What Is A Quality Plan And Why Does Your Business Need One?
A quality plan serves as the foundation of successful project execution and product development.
This strategic document outlines the standards, practices, resources, and procedures needed to deliver products or services that meet customer requirements and industry standards.
For businesses aiming to maintain consistent quality across operations, a well-structured quality plan becomes essential for success.
What You’ll Learn About Quality Planning
- Creating effective quality control procedures
- Implementing quality assurance measures effectively
- Managing resources for optimal results
- Measuring and improving quality outcomes
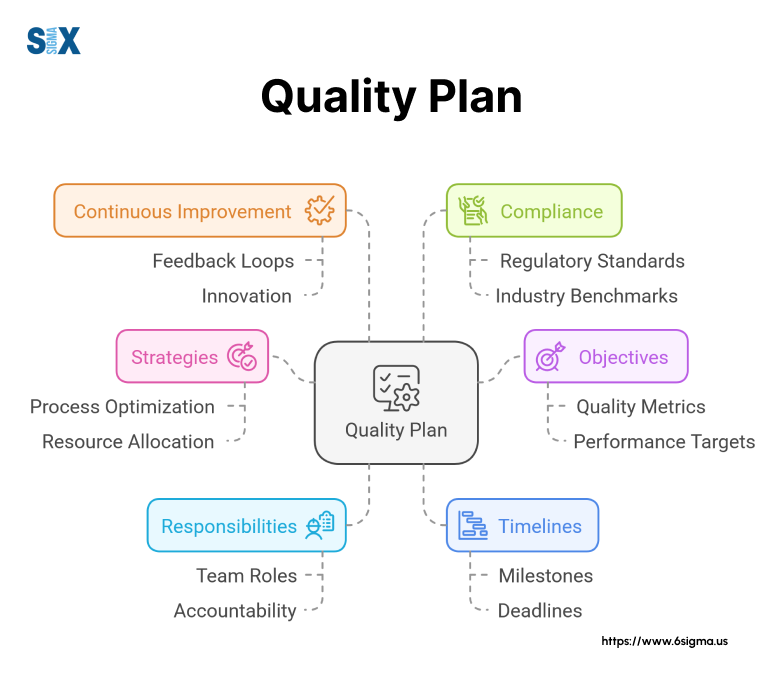
What are Quality Plans?
A quality plan functions as a roadmap that guides organizations through their quality management journey.
This document outlines specific standards, practices, and procedures required to meet customer expectations and industry requirements.
Quality plans help businesses maintain consistency while delivering products or services that align with predetermined specifications.
The Strategic Value Of Quality Plans
Quality plans drive operational excellence by establishing clear guidelines for quality control and assurance.
They enable organizations to detect and prevent defects early in the production cycle, reducing costly rework and customer complaints.
These plans also support regulatory compliance and help businesses maintain their industry certifications.
Manufacturing companies use quality plans to ensure product consistency across production batches.
Essential Components Of An Effective Quality Plan
The structure of a quality plan includes several key elements. Quality objectives define measurable targets for product or service delivery.
Resource allocation sections detail the required personnel, equipment, and materials.
Testing protocols specify inspection methods and acceptance criteria. Documentation requirements ensure proper record-keeping throughout the process.
Standard operating procedures form another crucial component, describing step-by-step processes for various quality-related activities.
These procedures help maintain consistency across different teams and locations while facilitating training for new staff members.
