Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP): Essential Guide
Delivering quality products and every expectations of customers is pathway towards the manufacturing success.
Organizations can accomplish their goals through a systematic planning and execution and a structured methodology called Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP).
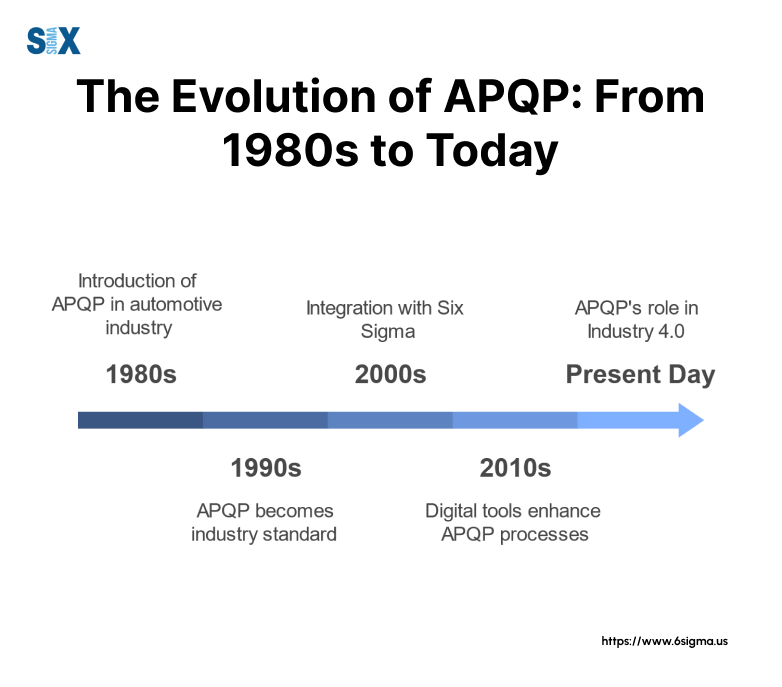
In the late 1980s when major manufacturers like Ford, General Motors, and Chrysler developed standardized quality planning processes, APQP was surfaced from the industry.
Key Highlights
- Strategic quality planning methods for manufacturing
- Systematic approach to product development
- Risk identification and mitigation strategies
- Cross-functional team collaboration techniques
What is Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)?
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) represents a structured method for product development and quality management in manufacturing.
This methodology ensures products meet customer requirements through systematic planning, risk assessment, and validation processes.
The framework establishes clear guidelines for developing products from concept to production.
Manufacturing teams use APQP to define quality standards, identify potential risks, and implement control measures before production begins.
This proactive approach reduces costly modifications during later stages of development.
APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) Meaning and Significance
APQP serves as the bridge between customer requirements and final product delivery. The significance lies in its ability to prevent quality issues rather than detecting them after production.
This methodology reduces development time, minimizes costs, and ensures consistent quality across production runs.
Manufacturing organizations implement APQP to:
- Streamline communication between departments
- Reduce product development cycles
- Minimize design changes during production
- Ensure regulatory compliance
- Improve first-time quality rates
Key Elements of APQP
The success of APQP depends on several crucial elements working together.
These elements include cross-functional team collaboration, risk assessment tools, control plans, and measurement systems analysis.
Quality planning tools form an essential part of APQP implementation. Design and Process Failure Mode Effects Analysis (DFMEA/PFMEA) help identify potential risks.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) monitors production stability, while Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) validates manufacturing processes.
Who Is Responsible for APQP?
APQP requires involvement from multiple departments within an organization. The quality management team typically leads the initiative, but success depends on active participation from:
- Design Engineers: Responsible for product specifications and design validation
- Manufacturing Engineers: Develop production processes and control plans
- Quality Engineers: Oversee quality planning and validation activities
- Production Teams: Implement control plans and maintain quality standards
- Suppliers: Ensure component quality and adherence to specifications
Industries That Use Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
While APQP originated in automotive manufacturing, its principles now extend across various industries.
The automotive sector remains the primary user, with major manufacturers requiring APQP compliance from their suppliers.
Other industries adopting APQP include:
- Aerospace manufacturers focusing on safety-critical components
- Medical device companies ensuring regulatory compliance
- Electronics manufacturers maintaining quality in complex assemblies
- Defense contractors meeting strict quality requirements
The methodology adapts to specific industry needs while maintaining its core focus on quality planning and risk prevention.
Organizations modify APQP elements based on their product complexity, regulatory requirements, and customer specifications.
