Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) in Six Sigma
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) serves as a standardized quality assurance method in manufacturing.
This systematic approach validates that suppliers can consistently produce parts meeting customer specifications.
Major automotive manufacturers developed PPAP to establish reliable quality standards across their supply chains.
Key Highlights
- PPAP validates consistent supplier part quality
- Five submission levels guide approval process
- Digital tools transform traditional PPAP methods
- Six Sigma principles enhance PPAP effectiveness
Understanding Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma methodology drives quality improvements in manufacturing through data-driven decision making and process optimization.
This statistical approach aims to reduce defects to 3.4 per million opportunities, creating reliable and efficient production systems.
Core Principles of Six Sigma
Manufacturing organizations implement Six Sigma through five key principles: customer focus, data measurement, process control, proactive management, and continuous improvement.
These principles guide quality teams in identifying and eliminating variations that cause defects in production processes.
Quality managers use statistical tools to measure process capability and identify areas for improvement.
This data-driven approach helps manufacturing teams set realistic quality targets and track progress toward zero-defect production.
The production part approval process fits naturally within this framework by establishing clear quality standards and verification methods.
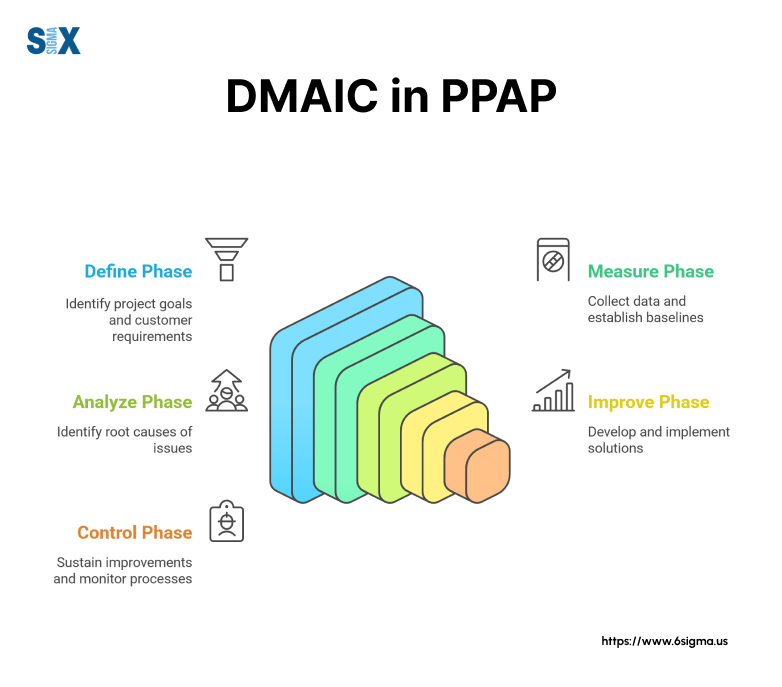
DMAIC Methodology in Practice
The DMAIC cycle (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) provides a structured approach to solving quality issues in manufacturing. Each phase serves specific purposes:
- Define: Teams identify quality problems and set project goals
- Measure: Data collection establishes current performance levels
- Analyze: Statistical analysis reveals root causes of issues
- Improve: Solutions are implemented and validated
- Control: New processes are standardized and monitored
Manufacturing professionals apply DMAIC principles when implementing PPAP requirements, ensuring systematic validation of part quality and production processes.
Quality Control Integration
Quality control processes in Six Sigma manufacturing focus on preventing defects rather than detecting them after production.
This preventive approach aligns perfectly with PPAP requirements, as both systems emphasize process validation before mass production begins.
Modern quality control systems integrate digital tools for:
- Real-time process monitoring
- Statistical process control (SPC)
- Automated inspection systems
- Quality data analysis
- Corrective action tracking
These digital solutions enable faster response to quality issues and better documentation for PPAP submissions.
Quality teams can now track process performance continuously and maintain detailed records for compliance requirements.
Process Optimization Through Six Sigma
Six Sigma tools help manufacturing teams optimize their PPAP implementation by:
- Reducing variation in production processes
- Improving measurement system accuracy
- Enhancing process control methods
- Standardizing quality documentation
- Supporting continuous improvement efforts
This systematic approach to quality management ensures that PPAP requirements become an integral part of the manufacturing process rather than just a documentation exercise.