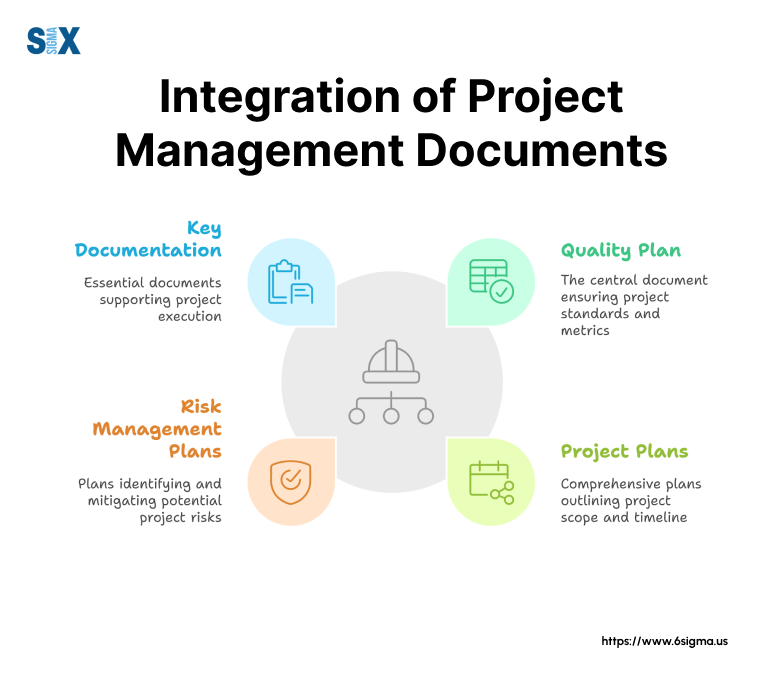
Quality Plans Versus Other Project Documentation
Quality plans differ from other project documents in their specific focus on quality aspects.
While project plans outline overall timelines and deliverables, quality plans concentrate on standards and verification methods.
Similarly, risk management plans address potential issues, but quality plans detail prevention and control measures specifically related to product or service quality.
The integration of digital tools has transformed how organizations develop and implement quality plans. Modern quality management software enables real-time monitoring, automated documentation, and data-driven decision-making.
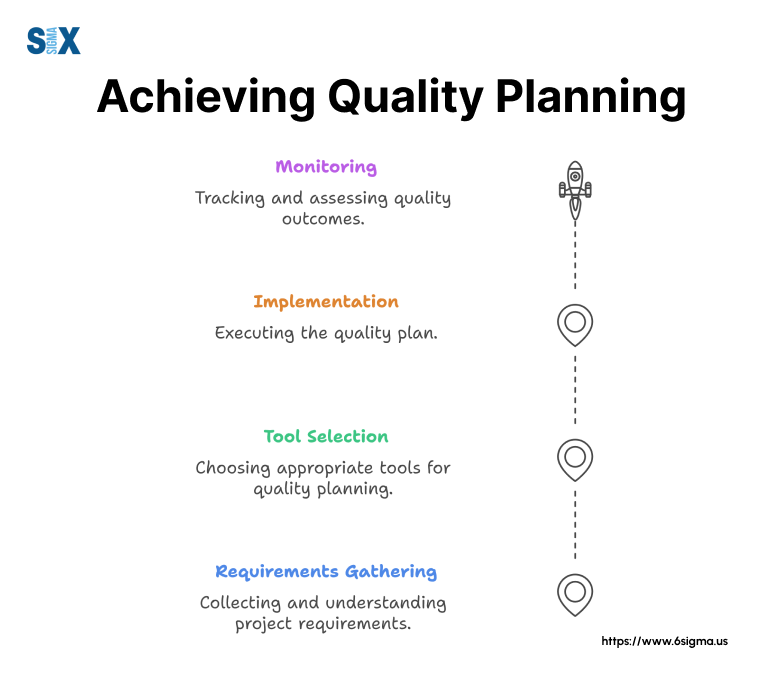
The Quality Planning Process: Building A Strong Foundation
A quality planning process establishes the framework for achieving quality objectives throughout a project’s lifecycle.
This systematic approach ensures that organizations meet customer requirements while maintaining efficiency in their operations.
Quality planning helps teams identify potential issues before they impact project outcomes.
Key Steps In The Quality Planning Process
The first step involves identifying customer requirements and quality standards. Project teams must gather input from stakeholders and review industry regulations to establish clear quality benchmarks.
This information forms the basis for developing specific quality metrics and acceptance criteria.
Next comes the development of quality control procedures. These procedures outline inspection methods, testing protocols, and documentation requirements. Teams must also establish clear roles and responsibilities for quality management activities.
