Right First Time (RFT): A Comprehensive Guide to Perfect Quality in Lean Six Sigma
Did you know that poor quality costs organizations an average of 15-20% of their annual revenue?
In some manufacturing sectors, this figure climbs even higher, with rework expenses alone accounting for up to 40% of production costs.
Right First Time (RFT) represents a fundamental quality principle focused on completing processes correctly on the initial attempt, eliminating the need for inspections, rework, or corrections.
Also known as First Time Right, this approach forms a critical component of Lean Six Sigma methodologies, helping organizations minimize waste while maximizing efficiency and customer satisfaction. Professionals can gain the skills to implement RFT effectively through six sigma certification programs, which teach proven techniques for quality improvement.
Key Highlights
- Perform tasks correctly first time.
- Eliminates rework, inspections, corrections.
- Key principle in Lean Six Sigma.
- Measure RFT score for performance.
- Build sustainable RFT culture.
What is Right First Time?
Right first time (RFT) is a quality management principle that focuses on performing tasks correctly during the initial attempt.
This approach eliminates the need for rework, inspections, and corrections, saving both time and resources.
In manufacturing environments, first time right in manufacturing has become particularly valuable as production complexities increase.
The principle stems from the belief that quality should be built into processes rather than inspected afterward.
When a product or service achieves right first time (FTR) status, it meets all specifications and customer requirements without any adjustments or rework. This represents the ideal state for any process.
Unlike traditional quality control that relies on catching defects after they occur, RFT shifts focus to prevention.
This proactive stance means designing processes that naturally produce correct outcomes, rather than depending on inspection to filter out mistakes.
Its Role in Quality Management
Right first time serves as a foundational element within broader quality management systems. Six Sigma practitioners view RFT as a key metric that indicates process capability and stability.
When processes consistently achieve right the first time results, they demonstrate statistical control and predictability.
The concept integrates seamlessly with Lean methodologies by directly addressing several forms of waste:
- Defects that require rework
- Excess processing through inspections
- Waiting time caused by quality issues
- Transportation of defective items
Organizations implementing Lean Six Sigma often track right first time scores as a primary performance indicator, and those with a six sigma certification are well-equipped to analyze and improve these metrics, driving measurable gains in quality and efficiency. Improvements in these scores correlate directly with reduced costs, increased throughput, and higher customer satisfaction.
For those new to these concepts, an introduction to lean can provide foundational knowledge on how RFT integrates with Lean methodologies to eliminate waste and boost efficiency.
Six Sigma’s Take on RFT
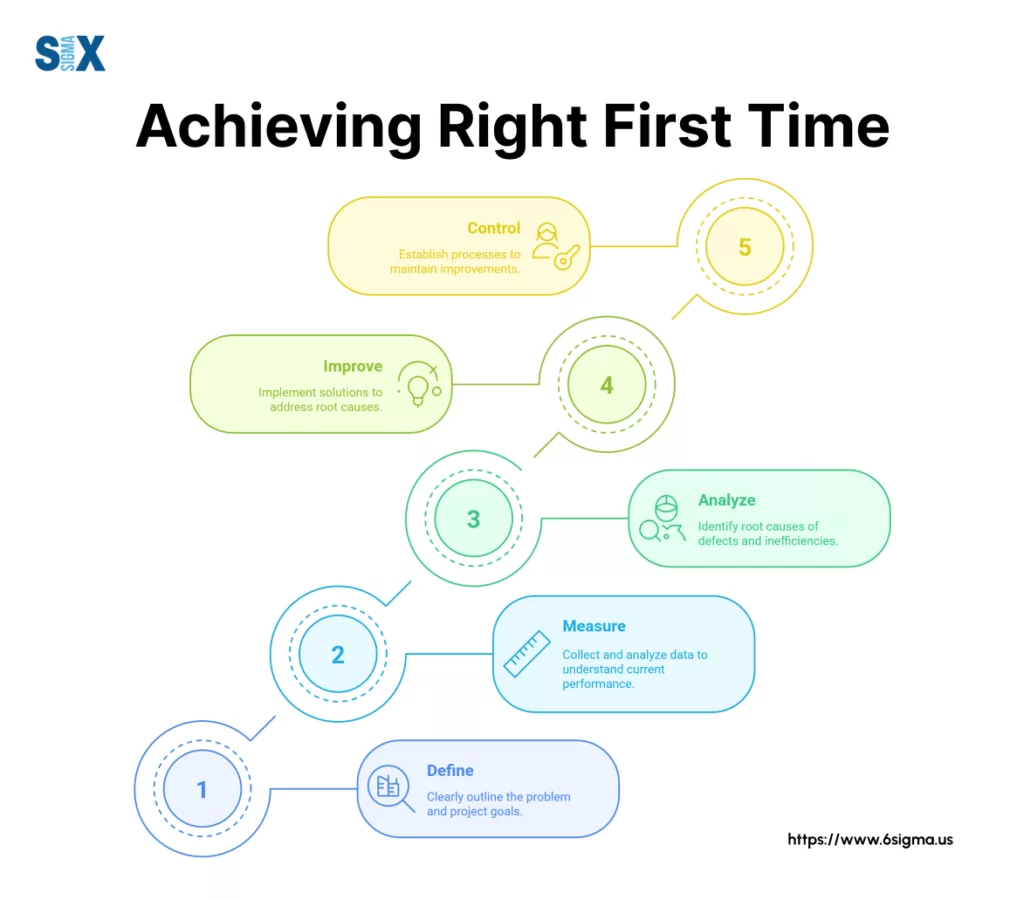
Six Sigma frameworks approach right first time through the DMAIC methodology (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control).