Manufacturing leaders recognize APQP as an essential tool for maintaining competitive advantage in global markets.
The methodology continues to evolve with digital transformation, incorporating new technologies for more efficient quality planning and control.
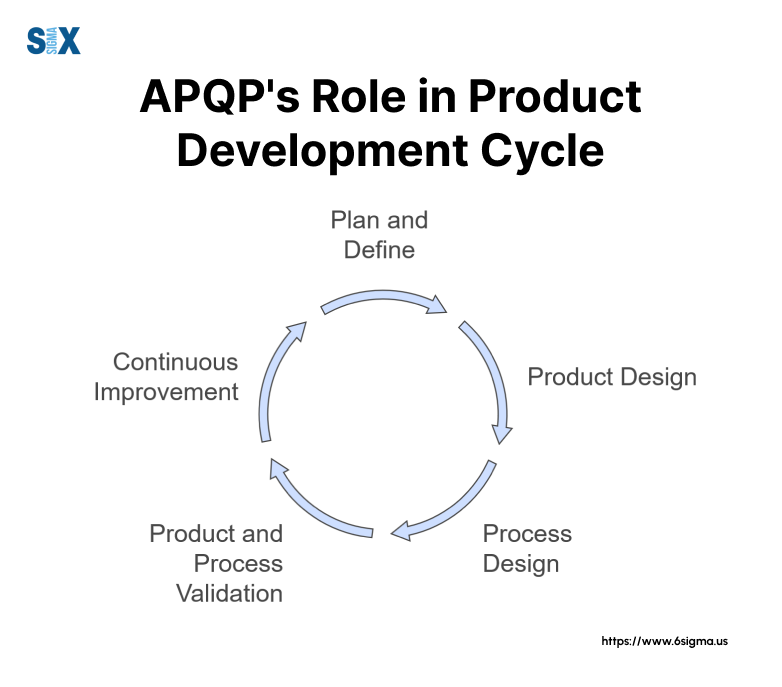
The 5 Phases of Advanced Product Quality Planning
The APQP process follows five distinct phases, each building upon the previous to ensure product quality from conception to production. These phases create a systematic approach to quality planning and validation.
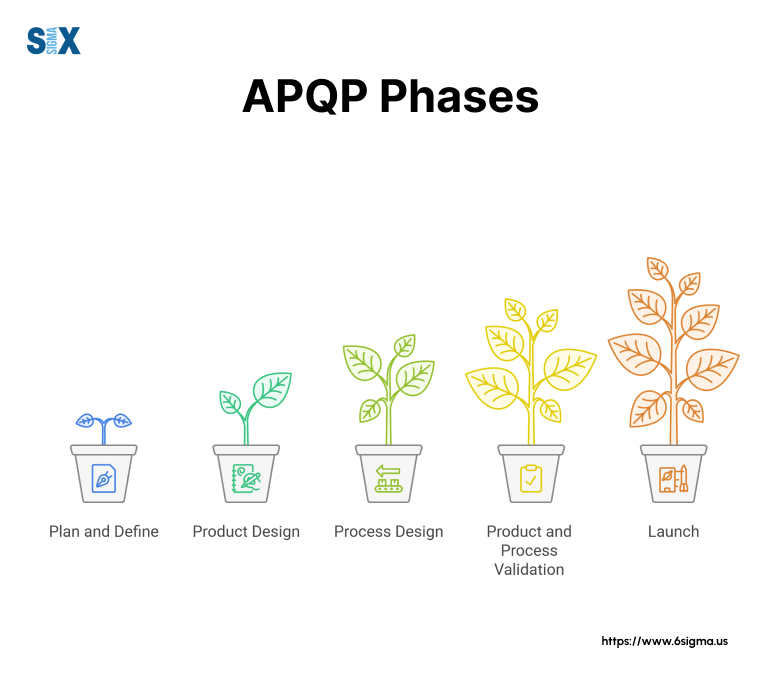
Phase 1: Planning and Defining the Program
The initial phase establishes the foundation for successful product development. Teams focus on understanding customer needs and translating them into specific requirements.
This phase includes defining quality goals, identifying preliminary special characteristics, and creating a preliminary bill of materials.
Key activities in Phase 1 include:
- Voice of customer analysis
- Design goals establishment
- Reliability targets definition
- Preliminary process flow development
- Special characteristics identification
The output of this phase guides all subsequent development activities and ensures alignment with customer expectations.
Phase 2: Product Design and Development
During the second phase, engineering teams transform customer requirements into detailed product specifications.