Resource allocation follows, determining the tools, personnel, and materials needed to implement quality control measures.
This step includes selecting appropriate quality management software and establishing training programs for team members.
Tools And Techniques For Quality Planning
Modern quality planning relies on various tools to ensure effectiveness. Statistical process control charts help monitor production variations.
Quality management software enables real-time tracking of quality metrics. Cause-and-effect diagrams assist in identifying potential quality issues before they occur.
Digital quality management platforms now integrate with production systems to provide automated monitoring and reporting.
These tools help organizations maintain consistent quality while reducing manual oversight requirements.
Master quality control tools with our Green Belt certification program.
Quality Planning In Different Industries
Manufacturing quality plans focus on product specifications and production processes. They typically include detailed inspection points and measurement criteria for each manufacturing stage.
Service industry quality plans emphasize customer satisfaction metrics and service delivery standards. These plans often incorporate feedback mechanisms and performance monitoring systems.
Construction projects require quality plans that address material specifications, workmanship standards, and safety requirements. These plans must align with building codes and regulatory requirements.
The evolution of quality planning continues as organizations adopt new technologies. Artificial intelligence now assists in predicting quality issues, while automation streamlines quality control processes.
These advancements help organizations maintain high quality standards while improving operational efficiency.
Lean Six Sigma Perspective
The article primarily focuses on the importance and elements of a quality plan, akin to quality management systems that are foundational in Lean Six Sigma. Key principles include:
- Customer Focus: Lean Six Sigma prioritizes understanding and meeting customer needs, directly reflected in the establishment of quality objectives aligned with customer requirements.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: It emphasizes measuring quality outcomes and deploying statistical process control, which are crucial to making informed decisions in the realm of Lean Six Sigma.
- Continuous Improvement: The integration of modern tools and the commitment to refining quality metrics mirrors the Cycle of Continuous Improvement seen in Lean Six Sigma practices.
Application within Six Sigma Projects
Quality planning is employed in all phases of the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) methodologies:
- Define: In this phase, quality plans help articulate clear quality objectives and document customer requirements that define project scope.
- Measure: Quality plans establish metrics and inspection protocols, setting baselines for current performance and targets to strive for.
- Analyze: Tools like cause-and-effect diagrams are integral for identifying potential quality issues, helping teams focus on root causes.
- Improve: Adaptation of quality control procedures assists teams in implementing effective changes based on analyzed data.
- Control: Quality management software maintains real-time monitoring and enables structured documentation of quality performance.
Contribution to Process Improvement Goals
Quality plans are instrumental in reducing variation, eliminating waste, and enhancing overall quality:
- Reducing Variation: Establishing precise quality metrics and control procedures allows teams to minimize inconsistency in product output.
- Eliminating Waste: By preventing defects early in the production cycle, organizations can significantly reduce costly rework and downtime, aligning seamlessly with Lean principles.
- Enhancing Quality: The systematic approach to quality objectives and the preventive focus contributes directly to lowering the Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) and improving overall Sigma levels.
Relationship with Lean Six Sigma Framework
Quality plans are a subset of the broader Lean Six Sigma framework. They interact effectively with tools like:
- Fishbone Diagrams (Cause-and-Effect): Help visualize potential quality issues.
- Control Charts: Monitor ongoing adherence to quality standards.
- 5 Whys Analysis: Assists in root cause determination for quality deviations.
Creating An Effective Quality Plan: A Practical Guide
Quality plan development requires input from multiple stakeholders across an organization.
The quality manager typically leads this process, working closely with project managers, department heads, and technical experts.
Senior management provides strategic direction and resource approval, while operational teams contribute practical insights from daily processes.
Key Roles In Quality Plan Development
The quality assurance team bears primary responsibility for drafting and maintaining the quality plan.
They coordinate with production managers to establish realistic quality targets and control measures.
Quality engineers provide technical specifications and testing protocols, while compliance officers ensure alignment with regulatory requirements.
Project managers play a crucial role by integrating quality requirements into project timelines and budgets.
