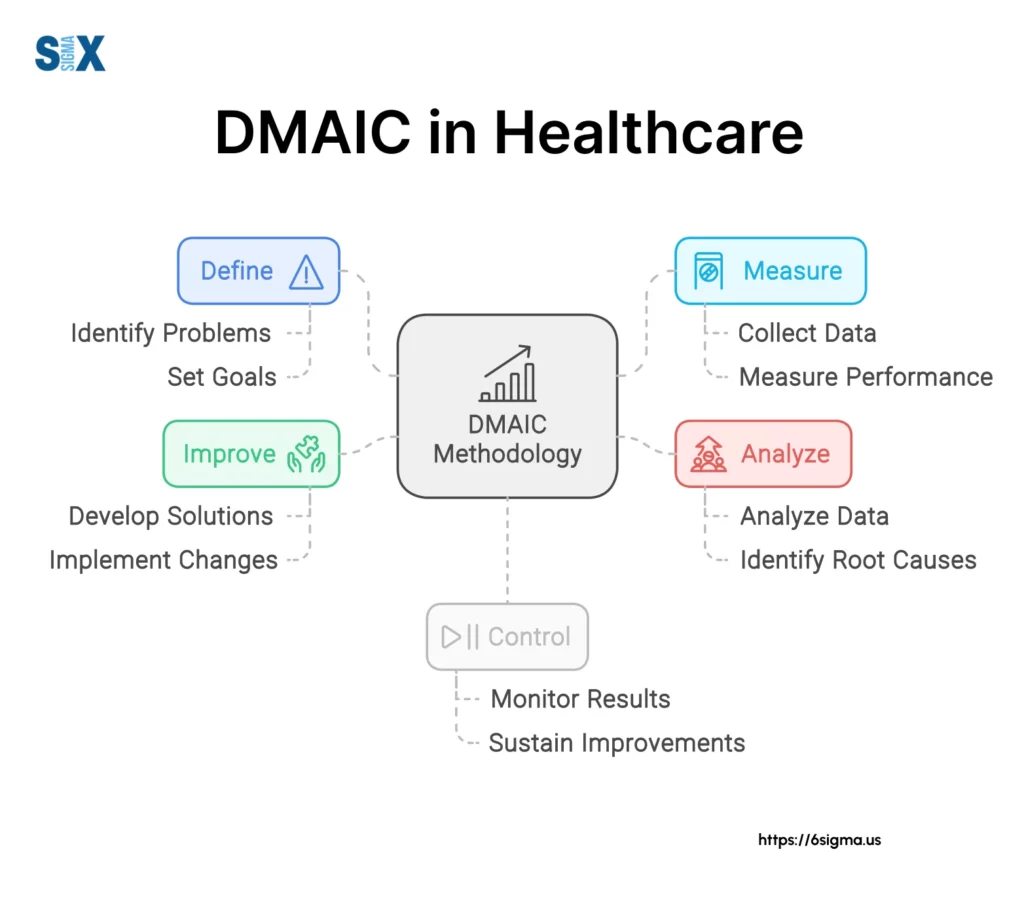
DMAIC, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, is a data-driven improvement cycle that forms the cornerstone of Lean Six Sigma.
DMAIC offers a structured approach to identifying and solving problems.
By implementing DMAIC in healthcare settings, organizations can systematically enhance patient care, streamline processes, and reduce costs.
Key Highlights
- DMAIC: Systematic approach for healthcare improvement
- Define phase: Identifying critical quality factors
- Measure: Quantifying processes with key performance indicators
- Analyze: Root cause analysis in healthcare settings
- Improve: Implementing efficiency and error reduction strategies
- Control: Sustaining improvements for long-term patient safety
- Benefits and challenges of DMAIC in healthcare
- Future trends in healthcare analytics and management
Introduction to DMAIC in Healthcare
DMAIC, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, is a data-driven improvement cycle that forms the backbone of Lean Six Sigma.