Master Six Sigma principles and lead PPAP implementation
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP): An Overview
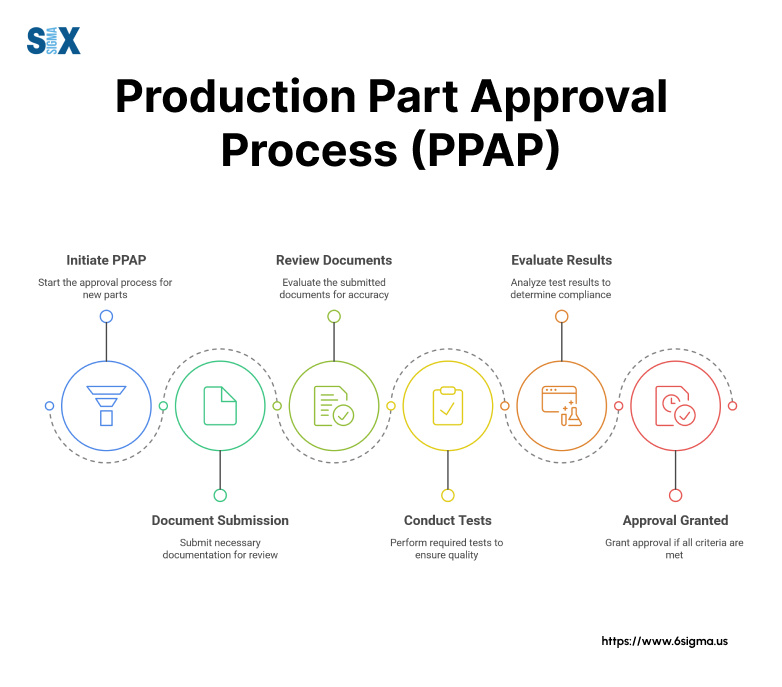
The production part approval process establishes a standardized method for validating new or modified parts in manufacturing.
This quality assurance system ensures that suppliers can consistently produce parts meeting all engineering and quality specifications before starting mass production.
Purpose and Definition of PPAP
PPAP serves as a formal verification system between suppliers and manufacturers.
The process validates that suppliers understand design specifications and can produce parts consistently at the required quality level during regular production runs.
This systematic approach reduces quality issues, minimizes production delays, and builds stronger supplier-manufacturer relationships.
Manufacturing teams use PPAP to verify several critical aspects:
- Design documentation accuracy
- Production process capability
- Quality control measures
- Material specifications compliance
- Statistical process controls
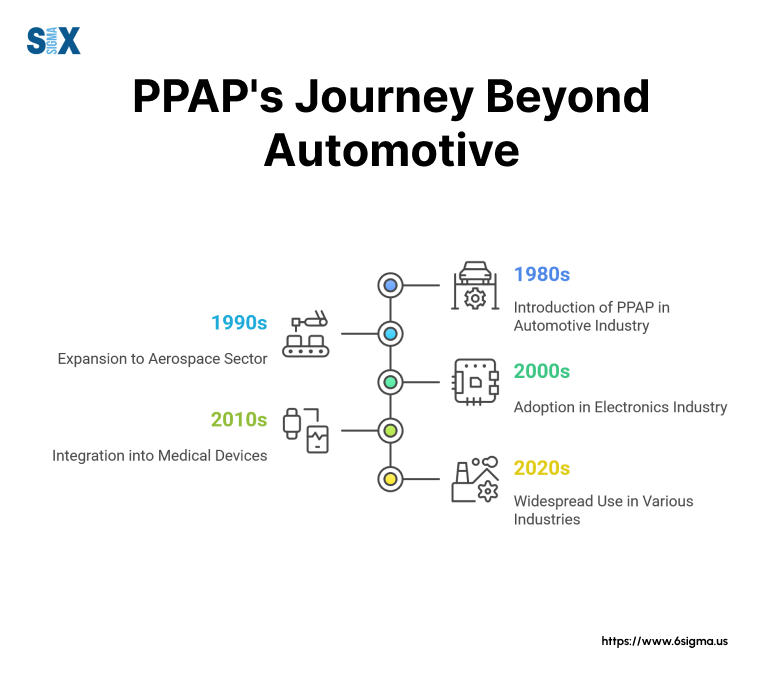
Automotive Industry Origins of Production Part Approval Process
Major automotive manufacturers developed PPAP in the 1980s to standardize part approval across their global supply chains.
The Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) formalized these requirements, creating a unified approach for supplier quality management.
This standardization helped automotive manufacturers maintain consistent quality while working with diverse supplier networks worldwide.
The automotive sector’s implementation of PPAP demonstrated significant benefits:
- Reduced warranty claims
- Improved first-time quality
- Lower production costs
- Faster time to market
- Enhanced supplier performance
Manufacturing Sector Expansion
The success of PPAP in automotive manufacturing led other industries to adopt similar approaches.
Aerospace manufacturers modified PPAP to meet their stringent safety requirements, while medical device makers adapted it for regulatory compliance.
Electronics manufacturers now use PPAP to manage complex supply chains and ensure component reliability.
Modern PPAP implementation spans various industries:
- Aerospace: Focus on safety-critical components and regulatory compliance
- Medical Devices: Emphasis on traceability and validation
- Electronics: Adaptation for high-volume production
- Heavy Equipment: Modified for low-volume, high-complexity parts
- Defense: Integration with military specifications
Evolution of Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Requirements
Today’s PPAP requirements reflect modern manufacturing needs through:
- Digital Documentation: Cloud-based systems replace paper records
- Real-time Monitoring: Connected sensors track process parameters
- Automated Validation: Software tools verify compliance automatically
- Global Collaboration: Online platforms enable remote approvals
- Data Analytics: Advanced tools identify quality trends
This evolution makes PPAP more efficient while maintaining its core purpose of ensuring consistent part quality.
Quality managers now leverage digital tools to streamline the approval process without compromising thoroughness or accuracy.
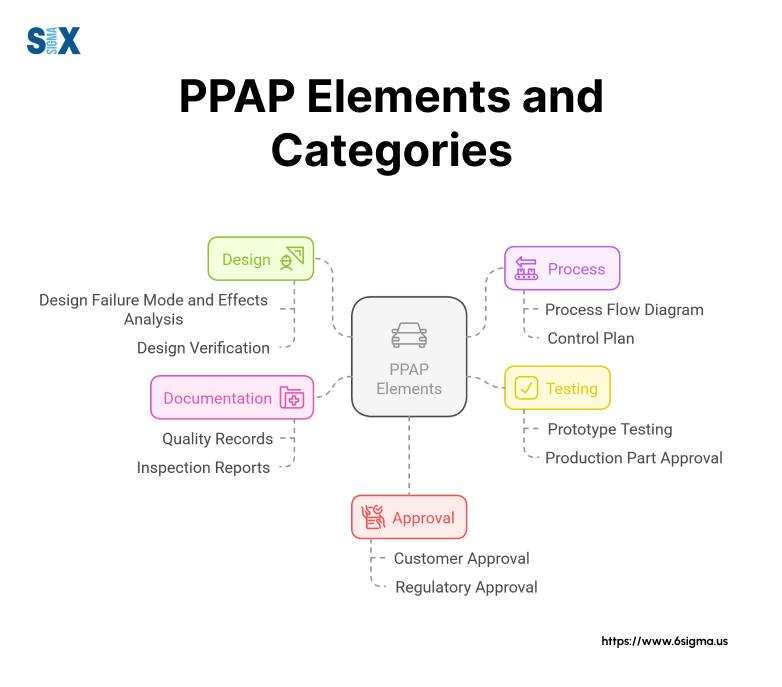
The 18 Elements of PPAP
The production part approval process consists of 18 distinct elements that ensure thorough quality validation.
Each element plays a crucial role in verifying part quality and production capability.
Design and Documentation Elements
Design Records form the foundation of PPAP, containing detailed product specifications and engineering requirements.
These records must match customer specifications exactly. Engineering Change Documentation tracks modifications to existing designs, ensuring proper approval and implementation of changes.