They work with quality teams to develop monitoring procedures and establish reporting mechanisms that track quality metrics throughout the project lifecycle.
Steps To Write An Effective Quality Plan
Start by defining clear quality objectives aligned with organizational goals. Document specific requirements from customers, regulators, and internal stakeholders.
These requirements form the foundation for developing quality standards and acceptance criteria.
Next, outline the quality control procedures and inspection points. Detail the methods for measuring quality metrics and specify acceptable tolerance ranges. Include procedures for handling non-conforming items and implementing corrective actions.
Establish documentation requirements and reporting structures. Define how quality data will be collected, analyzed, and shared across teams. Specify the frequency of quality reviews and the format for presenting quality metrics to stakeholders.
Quality Standards And Compliance Requirements
ISO 9001 provides the fundamental framework for quality management systems. Industry-specific standards may apply, such as AS9100 for aerospace or ISO 13485 for medical devices.
The quality plan must align with these standards while addressing unique organizational requirements.
Document control procedures ensure that all team members work with current versions of the quality plan. Regular reviews and updates maintain the plan’s relevance as processes evolve and new requirements emerge.
Overcoming Common Quality Planning Challenges
Resource constraints often impact quality plan implementation. Address this by prioritizing critical quality controls and leveraging automated monitoring tools where possible.
Resistance to change requires clear communication of quality benefits and comprehensive training programs.
Data management challenges arise as quality monitoring generates large volumes of information. Modern quality management software helps organize and analyze this data, enabling informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
The digital transformation of quality management continues to evolve. Organizations now integrate artificial intelligence for predictive quality analysis and automation for routine quality checks.
These technological advances help teams maintain consistent quality while improving operational efficiency.
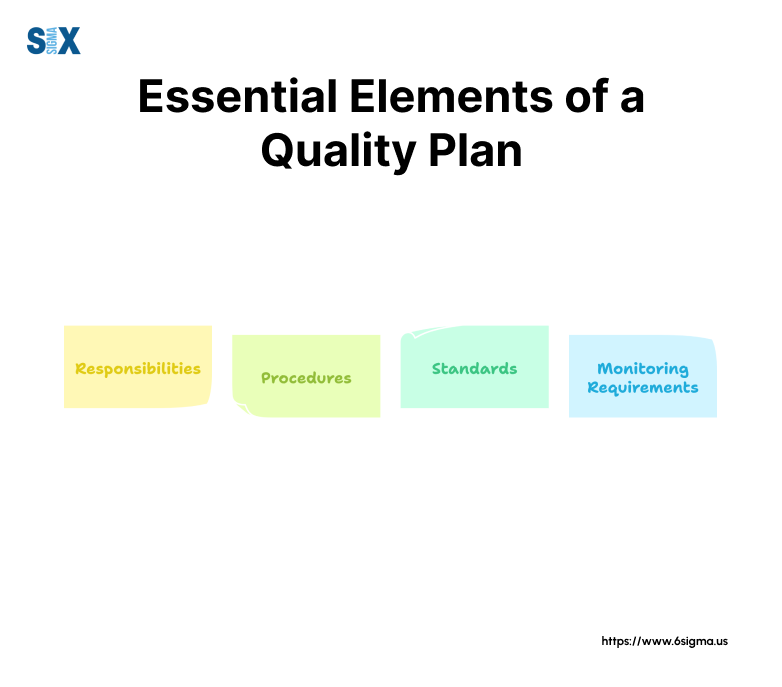
Essential Components That Make Up A Quality Plan
The structure of a quality plan determines its effectiveness in maintaining product and service standards.
Each component serves a specific purpose, working together to create a robust quality management system that drives organizational success.
Quality Objectives And Policy Framework
Quality objectives must align with organizational goals while remaining specific and measurable. These objectives guide daily operations and provide benchmarks for success.
The policy framework outlines the organization’s commitment to quality and establishes guidelines for achieving these objectives.
Performance metrics help track progress toward quality goals. These metrics might include defect rates, customer satisfaction scores, or process efficiency measurements.
Regular review of these metrics ensures the organization stays on track with its quality targets.
Defining Roles And Quality Responsibilities
Clear role definitions prevent confusion and ensure accountability in quality management. Quality teams need specific assignments for monitoring, testing, and reporting activities.
Department managers must understand their quality oversight responsibilities, while front-line workers require clear guidelines for quality-related tasks.
Training requirements for each role should be documented in the quality plan. This includes initial training programs and ongoing professional development needs. Regular skill assessments help maintain team competency levels.
Quality Assurance And Control Mechanisms
Quality assurance procedures focus on preventing defects through systematic monitoring and process improvement. These procedures include regular audits, process reviews, and preventive maintenance schedules.
Control procedures detail inspection points, testing methods, and acceptance criteria.
Documentation requirements ensure proper recording of quality-related activities and results. Non-conformance procedures outline steps for handling and correcting quality issues.
Resource Allocation And Management
Equipment requirements specify the tools and technology needed for quality control activities. Personnel allocations detail staffing needs for quality-related functions.
Budget considerations include costs for testing equipment, training programs, and quality management software.
Communication Strategies And Reporting
The communication plan establishes channels for sharing quality-related information across teams.
Regular reporting schedules keep stakeholders informed of quality performance. Escalation procedures ensure quick response to quality issues when they arise.
Risk Management Integration
Risk assessment procedures help identify potential quality threats. Mitigation strategies outline steps to prevent or minimize quality risks. Contingency plans provide guidance for responding to quality emergencies or failures.
Modern quality plans increasingly incorporate digital tools for monitoring and control.
Automated systems track quality metrics in real-time, while artificial intelligence helps predict potential quality issues before they occur.
These technological advances strengthen traditional quality management approaches while improving efficiency and effectiveness.
Implementing Your Quality Plan: From Paper To Practice
Successful implementation of a quality plan requires careful planning and systematic execution.
The transition from documentation to active quality management demands clear communication, proper resource allocation, and sustained commitment from all organizational levels.
Steps For Effective Quality Plan Implementation
Begin implementation by conducting thorough team training sessions. Each department needs to understand their role in the quality plan and the specific procedures they must follow.
Documentation should be readily accessible, and initial monitoring systems must be in place before full implementation begins.
Phase the implementation process to manage change effectively. Start with pilot areas or smaller departments to identify and resolve potential issues. This approach allows for refinement of procedures before organization-wide rollout.
Team engagement proves crucial during implementation. Regular meetings help address concerns and share early successes.
Support from management demonstrates organizational commitment to quality objectives and encourages staff participation.
Quality Monitoring And Control Methods
Establish baseline measurements before implementation to track improvements accurately. Regular data collection and analysis help identify trends and potential issues early.
Quality metrics should align with organizational goals while providing actionable insights for process improvement.
Digital monitoring tools streamline data collection and analysis. Modern quality management software provides real-time tracking capabilities and automated alerts for quality issues.
These systems help maintain consistent oversight while reducing manual monitoring requirements.
Driving Continuous Quality Improvement
Regular assessment of quality metrics reveals opportunities for improvement. Process optimization should focus on areas showing consistent quality challenges or inefficiencies.
Employee feedback often provides valuable insights for practical improvements.
Quality improvement initiatives should follow structured methodologies. Six Sigma and Lean principles offer proven frameworks for process optimization. These approaches help teams identify root causes and implement effective solutions.
Technology integration supports improvement efforts through advanced analytics and automation. Artificial intelligence helps predict quality issues before they occur. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns that might escape human observation.
Success measurement requires both quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Hard metrics track specific quality parameters, while feedback from staff and customers provides context for improvement efforts. Regular reporting keeps stakeholders informed of progress and challenges.
Digital Tools That Transform Quality Planning
Modern quality planning relies heavily on digital solutions to streamline processes and improve accuracy.
Quality management software has evolved from simple documentation tools to sophisticated platforms that integrate with enterprise systems and provide real-time monitoring capabilities.
Quality Management Software Essentials
Digital quality planning tools offer centralized document control and version management. These systems maintain quality procedures, work instructions, and compliance records in easily accessible formats. Advanced platforms include workflow automation features that route documents for review and approval.
Mobile capabilities allow quality teams to conduct inspections and record data from anywhere in the facility.
Cloud-based solutions enable remote access to quality documentation and real-time collaboration between team members. These features prove particularly valuable for organizations with multiple locations or remote workers.
The Digital Advantage In Quality Planning
Automated data collection reduces manual entry errors and saves time. Digital systems track quality metrics continuously, providing instant alerts when parameters drift outside acceptable ranges.
This immediate feedback allows quality teams to address issues before they become serious problems.
Analytics capabilities help organizations identify trends and patterns in quality data. Predictive algorithms forecast potential quality issues based on historical information.
These insights enable proactive quality management rather than reactive problem-solving.
Integration with production systems provides end-to-end visibility of quality parameters. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) connectivity ensures quality data flows seamlessly between departments.
This integration supports better decision-making across the organization.
Leading Quality Management Platforms
Enterprise-level quality management systems offer modules for document control, training management, audit planning, and corrective action tracking. These platforms typically include reporting tools that generate customized quality metrics dashboards.
Mid-range solutions focus on core quality planning functions while maintaining user-friendly interfaces. These systems suit organizations transitioning from paper-based systems to digital quality management.
Industry-specific tools address unique quality requirements in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and food production. These specialized platforms include features tailored to specific regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Artificial intelligence enhances quality planning software capabilities. Machine learning algorithms analyze quality data to identify improvement opportunities.
Natural language processing helps extract insights from customer feedback and quality reports.
Transform your quality management career
With Green Belt certification become an internationally-recognized Lean Six Sigma professional.

Moving Forward With Quality Planning Excellence
Quality plans serve as the backbone of successful quality management systems across industries.
The evolution of quality planning from paper-based documentation to digital systems demonstrates its crucial role in modern business operations.
Organizations that master quality planning position themselves for sustained success in increasingly competitive markets.
Key Elements Of Successful Quality Planning
Effective quality plans begin with clear objectives and measurable goals. The integration of proper documentation, monitoring systems, and control procedures ensures consistent quality delivery.
Regular reviews and updates keep quality plans aligned with changing business needs and industry requirements.
Digital transformation continues to reshape quality planning practices. Advanced software solutions, artificial intelligence, and automation tools enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of quality management efforts.
These technological advances enable more precise monitoring and faster response to quality issues.
Adapting Quality Plans For Organizational Success
Each organization requires a tailored approach to quality planning. Manufacturing facilities need robust inspection protocols and statistical process control.
Service organizations focus on customer satisfaction metrics and service delivery standards. Healthcare providers emphasize patient safety and regulatory compliance.
The success of quality planning initiatives depends on strong leadership commitment and employee engagement.
Regular training programs ensure teams understand and follow quality procedures. Clear communication channels support the sharing of quality-related information across departments.
The Future Of Quality Planning
Industry 4.0 technologies will further transform quality planning practices. Internet of Things devices will provide more detailed quality data.
Artificial intelligence will enhance predictive capabilities for quality issues. These advances will help organizations maintain higher quality standards while improving operational efficiency.
Sustainability considerations increasingly influence quality planning decisions. Organizations must balance traditional quality metrics with environmental impact and resource efficiency.
This evolution reflects growing awareness of corporate responsibility and stakeholder expectations.
Quality planning remains essential for organizations seeking operational excellence. The investment in proper quality planning tools and processes yields returns through improved product quality, reduced waste, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
As business environments evolve, quality plans must adapt while maintaining their fundamental role in ensuring consistent quality delivery.
The path to quality excellence requires commitment, resources, and continuous improvement. Organizations that embrace modern quality planning approaches position themselves for success in an increasingly complex business environment.
Through proper implementation and ongoing refinement, quality plans will continue to drive organizational success and customer satisfaction.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