In healthcare, where patient outcomes and operational efficiency are critical, DMAIC offers a structured approach to problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Understanding Lean Six Sigma in Healthcare Settings
Lean Six Sigma in healthcare combines the waste-reduction principles of Lean with the variability-reduction focus of Six Sigma.
This powerful combination addresses the unique challenges faced by healthcare providers, from reducing patient wait times to minimizing medical errors.
The Importance of Quality Improvement in Healthcare
Quality improvement in healthcare is not just about enhancing operational efficiency; it’s about saving lives and improving patient experiences.
As healthcare costs continue to rise and patient expectations evolve, organizations must focus on delivering high-quality care while optimizing resources.
DMAIC provides a systematic framework for achieving these goals, enabling healthcare providers to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, reduce errors, and enhance patient satisfaction.
Define Phase: Setting the Foundation for DMAIC in Healthcare
The Define phase is crucial in setting the stage for a successful DMAIC project in healthcare.
It’s where we clearly articulate the problem, define the scope, and align the project with organizational goals.
Identifying Critical to Quality (CTQ) Factors
In healthcare, CTQ factors are the key measurable characteristics of a process or product that are critical to patient satisfaction.
These might include metrics like wait times, infection rates, or medication errors.
Capturing the Voice of Customer (VOC) in Healthcare
The voice of the customer in healthcare extends beyond just the patients to include families, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders.
Capturing VOC involves gathering data through surveys, interviews, and feedback forms to understand the needs and expectations of all parties involved.
This approach ensures that improvement efforts are aligned with the actual needs of those we serve.
Defining Project Scope and Objectives for DMAIC in Healthcare
Clear project scope and objectives are essential for keeping DMAIC projects on track.
In healthcare, where resources are often stretched thin, it’s crucial to define realistic, achievable goals that align with the organization’s strategic priorities.
This might involve focusing on specific departments or processes rather than trying to overhaul the entire system at once.
Measure Phase: Quantifying Healthcare Processes with DMAIC in Healthcare
The Measure phase is where we start to quantify the current state of the process we’re looking to improve.
This phase is critical in healthcare, where data-driven decision-making is essential for patient safety and operational efficiency.
Selecting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Healthcare
Choosing the right KPIs is crucial for measuring the success of improvement efforts.
In healthcare, these might include metrics like patient satisfaction scores, length of stay, readmission rates, or cost per patient.
The key is to select KPIs that are directly related to the CTQ factors identified in the Define phase.
Data Collection Methods in Healthcare Settings
Data collection in healthcare can be challenging due to privacy concerns and the complexity of healthcare systems.
Methods might include electronic health record (EHR) data extraction, direct observation, time studies, and patient surveys.
It’s important to ensure that data collection methods are reliable, consistent, and compliant with healthcare regulations.
Establishing Baseline Performance Metrics with DMAIC in Healthcare
Before implementing any improvements, it’s crucial to establish a clear baseline of current performance.
This involves analyzing historical data and conducting current state measurements.
Analyze Phase: Uncovering Root Causes with DMAIC in Healthcare
The Analyze phase is where we dig deep into the data to identify the root causes of problems and inefficiencies in healthcare processes.
Applying Root Cause Analysis in Healthcare
Root cause analysis is a critical tool in healthcare improvement.
It helps identify the underlying causes of issues rather than just treating symptoms.
Techniques like the 5 Whys and fishbone diagrams can be particularly effective in healthcare settings, helping teams to drill down to the core issues behind patient safety incidents or process inefficiencies.
Using Statistical Process Control in Healthcare
Statistical process control (SPC) is a powerful tool for understanding and reducing variation in healthcare processes.
By applying SPC techniques, healthcare organizations can monitor processes in real-time, identifying when a process is going out of control before it impacts patient care.
This proactive approach is essential for maintaining high standards of care and operational efficiency.
Value Stream Mapping for Healthcare Operations
Value stream mapping is a lean technique that’s particularly useful in healthcare for visualizing the flow of patients, information, and materials through the system.
By mapping out current processes, we can identify non-value-added activities and bottlenecks, paving the way for targeted improvements that enhance patient flow and reduce waste.
Improve Phase: Implementing Solutions with DMAIC in Healthcare
The Improve phase is where we put our analysis into action, developing and implementing solutions to address the root causes identified in the previous phase.
Developing Improvement Strategies for Healthcare Efficiency
Improvement strategies in healthcare often involve a combination of process redesign, technology implementation, and cultural change.
This might include streamlining patient flow, optimizing staffing levels, or implementing new technologies to reduce errors.
The key is to develop strategies that are both effective and sustainable in the long term.
Workflow Optimization and Process Standardization with DMAIC in Healthcare
Standardizing processes and optimizing workflows can significantly improve efficiency and reduce errors in healthcare settings.
This might involve creating standard operating procedures, implementing checklists, or redesigning physical spaces to improve flow.
The goal is to reduce variability and ensure that best practices are consistently followed.
Implementing error reduction and waste elimination techniques
Error reduction is critical in healthcare, where mistakes can have serious consequences.
Techniques like Poka-Yoke (mistake-proofing) can be adapted for healthcare settings to prevent errors before they occur.
Similarly, waste elimination techniques from lean methodology can be applied to reduce non-value-added activities and improve resource utilization.
Control Phase: Sustaining Healthcare Improvements with DMAIC in Healthcare
The Control phase is crucial for ensuring that improvements are sustained over time.
In healthcare, where maintaining high standards of care is paramount, this phase is particularly important.
Monitoring and Maintaining Performance Improvements
Implementing robust monitoring systems is essential for maintaining improvements.
This might involve regular audits, continuous data collection, and real-time performance dashboards.
The key is to create systems that allow for quick identification and response to any deviations from the improved state.
Continuous Improvement Strategies in Healthcare
The Control phase isn’t just about maintaining improvements; it’s about fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
This might involve implementing regular process reviews, encouraging staff feedback, and providing ongoing training in quality improvement methodologies.
Ensuring Long-term Patient Safety and Satisfaction with DMAIC in Healthcare
Ultimately, the goal of DMAIC in healthcare is to improve patient outcomes and experiences.
Long-term strategies for maintaining patient safety and satisfaction might include regular patient feedback surveys, ongoing staff training, and continuous monitoring of key safety indicators.
Benefits and Challenges of DMAIC in Healthcare
Impact on clinical outcomes and patient experience
When properly implemented, DMAIC can lead to significant improvements in clinical outcomes and patient experiences.
This might include reduced infection rates, shorter wait times, and improved patient satisfaction scores.
However, it’s important to note that these benefits often take time to materialize and require sustained effort to maintain.
Cost Reduction and Operational Excellence in Hospitals with DMAIC in Healthcare
DMAIC can lead to substantial cost savings through improved efficiency and reduced waste.
However, it’s crucial to balance cost reduction efforts with maintaining high standards of care.
The goal should be to achieve operational excellence that benefits both the organization and its patients.
Overcoming barriers to healthcare innovation
Implementing DMAIC in healthcare can face several challenges, including resistance to change, complex regulatory environments, and the need for extensive training.
Overcoming these barriers requires strong leadership support, effective change management strategies, and a commitment to long-term cultural change.
The Future of DMAIC in Healthcare
The future of DMAIC in healthcare is closely tied to advancements in data analytics and technology.
Emerging trends include the use of artificial intelligence for predictive analytics, the integration of wearable devices for real-time patient monitoring, and the use of blockchain for secure data sharing.
Integrating DMAIC with oOther Quality Improvement Methodologies
As healthcare continues to evolve, we’re likely to see DMAIC integrated with other quality improvement methodologies and emerging technologies.
This might include combining DMAIC with agile methodologies for faster improvement cycles or integrating it with design thinking approaches for more patient-centered improvements.
In conclusion, DMAIC in healthcare offers a powerful framework for driving meaningful improvements in patient care, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
As we look to the future, DMAIC will undoubtedly continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery, driving innovations that benefit patients, providers, and healthcare systems alike.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