Customer Engineering Approval provides formal validation of design requirements, while Design FMEA identifies potential failure modes during product development.
These elements create a solid foundation for quality assurance throughout the production lifecycle.
Process Control Elements of Production Part Approval Process
Process Flow Diagrams map the manufacturing sequence from raw materials to finished products. Process FMEA identifies potential failures in manufacturing steps, leading to preventive actions.
The Control Plan outlines inspection methods and quality checks throughout production.
Measurement System Analysis validates testing equipment accuracy, while Dimensional Results verify product specifications.
Material and Performance Test Results confirm that products meet functional requirements under various conditions.
Statistical and Laboratory Elements
Initial Process Studies demonstrate manufacturing capability through statistical analysis.
Qualified Laboratory Documentation ensures testing validity through proper certifications. These elements provide quantitative proof of process capability and product quality.
Manufacturing teams use these elements to:
- Validate measurement systems
- Verify process capabilities
- Document test results
- Maintain quality standards
- Track process performance
Production Validation Elements of Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
Sample Production Parts provide physical evidence of manufacturing capability. Master Samples serve as reference standards for future production.
The Appearance Approval Report confirms aesthetic requirements for visible components.
Checking Aids documentation ensures proper calibration and maintenance of inspection equipment. Customer-Specific Requirements address unique needs beyond standard PPAP elements.
Final Approval Element
The Part Submission Warrant serves as the formal approval document, summarizing all PPAP elements and confirming compliance with requirements.
This final element requires supplier certification that all PPAP requirements have been met.
Quality managers must ensure each element receives proper attention:
- Design Records: Foundation for all quality requirements
- Process Controls: Manufacturing consistency verification
- Testing Results: Product performance validation
- Documentation: Complete quality record maintenance
- Final Approval: Formal process completion
Transform your PPAP implementation with Lean Six Sigma
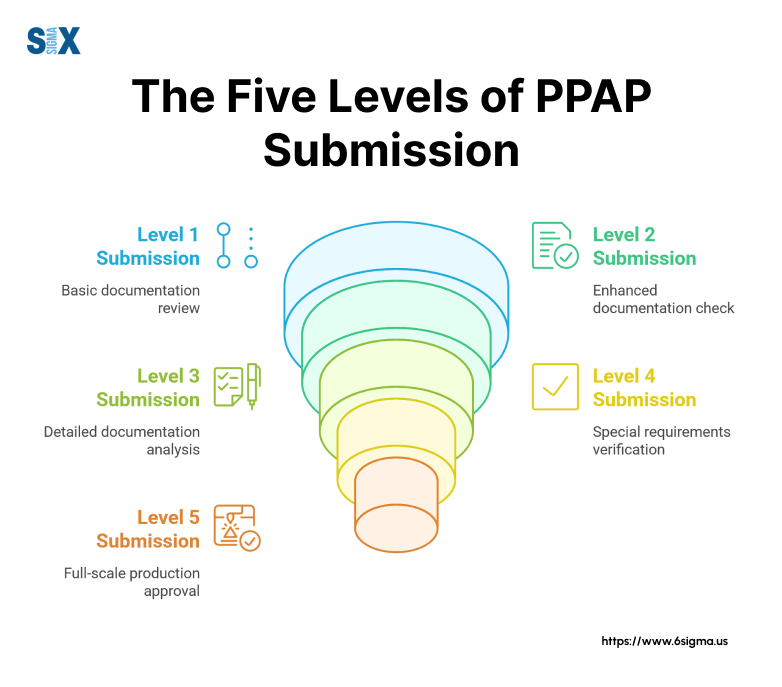
The Five Levels of PPAP Submission
The production part approval process includes five distinct submission levels, each designed for specific situations and requirements.
These PPAP levels determine the depth of documentation and validation needed for part approval.
Understanding Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Submission Levels
Level 1 requires only the Part Submission Warrant (PSW), suitable for minor changes to existing approved parts. This basic level maintains quality records while minimizing documentation requirements.
Level 2 adds product samples and limited supporting data to the PSW. Quality teams typically use this level for minor design modifications or previously approved parts from different manufacturing locations.
Level 3 serves as the default submission level, requiring complete documentation and product samples. Manufacturing teams submit all applicable PPAP elements, making this level ideal for new parts or significant changes.
Level 4 addresses customer-specific requirements beyond standard documentation. This level meets unique industry needs or special customer demands through additional verification steps.
Level 5 requires complete documentation review at the supplier’s location. This level suits complex parts or processes requiring detailed on-site verification.
Selecting the Appropriate PPAP Level
Several factors influence PPAP level selection:
- Part complexity and criticality
- Manufacturing process changes
- Customer requirements
- Industry regulations
- Previous quality history
| Level | Documentation Required | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PSW only | Minor changes to approved parts |
| 2 | PSW + Samples + Limited data | Design modifications |
| 3 | Complete documentation | New parts or major changes |
| 4 | Customer-specific requirements | Special verification needs |
| 5 | Full review at supplier location | Complex parts/processes |
Industry-Specific Applications of Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
Different industries adapt PPAP levels to their needs:
Automotive manufacturers often default to Level 3 for new components, ensuring thorough validation of critical parts.
Aerospace companies frequently require Level 4 submissions with additional testing and documentation for safety-critical components.
Medical device manufacturers modify PPAP levels to incorporate FDA requirements and traceability documentation.
Electronics manufacturers adjust submission levels based on component complexity and production volume.
Digital Implementation of Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Levels
Modern quality management systems streamline PPAP submissions through:
- Digital Documentation: Cloud storage for easy access
- Automated Workflows: Systematic review processes
- Real-time Updates: Instant status tracking
- Electronic Signatures: Faster approval cycles
- Data Integration: Connected quality systems
These digital tools help quality teams manage different PPAP levels efficiently while maintaining documentation accuracy and traceability.
Implementing PPAP Within a Six Sigma Framework
The production part approval process gains additional strength when integrated with Six Sigma methodologies.
This combination creates a robust quality system that drives continuous improvement while ensuring consistent part quality.
DMAIC Integration in Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
The Define phase establishes clear PPAP requirements and project scope. Quality teams identify critical characteristics, customer requirements, and necessary documentation.
This initial step ensures alignment between Six Sigma goals and PPAP objectives.
Measure activities focus on gathering baseline data for PPAP submissions. Teams collect process capability data, measurement system analysis results, and other quality metrics required for approval documentation.
Analysis tools help evaluate process performance and identify potential issues before PPAP submission. Statistical analysis validates that processes meet quality requirements and capability targets.
Improve phase activities implement necessary changes to meet PPAP requirements. Teams optimize processes, update control plans, and refine documentation based on analysis results.
Control methods ensure sustained compliance with PPAP requirements through monitoring systems and standardized procedures.
Essential Six Sigma Tools for Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
Statistical Process Control (SPC) monitors key characteristics during PPAP validation. Quality teams use control charts to demonstrate process stability and capability.
Measurement System Analysis verifies testing equipment accuracy and reliability. This critical tool ensures trustworthy data for PPAP submissions.
Process capability studies determine whether manufacturing processes can consistently meet specifications. These studies provide crucial evidence for PPAP approval.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis helps identify potential issues early in the PPAP process. Teams use FMEA results to strengthen control plans and prevention measures.
Quality Professional Responsibilities
Six Sigma professionals play key roles in PPAP implementation:
Black Belts lead complex PPAP projects and provide statistical expertise. They guide teams through process optimization and problem-solving activities.
Green Belts manage specific PPAP elements and coordinate documentation. Their hands-on involvement ensures proper execution of quality requirements.
Quality Engineers maintain PPAP systems and oversee submission processes. They work closely with suppliers to ensure documentation accuracy and completeness.
Digital Quality Management Integration
Modern PPAP implementation leverages digital tools for:
- Real-time process monitoring and data collection
- Automated statistical analysis and reporting
- Electronic document management and approval
- Integration with existing quality systems
- Performance tracking and trend analysis
These digital solutions streamline PPAP activities while maintaining Six Sigma rigor. Quality teams can now manage complex PPAP requirements more efficiently through connected systems and automated workflows.
Common Challenges and Solutions in PPAP Implementation
The production part approval process presents several challenges that quality teams must address to ensure successful implementation.
Understanding these obstacles and their solutions helps organizations maintain efficient PPAP systems.
Documentation Management Challenges of Production Part Approval Process (PPA)
Missing or incomplete documentation often delays PPAP approval. Quality teams struggle with tracking multiple revisions, maintaining current versions, and ensuring proper signatures across numerous documents.
Digital document management systems offer practical solutions through:
- Centralized document storage
- Automated version control
- Electronic signature capabilities
- Document completion tracking
- Standardized templates
These systems reduce errors while speeding up the approval process. Quality managers can quickly identify missing documents and track completion status in real-time.
Supplier-Customer Communication Issues
Miscommunication between suppliers and customers creates confusion about PPAP requirements. Different interpretations of specifications, unclear revision controls, and delayed responses impact submission quality.
Effective solutions include:
Web-based collaboration platforms enable real-time communication and document sharing. Regular virtual meetings help clarify requirements and address concerns promptly.
Standardized communication protocols establish clear channels for questions and answers. These protocols reduce confusion and ensure consistent information flow between parties.
Training programs help align understanding of PPAP requirements across organizations. Both suppliers and customers benefit from shared knowledge and expectations.
Global Supply Chain Quality Control
Manufacturing across multiple locations creates challenges in maintaining consistent quality standards. Different regional interpretations of PPAP requirements can lead to varying submission quality.
Cloud-based quality management systems enable:
- Standardized processes across locations
- Real-time monitoring of global operations
- Consistent document templates
- Unified approval workflows
- Centralized data collection
These digital solutions help maintain PPAP consistency while accommodating regional variations in manufacturing processes.
Technical Implementation Solutions of Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
Modern technology addresses traditional PPAP challenges through:
Automated Measurement Systems reduce human error in data collection. These systems provide accurate, consistent measurements across all manufacturing locations.
Digital Process Controls ensure consistent application of quality standards. Real-time monitoring helps identify and address issues before they affect PPAP submissions.
Integrated Quality Platforms connect various quality tools and systems. This integration streamlines data collection and analysis for PPAP documentation.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Regular system audits identify areas for PPAP process improvement. Quality teams use audit results to refine procedures and enhance efficiency.
Performance metrics track PPAP submission success rates and identify common failure points. This data drives targeted improvements in problem areas.
Training programs keep teams updated on PPAP requirements and best practices. Regular updates ensure all stakeholders maintain current knowledge of quality standards.
The Future of Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) in Modern Manufacturing
The production part approval process remains a cornerstone of quality management systems across manufacturing industries.
Its integration with Six Sigma methodologies creates powerful quality assurance frameworks that drive continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Strategic Value in Quality Management
PPAP delivers significant benefits to manufacturing organizations through standardized quality validation processes.
The systematic approach ensures consistent part quality while reducing defects and warranty claims. This standardization proves particularly valuable as supply chains become increasingly global and complex.
Digital transformation continues to enhance PPAP effectiveness through automated documentation, real-time monitoring, and integrated quality systems.
These technological advances streamline approval processes while maintaining rigorous quality standards.
Evolution of Quality Standards of Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
Modern manufacturing demands push PPAP to evolve beyond traditional paper-based systems. Industry 4.0 technologies enable:
- Smart factory integration with quality systems
- Automated data collection and analysis
- Predictive quality monitoring
- Digital twin simulations
- Enhanced supplier collaboration
These advancements help quality teams maintain PPAP requirements more efficiently while adapting to changing industry needs.
Future Opportunities
The manufacturing sector continues to discover new applications for PPAP across various industries. Emerging technologies create opportunities for:
- Enhanced process control through artificial intelligence
- Improved supplier collaboration via digital platforms
- Better quality predictions using advanced analytics
- Streamlined approval processes through automation
- Greater visibility into supply chain quality
Quality professionals must stay current with these developments to maximize PPAP effectiveness in their organizations.
Regular training and knowledge sharing help teams adapt to evolving quality requirements and technological capabilities.
Moving Forward
Success in modern manufacturing requires embracing both established quality methods and new technologies.
PPAP provides the foundation for quality assurance while digital tools enable more efficient implementation.
Organizations that combine these elements position themselves for continued success in quality management.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs








