Agile Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide to Revolutionizing Production
Agile manufacturing turns traditional manufacturing operations into dynamic, customer-centric systems capable of keeping pace with rapidly changing market demands. It enables organizations to evolve rapidly while maintaining costs and quality.
This article will equip you with:
- Fundamental principles
- Implementation strategies
- Practical applications of agile manufacturing
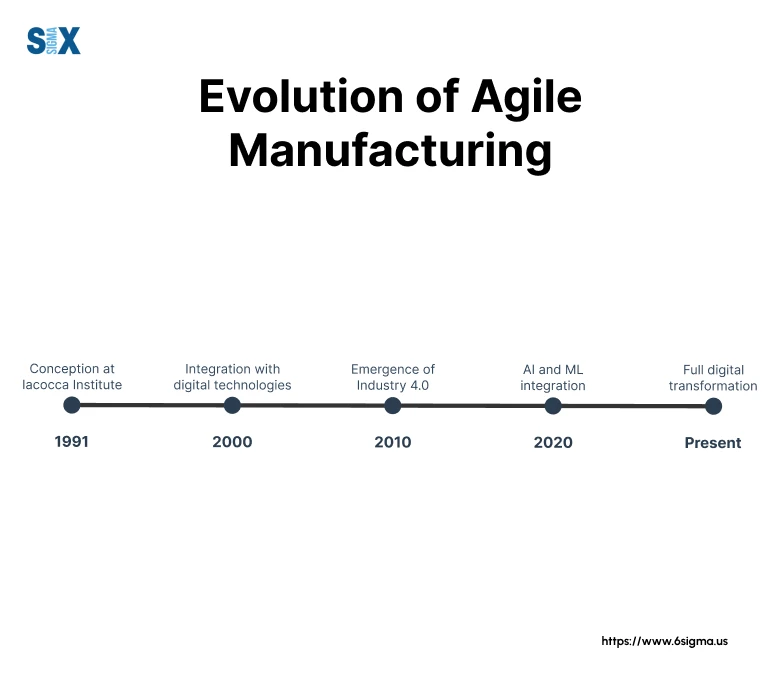
The evolution of agile manufacturing has been remarkable. When I began implementing these systems, we focused primarily on physical process flexibility.
The Four Key Elements of Agile Manufacturing
Success depends on four fundamental elements. These core components work together to create truly responsive manufacturing operations.
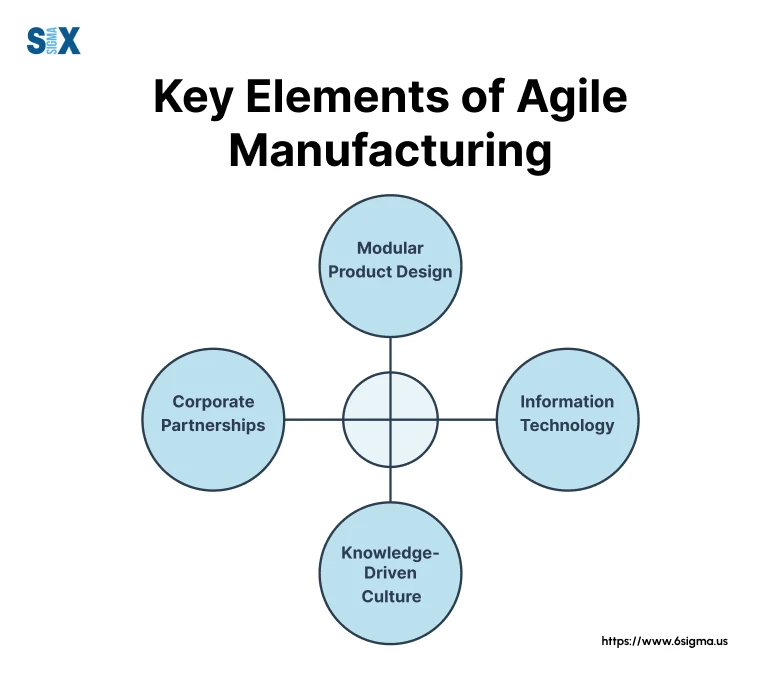
- The first pillar, modular product design, forms the foundation of agile manufacturing. Modular design enables rapid reconfiguration to meet changing market demands. This approach involves creating standardized, interchangeable components that can be quickly adapted while maintaining quality standards.
- Information technology serves as the second critical element, acting as the nervous system of agile manufacturing. An integrated IT infrastructure can connect every aspect of the manufacturing process. Modern agile manufacturing uses real-time data flow and analysis, with IoT sensors, cloud-based manufacturing execution systems, and AI-driven predictive maintenance.
- The third element, corporate partnerships, extends an organization’s agile capabilities. Use a network of strategic partnerships that enable rapid scaling without significant capital investment. These collaborative relationships with suppliers, technology providers, and even competitors create what I call “ecosystem agility” – the ability to leverage external resources for enhanced responsiveness.
- Finally, a knowledge-driven culture forms the fourth essential element. Fostering continuous learning consistently outperforms their peers in agile manufacturing implementation. This culture of knowledge-sharing and adaptation enables rapid problem-solving and innovation, creating a foundation for sustained agility.
These four elements of agile manufacturing work synergistically, creating a framework that enables organizations to respond swiftly to market changes while maintaining operational excellence.
Master the Voice of Customer and Risk Management in Your Agile Manufacturing Journey!
Our DFSS Green Belt course equips you with essential tools for customer-centric design and process optimization. Join industry leaders who’ve achieved 40%+ improvements in first-pass yield!
Agile Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing: A Paradigm Shift
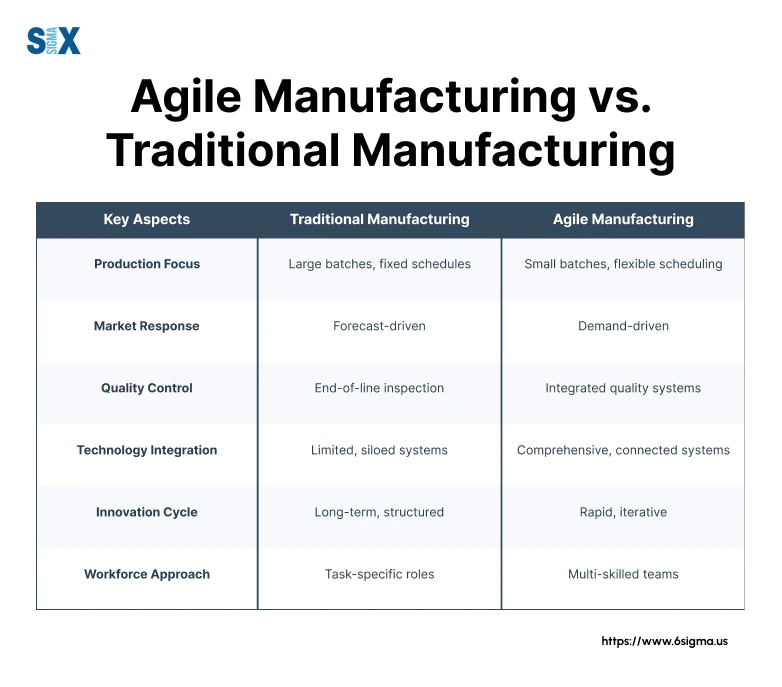
The fundamental difference lies in how these approaches respond to market dynamics. Traditional manufacturing focuses on maximizing efficiency through large production runs and standardized processes. In contrast, agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and rapid response to changing customer demands.
I’ve observed that agile systems offer several distinct advantages. The ability to quickly reconfigure production lines and adjust output based on real-time demand has become increasingly crucial in today’s volatile market conditions.
However, the transition to agile manufacturing isn’t without challenges. There are several common obstacles that most organizations face. The most significant is often cultural resistance to change.
You can overcome this by implementing a comprehensive change management program that includes extensive training and clear communication of benefits. Technical challenges, such as legacy system integration and process standardization, also require careful consideration and strategic planning.
The key to a successful transition lies in what I call the “agile mindset shift”. This involves moving from a production-centric to a customer-centric approach, where flexibility and responsiveness become core operational values.
Implementing Agile Manufacturing
Successful implementation begins with a thorough assessment of organizational readiness. Use a comprehensive framework for evaluating and implementing agile manufacturing systems.
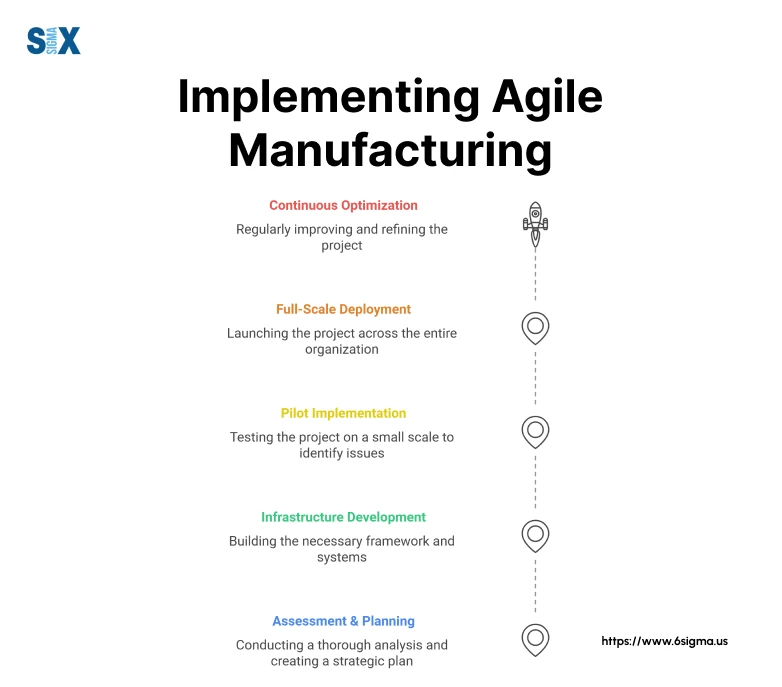
The first critical step in implementing agile manufacturing is assessing your organization’s current state. Use a readiness assessment matrix that evaluates five key areas:
- Technological infrastructure
- Workforce capabilities
- Process flexibility
- Supply chain integration
- Organizational culture
This assessment typically reveals gaps that need addressing before full implementation can begin.
A phased implementation approach yields the best results. Begin with a pilot program in a single production line. This will allow you to refine your agile methodology in manufacturing while minimizing risk.
Common challenges often emerge during implementation. Technical integration challenges can be addressed through careful system architecture planning. Resistance to change, perhaps the most significant hurdle, requires a comprehensive change management strategy.
One particularly successful case study comes from my work with a global automotive parts manufacturer. By implementing an agile manufacturing strategy focused on modular production cells and real-time data analytics, they achieved:
- 60% reduction in changeover times
- 40% improvement in first-pass yield
- 35% decrease in inventory carrying costs
The key to successful implementation lies in what I call the “adaptive deployment model”. This approach allows organizations to adjust their implementation strategy based on continuous feedback and learning.
You can refine this model further to include regular assessment checkpoints and adjustment periods, ensuring that the transition to agile manufacturing is aligned with both operational capabilities and business objectives.
Struggling with Recurring Issues in Your Agile Manufacturing Implementation?
Our Root Cause Analysis training will help you identify and eliminate the underlying causes of production problems. Learn structured problem-solving techniques with expert coaching support.
Agile Manufacturing in Different Industries: Applications and Success Stories
Through my extensive experience implementing agile manufacturing systems across diverse sectors, I’ve witnessed how this methodology adapts to different industry requirements. Let me share some compelling examples from my work with leading organizations across multiple sectors.
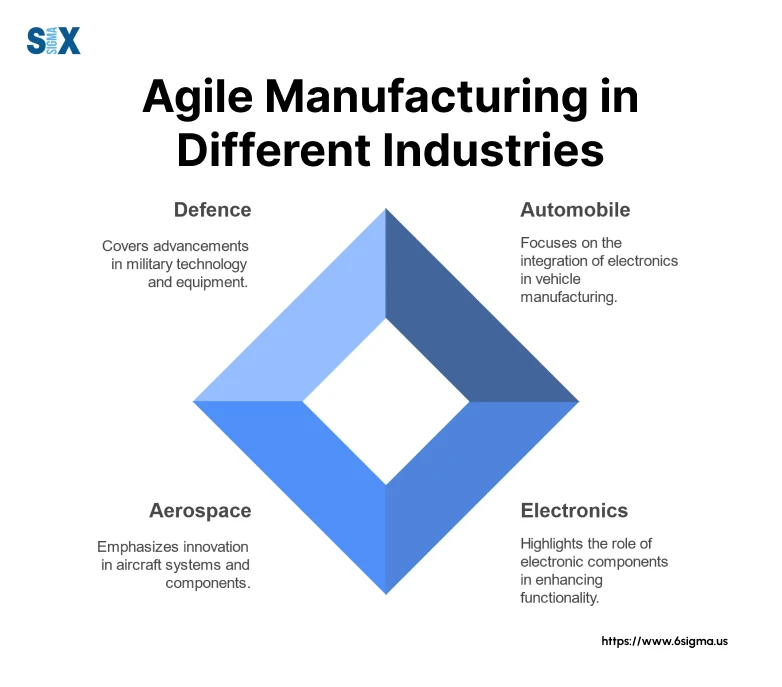
Automobile
In the automotive industry, a major components manufacturer implemented agile manufacturing systems that revolutionized their production approach.
By introducing flexible assembly lines and real-time inventory management, they achieved a 50% reduction in lead times while maintaining superior quality standards.
The key success factor was integrating modular production cells that could quickly switch between different product variants based on real-time demand signals.
Electronics
The electronics sector presents some of the most dramatic examples of successful agile manufacturing implementation.
A technology hardware and software company developed a responsive production system that could adjust output within hours rather than weeks.
This agile approach enabled the company to reduce inventory costs by 40% while improving customer satisfaction scores by 35%. The system’s success relied heavily on advanced data analytics and flexible workforce deployment strategies.
Aerospace and Defence
In the aerospace and defense sector, agile manufacturing takes on a unique character due to stringent quality requirements.
A military equipment manufacturer implemented an agile system that balanced flexibility with strict compliance needs.
The result was a 30% improvement in production efficiency without compromising regulatory requirements.
Manufacturing
Perhaps most interesting is a small business adaptation I’ve helped develop. Working with a custom furniture manufacturer, we scaled down traditional agile manufacturing principles to create what I call a “micro-agile” system.
This approach enabled them to compete effectively with larger manufacturers by offering customized products with delivery times that matched mass-produced alternatives.
Technology Integration in Agile Manufacturing
I’ve witnessed a dramatic evolution in the role of technology. Industry 4.0 technologies have become fundamental enablers of manufacturing agility, rather than mere support tools.
Industry 4.0 has revolutionized agile manufacturing by creating a “digital thread” – a seamless connection between design, production, and delivery. The key is to establish a cohesive ecosystem where different technologies work in concert to enable true agility.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced analytics have transformed how we approach agile production. You can use a network of smart sensors that provide real-time production data, enabling immediate response to quality variations and demand changes. This system, combined with predictive analytics, can help reduce downtime while improving product quality metrics across all production lines.
Automation and robotics play a crucial role in modern agile manufacturing systems. The goal shouldn’t be to replace human workers but to create “collaborative agility”. You can implement flexible robotics systems that can be quickly reprogrammed to handle different products, working alongside human operators who focus on more complex, decision-making tasks.
Perhaps the most exciting development is digital twin technology. With this, you can create virtual replicas of production lines that enable you to simulate and optimize processes before implementing changes in the physical world. This approach will reduce implementation risks and accelerate the deployment of new agile manufacturing processes.
Build the Foundation For Your Agile Manufacturing Transformation
Start with our Lean Fundamentals course – the essential step towards mastering agile principles. Learn how to reduce waste, optimize processes, and create the flexible, responsive systems your organization needs. Required prerequisite for Lean Master certification!
Measuring Success in Agile Manufacturing: Quantifying the Impact of Agility
An effective measurement combines traditional metrics with agile-specific indicators to provide a complete picture of performance improvements.
The key to measuring agile manufacturing success lies in the “Agile Performance Triangle” – flexibility, speed, and quality. You can implement a balanced scorecard approach that tracks these three dimensions through specific KPIs. This approach can help you achieve improvement in production flexibility while maintaining Six Sigma quality levels.
When calculating ROI for agile manufacturing initiatives, use a framework that considers both tangible and intangible benefits. Quantify not only direct cost savings but also the value of increased market responsiveness.
Continuous improvement in agile manufacturing requires “dynamic measurement” – metrics that evolve with your operational maturity. You can implement a tiered measurement system that begins with basic agility metrics and progressively incorporates more sophisticated indicators as the organization’s capabilities grow. This approach will ensure that your measurement system supports rather than hinders agile development.
Successful measurement systems typically track:
- Cycle time reduction
- Setup time optimization
- Customer responsiveness
- Quality metrics
- Resource utilization
The key is to integrate these measurements into daily operations without creating bureaucratic overhead that could impede agility.
Future Trends in Agile Manufacturing: The Next Evolution
The convergence of new technologies and recent global challenges has accelerated innovation in barely imaginable ways.
Post-pandemic Adaptations
Post-pandemic adaptations have fundamentally reshaped agile project management in manufacturing. Organizations have implemented “resilient agility” – systems that combine the flexibility of agile manufacturing with robust risk mitigation strategies.
These adaptations typically include distributed production networks and enhanced digital capabilities that enable remote operations management, which reduces operational vulnerabilities.
Sustainability
Sustainability has emerged as a critical driver of agile manufacturing evolution. Integrate environmental metrics into our agile framework, creating “sustainable agility”.
This approach has delivered impressive results: a 40% reduction in energy consumption while maintaining the responsiveness that characterizes agile systems.
The history of agile manufacturing shows steady progress, but this sustainability integration represents a quantum leap forward.
AI & ML
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing how we approach agile manufacturing. You can implement AI-driven decision-making systems that can anticipate market changes and automatically adjust production parameters.
This predictive capability reduced response times compared to traditional agile systems while improving accuracy in demand forecasting.
Conclusion: Embracing Agile Manufacturing for Competitive Advantage
Agile manufacturing is more than just a process change, it’s how modern organizations take on production and market responsiveness. In the coming times, it’ll become increasingly critical for business success.
Start with a thorough assessment of your current operations, identify opportunities for implementing agile principles, and develop a roadmap for transformation. The future belongs to organizations that can respond quickly and effectively to market changes – and agile manufacturing provides the framework to achieve this goal.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