This structured problem-solving approach helps teams systematically improve processes to achieve first time right outcomes.
During the Define phase, teams identify Critical to Quality (CTQ) characteristics—the specific requirements that must be met for a process to achieve right first time status.
These CTQs translate customer needs into measurable specifications that guide improvement efforts.
Six Sigma practitioners then measure current performance, analyze root causes of failures, implement improvements, and establish controls to maintain gains.
This disciplined approach transforms processes that struggle with quality issues into ones that consistently deliver right first time results.
The connection between Six Sigma and right first time is fundamental—both focus on reducing variation and eliminating defects.
While Six Sigma provides the methodology and tools, RFT represents the goal: processes that work correctly every time without inspection or rework.
Ready to understand the DMAIC framework mentioned above?
Gain foundational knowledge to contribute effectively to improvement projects with Yellow Belt Certification.

Measuring Right First Time Performance
Measuring right first time performance requires precise calculation methods that accurately reflect process quality.
The most common formula for calculating the right first time score uses the ratio of defect-free units to total units produced:
RFT = (Total Units – Defective Units) / Total Units × 100%
For example, if a production line manufactures 500 units and 25 contain defects, the right first time score would be 95%. This straightforward calculation provides a clear snapshot of process performance, though it doesn’t account for multiple defect opportunities within a single unit.
More sophisticated operations often employ a weighted first time right score that assigns different values to various types of defects based on their severity or impact. This nuanced approach helps prioritize improvement efforts by highlighting the most critical issues.
Six Sigma practitioners, especially those with a six sigma green belt certification, connect right first time measurements to advanced statistical metrics like DPMO, enabling deeper process analysis
Many manufacturing facilities display these metrics on production floor dashboards, allowing teams to monitor performance in real-time. This visibility creates accountability and enables quick responses to emerging quality issues before they affect significant production volumes.
Calculate your Percentage here →
Right First Time (RFT) Calculator
Key Performance Indicators
While right first time serves as a fundamental quality metric, it works best alongside complementary indicators that provide a more complete picture of process performance.
First Pass Yield (FPY) and First Time Right often get confused, but they measure slightly different aspects of quality. FPY specifically tracks units that pass through a process without rework, while right first time can encompass broader quality criteria including documentation, timeliness, and customer requirements.
For multi-step processes, Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY) offers valuable insights by multiplying the first time right rates of each process step. This reveals the cumulative impact of quality issues across the entire production sequence.
Six Sigma Metrics
Six Sigma practitioners connect right first time measurements to more advanced statistical metrics that gauge process capability and performance.
Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) converts right first time data into a standardized format that enables comparison across different processes and industries.
A process with a 95% right first time score translates to 50,000 DPMO, assuming one opportunity per unit.
This DPMO value corresponds to a specific Sigma level on the Six Sigma scale.
A 95% right first time process operates at approximately 3.1 Sigma, still far from the Six Sigma goal of 3.4 defects per million opportunities (equivalent to 99.9997% right first time).
Understanding these correlations helps quality professionals communicate process performance in terms that resonate with different stakeholders.
While production teams might focus on the right first time percentage, executives often prefer seeing performance expressed as a Sigma level that benchmarks against world-class quality standards.
Accurately measure RFT, understand capability, and use tools like Minitab.
Start with online training!
Know all the statistical techniques essential for process improvement.
Learn RFT Analysis with our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification.
Implementing RFT in Six Sigma Projects
Six Sigma’s DMAIC framework provides a structured approach to implement right first time principles in manufacturing and service operations.
Organizations seeking to improve their right first time performance can leverage proven Six Sigma methodologies that systematically eliminate defect sources. Mastering these techniques through six sigma certification is key to identifying and resolving quality issues that hinder RFT success.
Each phase contributes specific elements to improve your right first time performance.
During the Define phase, teams establish clear quality standards and identify critical customer requirements.
This clarity ensures everyone understands what “right” means for each process. Teams also quantify the financial impact of quality failures, building a compelling business case for improvement.
The Measure phase involves collecting baseline data on current right first time performance. This often reveals surprising gaps between perceived and actual quality levels.
Teams document process variables that influence outcomes and establish measurement systems that accurately capture defects.
Analysis digs into root causes of failures using statistical tools like Pareto analysis, fishbone diagrams, and hypothesis testing. Formal root cause analysis training, ensures teams systematically identify and address defect sources. This phase moves beyond symptoms to identify fundamental process weaknesses that prevent right first time achievement.
The Improve phase develops and tests solutions that address root causes. Teams pilot changes in controlled environments before full implementation.
Solutions might include process redesigns, new equipment, or revised work methods—all aimed at making right first time the natural outcome.
Control establishes mechanisms to sustain improvements, including statistical process control, standard work procedures, and regular audits.
This phase ensures that right first time doesn’t become a temporary initiative but instead becomes the normal operating standard.
Process Mapping and Analysis
Detailed process mapping forms the foundation of right first time implementation. These visual representations document each step in a process, highlighting decision points, handoffs, and quality checkpoints.
Value Stream Maps identify where defects occur and quantify their impact on downstream operations. By mapping the entire process flow, teams spot opportunities to build in quality rather than inspect it afterward.
Critical right first time checkpoints get strategically positioned at points where defects would cause the most significant downstream consequences.
Process capability studies compare actual performance against specifications, revealing whether processes can consistently deliver right first time results.
When capability indices (Cp, Cpk) fall below 1.33, processes typically struggle to achieve acceptable right first time rates without extraordinary effort.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) helps teams anticipate potential failure points before they impact production, a skill honed through root cause analysis training, included in our Six Sigma certification programs.
This proactive approach assigns risk priority numbers to potential failures based on severity, occurrence, and detection difficulty, directing resources toward the most critical issues.
Common Tools and Techniques
Several proven tools support right first time implementation across industries. Control charts monitor process stability and signal when interventions are needed.
These statistical tools distinguish between normal variation and special causes that require immediate attention.
Poka-yoke (mistake-proofing) systems prevent errors through physical constraints or warning signals. These elegant solutions make it difficult or impossible to perform tasks incorrectly.
Examples include parts that only fit one way, color-coded connections, or sensors that detect missing components before assembly continues.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) document the one best way to perform tasks. These detailed instructions eliminate variation between operators and shifts, ensuring consistent execution.
Effective SOPs include visual aids, clear steps, and quality checkpoints that verify right first time performance.
Training matrices ensure operators possess the skills needed for right first time execution. These tools track competencies across the workforce and identify gaps requiring additional training.
When combined with certification programs, they create accountability for quality at the individual level.
Visual management tools make quality standards visible and accessible.
Dashboards displaying right first time metrics, color-coded status indicators, and sample boards showing acceptable versus defective work all reinforce quality expectations and provide immediate feedback on performance.
Apply tools like Process Mapping, FMEA, and Control Plans to achieve RFT.
Develop the skills to manage and execute successful Six Sigma projects with our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
The manufacturing sector has pioneered right first time methodologies with remarkable results.
Automotive manufacturers have been particularly successful implementing first time right in manufacturing environments.
Toyota’s production system famously established the benchmark, achieving right first time rates exceeding 99% on complex vehicle assembly lines through standardized work and error-proofing systems.
Electronics manufacturers face unique challenges with miniaturization and increasingly dense circuit boards.
Companies like Motorola and Siemens have implemented right first time principles in their production facilities, using automated optical inspection and statistical process control to detect and eliminate defect sources.
One semiconductor fabrication plant reported a 67% reduction in rework costs after implementing right first time programs across their clean room operations.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing demands perfect quality due to regulatory requirements and patient safety concerns.
GlaxoSmithKline implemented right first time principles across their tablet production lines, resulting in batch rejection rates dropping from 5.2% to 0.8% within eight months.
Their approach combined rigorous process validation with operator certification programs.
Service Industry Implementation
While manufacturing applications receive more attention, service industries have adapted right first time principles with impressive results.
Financial services firms apply these concepts to transaction processing, loan approvals, and customer onboarding.
One major bank reduced new account errors by 83% by redesigning their application process with right first time principles.
Healthcare organizations implement right first time methodologies to medication administration, surgical procedures, and patient transfers.
A regional hospital network reduced medication administration errors by 92% through a combination of barcode verification, standardized procedures, and staff training focused on right first time execution.
Software development teams increasingly adopt right first time approaches through test-driven development and continuous integration practices.
These methodologies build quality verification into each development step rather than relying on end-stage testing to catch defects.
Case Study Examples
A medium-sized auto parts manufacturer struggled with high scrap rates on precision-machined components.
Their right first time score hovered around 82%, well below industry standards. After implementing a Six Sigma project focused specifically on right first time improvement, they:
- Mapped their entire production process
- Identified critical control points
- Implemented statistical process control
- Developed operator training and certification
- Installed vision systems at key inspection points
Within six months, their right first time score reached 97.3%, generating annual savings of $1.2 million through reduced scrap, rework, and warranty claims.
A telecommunications service provider tackled installation quality issues by applying right first time principles to their field operations.
By standardizing installation procedures, providing technicians with digital work instructions, and implementing post-installation verification steps, they improved their right first time rate from 76% to 94%. This reduced costly repeat visits and significantly improved customer satisfaction scores.
These examples demonstrate how right first time principles deliver measurable benefits across diverse industries when implemented with proper planning, tools, and management commitment.