Design verification plays a crucial role in ensuring the product meets all functional and quality requirements.
- This phase encompasses:
- Design FMEA development
- Prototype build planning
- Engineering drawings creation
- Material specifications development
- Design verification testing
Teams must complete design reviews and obtain necessary approvals before moving to the next phase.
Phase 3: Process Design and Development
The third phase focuses on creating manufacturing processes that consistently produce quality products.
Manufacturing engineers develop detailed process flows, control plans, and work instructions.
- Essential elements include:
- Process flow diagrams
- Process FMEA creation
- Measurement systems planning
- Pre-launch control plans
- Operator instructions development
This phase establishes the manufacturing system’s capability to produce products meeting design specifications.
Phase 4: Product and Process Validation
Validation activities confirm that both the product design and manufacturing process meet requirements.
Teams conduct production trials and evaluate results against established criteria.
- Major validation activities include:
- Production trial runs
- Measurement system evaluation
- Process capability studies
- Production part approval
- Packaging evaluation
Successful completion of this phase indicates readiness for full-scale production.
Phase 5: Feedback, Assessment, and Corrective Action
The final phase focuses on continuous improvement through regular assessment and corrective actions.
Teams monitor production data, customer feedback, and quality metrics to identify improvement opportunities.
- Regular activities include:
- Production monitoring
- Customer satisfaction evaluation
- Quality data analysis
- Process improvement implementation
- Lessons learned documentation
This phase ensures ongoing product quality and process optimization throughout the product lifecycle.
Integration Across Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) Phases
Success in the APQP process requires seamless integration between phases. Each phase builds upon previous work while preparing for subsequent activities.
Quality teams must maintain clear documentation and communication throughout the process.
Manufacturing organizations often use specialized software tools to manage APQP phases.
These tools help track deliverables, maintain documentation, and facilitate communication between team members.
Regular phase reviews ensure teams meet all requirements before proceeding.
These gateway reviews prevent quality issues from propagating through the development cycle and help maintain project timelines.
The APQP phases provide a structured approach to product quality planning.
When properly executed, this methodology reduces development time, minimizes costly changes, and ensures consistent product quality.
Implementing Advanced Product Quality Planning
Successful APQP implementation requires careful planning, dedicated resources, and strong organizational commitment.
Manufacturing organizations must establish clear processes and responsibilities to ensure effective execution.
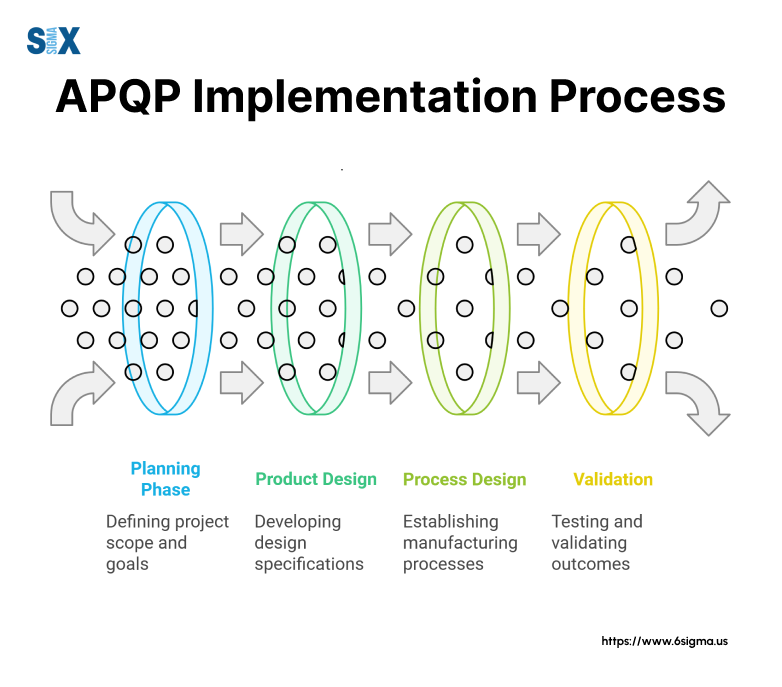
How to Perform Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
The implementation process begins with establishing a dedicated project team and defining clear objectives.
Organizations should start by assessing their current quality planning processes and identifying gaps that need addressing.
Key implementation steps include:
- Selecting team members and defining roles
- Setting project timelines and milestones
- Establishing communication protocols
- Creating documentation standards
- Defining review and approval processes
Manufacturing leaders must ensure adequate resources and training for team members before beginning implementation.
APQP Checklist and Key Business Deliverables
The APQP checklist serves as a roadmap for implementation, ensuring teams complete all necessary activities. This checklist typically includes:
Design Requirements:
- Engineering drawings and specifications
- Design FMEA completion
- Design verification results
- Material specifications
Process Requirements:
- Process flow diagrams
- Process FMEA documentation
- Control plan development
- Work instruction creation
Validation Requirements:
- Measurement system analysis
- Process capability studies
- Production trial results
- PPAP submission package
Cross-Functional Team Involvement
APQP success depends heavily on effective cross-functional collaboration. Teams must include representatives from:
Engineering teams develop product specifications and validate designs. Quality teams oversee planning and verification activities.
Production teams provide manufacturing expertise and implement controls. Purchasing teams manage supplier relationships and component quality.
Regular team meetings ensure alignment and timely issue resolution. Teams should establish clear decision-making processes and escalation procedures for addressing challenges.
APQP Techniques and Tools
Organizations employ various tools throughout the APQP process:
Quality Planning Tools:
- Design and Process FMEA
- Control Plan Methodology
- Statistical Process Control
- Measurement Systems Analysis
Project Management Tools:
- Timeline tracking software
- Documentation management systems
- Communication platforms
- Risk assessment matrices
Common Challenges and Solutions for Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
Organizations often face several challenges during APQP implementation:
Resource Constraints:
Solution: Prioritize projects and allocate resources based on risk and impact. Consider using external expertise for specialized needs.
Communication Barriers:
Solution: Implement structured communication protocols and utilize digital collaboration tools. Schedule regular status meetings and updates.
Documentation Management:
Solution: Deploy electronic document management systems. Establish clear naming conventions and version control procedures.
Resistance to Change:
Solution: Provide adequate training and demonstrate benefits through pilot projects. Celebrate early successes and share positive results.
Timeline Pressure:
Solution: Develop realistic schedules that account for potential delays. Build contingency time into project plans for unexpected issues.
Best Practices for Implementation Success
Several best practices help ensure successful APQP implementation:
Start with pilot projects to build experience and demonstrate value. Establish clear metrics to measure implementation progress.
Provide ongoing training and support for team members. Document lessons learned and update procedures accordingly. Maintain regular communication with stakeholders.
Organizations should also consider:
- Regular audits of APQP processes
- Feedback collection from team members
- Continuous improvement initiatives
- Recognition of team achievements
- Updates to procedures based on lessons learned
The implementation process requires patience and persistence.
Manufacturing leaders must maintain focus on long-term quality improvements while addressing short-term challenges.
Transform your quality management approach with advanced APQP leadership training.
Benefits of Advanced Product Quality Planning
Organizations implementing APQP gain significant advantages in product development, manufacturing efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
These benefits directly impact business performance and market competitiveness.
Improved Product Quality
APQP drives superior product quality through structured planning and validation processes.
Manufacturing organizations report significant reductions in defect rates and warranty claims after implementation.
The systematic approach to quality planning helps identify and address potential issues before they affect production.
Quality improvements manifest through:
- Reduced defect rates in production
- Fewer field failures and warranty claims
- More consistent product performance
- Better conformance to specifications
- Enhanced product reliability
Reduced Development Time and Costs
Early problem identification through APQP significantly reduces development cycles and associated costs. Organizations typically see decreased expenses related to:
- Design Changes: Early validation reduces costly late-stage modifications
- Scrap and Rework: Improved processes minimize waste and repairs
- Testing: Structured validation reduces repeated testing needs
- Launch Delays: Better planning prevents production startup issues
The financial impact extends beyond direct costs, including improved resource utilization and faster time-to-market for new products.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction with Advanced Product Quality Planning
APQP focuses on translating customer requirements into product specifications, leading to higher satisfaction levels. Organizations experience:
- Increased customer retention rates
- Higher product satisfaction scores
- Fewer customer complaints
- Stronger brand reputation
- Expanded business opportunities
The structured approach ensures customer needs remain central throughout development and production phases.
Better Risk Management
Risk identification and mitigation form key components of the APQP process. Organizations benefit from:
- Systematic risk assessment methods
- Proactive issue identification
- Documented mitigation strategies
- Clear contingency planning
- Reduced quality-related risks
These elements create a more stable and predictable manufacturing environment, reducing unexpected disruptions and quality issues.
Improved Communication Across Teams
APQP establishes clear communication channels between different functional groups.
This improved communication results in:
- Faster decision-making processes
- Better alignment between departments
- Reduced misunderstandings
- More efficient problem-solving
- Enhanced knowledge sharing
Cross-functional collaboration becomes more effective as teams work within the structured APQP framework.
Measurable Business Impact
Organizations implementing APQP often report quantifiable improvements in key performance indicators:
Quality Metrics:
- 50-70% reduction in defect rates
- 30-40% decrease in warranty claims
- 25-35% improvement in first-time quality
Financial Benefits:
- 20-30% reduction in development costs
- 15-25% decrease in launch expenses
- 40-50% fewer costly late-stage changes
Operational Improvements:
- 30-40% shorter development cycles
- 25-35% faster problem resolution
- 45-55% reduction in quality-related delays
Long-Term Strategic Benefits with Advanced Product Quality Planning
Beyond immediate operational improvements, APQP delivers strategic advantages:
Market Position:
Organizations strengthen their competitive position through improved quality and reliability. The structured approach to quality planning becomes a differentiator in the marketplace.
Supplier Relations:
APQP implementation improves supplier management and collaboration. Clear requirements and expectations lead to stronger supplier partnerships.
Organizational Culture:
The methodology fosters a quality-focused culture throughout the organization. Teams develop stronger problem-solving capabilities and quality awareness.
These benefits compound over time as organizations refine their APQP processes and build upon successful implementations.
Manufacturing leaders should monitor and document these improvements to demonstrate the value of their APQP investment.
APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) and Other Quality Management Tools
Advanced Product Quality Planning works in conjunction with several other quality management tools to create a robust quality assurance system. These tools complement each other, enhancing the overall effectiveness of quality management efforts.
Relationship Between APQP and PPAP
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) serves as a critical validation step within the APQP framework.
While APQP provides the planning structure, PPAP delivers the evidence that planning efforts have succeeded.
PPAP documentation requirements include:
- Design records and engineering changes
- Process flow diagrams
- Control plans
- Measurement system analysis results
- Initial process capability studies
Manufacturing organizations must complete PPAP requirements before moving into full production. This ensures all quality planning elements translate into actual production capability.
APQP and FMEA Integration
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) represents a crucial risk assessment tool within the APQP process.
Design FMEA examines potential product failures, while Process FMEA focuses on manufacturing process risks.
FMEA activities occur throughout APQP phases:
- Phase 2: Design FMEA development
- Phase 3: Process FMEA creation
- Phase 4: FMEA validation
- Phase 5: FMEA updates and improvements
The systematic risk assessment approach of FMEA strengthens APQP effectiveness by identifying and addressing potential failures early in development.
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) and Six Sigma
APQP and Six Sigma methodologies share common goals of reducing variation and improving quality.
Six Sigma tools enhance APQP implementation through:
Statistical Analysis:
- Process capability studies
- Measurement system evaluation
- Variation reduction techniques
Problem-Solving Methods:
- Root cause analysis
- Data-driven decision making
- Process optimization
Organizations often integrate Six Sigma methods into their APQP processes to achieve better results.
Advanced Product Quality Planning and Control Plan Development
Control plans represent essential documents within the APQP framework. These plans detail:
Process Controls:
- Methods for monitoring key characteristics
- Measurement frequencies and techniques
- Response plans for out-of-control conditions
Quality Checks:
- Inspection requirements
- Testing procedures
- Documentation needs
The control plan evolves through three stages:
- Prototype control plan
- Pre-launch control plan
- Production control plan
Integration of Quality Tools
Successful quality management requires seamless integration of various tools and methodologies. Organizations should focus on:
Tool Selection:
- Choose appropriate tools based on specific needs
- Ensure tools complement existing processes
- Consider resource requirements
Implementation Strategy:
- Train teams on tool usage
- Establish clear procedures
- Monitor tool effectiveness
Documentation Requirements:
- Maintain required records
- Ensure proper revision control
- Enable easy access to information
Digital Integration Opportunities
Modern quality management software enables better integration between different tools:
Data Management:
- Centralized information storage
- Automated document control
- Real-time data access
Process Automation:
- Workflow management
- Notification systems
- Report generation
These digital solutions improve efficiency and reduce manual effort in managing quality tools.
Manufacturing organizations achieve better results when they understand and leverage the relationships between different quality tools.
The integration of these tools creates a more effective quality management system that drives continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) Applications Across Industries
While Advanced Product Quality Planning originated in automotive manufacturing, its principles now extend across multiple industries.
APQP in Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry continues to lead APQP implementation and development.
Major manufacturers require suppliers to follow standardized APQP processes, ensuring consistent quality throughout the supply chain.
Automotive APQP focuses on:
- Safety-critical components
- High-volume production requirements
- Complex assembly processes
- Supply chain management
- Regulatory compliance
Industry standards like IATF 16949 incorporate APQP requirements, making it essential for automotive suppliers to maintain certification and customer approval.
APQP in Aerospace and Defense
Aerospace manufacturers modify APQP to address industry-specific challenges. The emphasis shifts toward:
Safety Requirements:
- Stringent documentation needs
- Enhanced traceability requirements
- Specialized testing protocols
Defense contractors often integrate APQP with military standards and specifications, creating hybrid quality planning systems that satisfy both commercial and military requirements.
APQP in Medical Device Industry
Medical device manufacturers adapt APQP to meet FDA requirements and ISO 13485 standards. Key modifications include:
The medical device industry emphasizes risk management and regulatory compliance throughout the APQP process.
Adapting Advanced Product Quality Planning for Other Sectors
Organizations in various industries modify APQP to suit their needs:
Electronics Manufacturing:
- Component qualification processes
- ESD control requirements
- Environmental testing
- Reliability verification
Consumer Products:
- Design for manufacturability
- Cost optimization
- Aesthetic requirements
- Market feedback integration
Industrial Equipment:
- Performance validation
- Maintenance considerations
- Installation requirements
- Service documentation
The Future
Advanced Product Quality Planning remains a vital methodology for manufacturing organizations seeking to maintain competitive advantage through superior quality.
The Strategic Value of APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning)
Manufacturing organizations implementing APQP gain significant advantages in today’s competitive market.
The methodology delivers measurable improvements in product quality, development efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
These benefits extend beyond individual projects, creating lasting improvements in organizational capabilities and market position.
The systematic approach to quality planning reduces development costs while improving product reliability
Moving Forward with Implementation
Organizations considering APQP implementation should recognize the methodology’s proven track record across industries.
The initial investment in training, tools, and processes yields substantial returns through improved quality and reduced development costs.
Looking Ahead: APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) Evolution
The future of APQP points toward increased integration with digital technologies and emerging manufacturing trends.
Industry 4.0 technologies offer new possibilities for data collection, analysis, and process control.
These advances will enhance APQP effectiveness while reducing implementation overhead.
Global supply chains demand more sophisticated quality planning approaches.
Organizations must adapt APQP practices to address international manufacturing challenges while maintaining consistent quality standards.
The methodology’s flexibility allows for these adaptations while preserving its fundamental principles.
Sustainability considerations will influence future APQP developments. Manufacturing organizations must integrate environmental and social responsibility into their quality planning processes.
Frequently Asked Questions About Advanced Product Quality Planning
A. Advanced Product Quality Planning represents a structured methodology for product development and manufacturing quality assurance. The process ensures products meet customer requirements through systematic planning, risk assessment, and validation procedures. Manufacturing organizations use APQP to prevent quality issues and optimize production processes.
The APQP process consists of five sequential phases: Planning and Program Definition, Product Design and Development, Process Design and Development, Product and Process Validation, and Launch, Feedback, Assessment, and Corrective Action. Each phase builds upon previous work while preparing for subsequent activities.
A. While APQP provides the framework for quality planning, PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) serves as the validation mechanism. PPAP demonstrates that manufacturing processes can consistently produce parts meeting all engineering requirements. Both elements work together to ensure product quality throughout development and production.
APQP and Six Sigma represent distinct but complementary methodologies. While APQP focuses on product quality planning, Six Sigma emphasizes process improvement and variation reduction. Organizations often integrate Six Sigma tools within their APQP processes to enhance quality outcomes.
A. Quality planning encompasses three primary areas: Product Quality Planning, focusing on design and specifications; Process Quality Planning, addressing manufacturing methods and controls; and Quality System Planning, covering organizational procedures and documentation requirements.
A. The APQP checklist guides teams through required activities and deliverables for each phase. This document includes design requirements, process specifications, validation criteria, and control plan elements. Teams use the checklist to track progress and ensure completion of all necessary tasks.
A. APQP requires involvement from cross-functional teams including quality engineers, design engineers, manufacturing engineers, and production personnel. Quality managers typically lead APQP initiatives, but success depends on active participation from all stakeholders.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs








