What is Process Modeling? Definition, Techniques, Benefits, and More
Process modeling offers a potent optimization technique when integrated with six sigma certification that lets firms visualize, review, and streamline techniques.
It involves crafting visual roadmaps portraying routines, calls, and sources crisscrossing method.
Overall process modeling sets enterprises up aptly—a springboard fueling businesses well-outfitted for high-paced, unpredictable climates through opportunistic scrutiny and recalibration.
Key Highlights
- Organizations leverage visual mapping to represent inner workings.
- This involves crafting diagrams outlining routines, sequences, and resource routes.
- Visualizing processes lets firms scrutinize and refine for optimized productivity.
- Crucial for process management, which targets techniques’ non-stop amelioration.
- Automation and digitization too depend on such cartography.
- Diverse modeling techniques/utilities/standards exist, and each fitting needs.
- Modeling enhances comprehension while decluttering workflows, cutting expenditures, and bettering client experience.
- Overall it charts enterprises optimized navigating transformation through empirical observation and calibration.
What is Process Modeling?
Drawing pictures of how work gets done in a business helps make processes better. This is called process modeling. It maps out the steps, choices, people roles, and info flows needed in a routine.
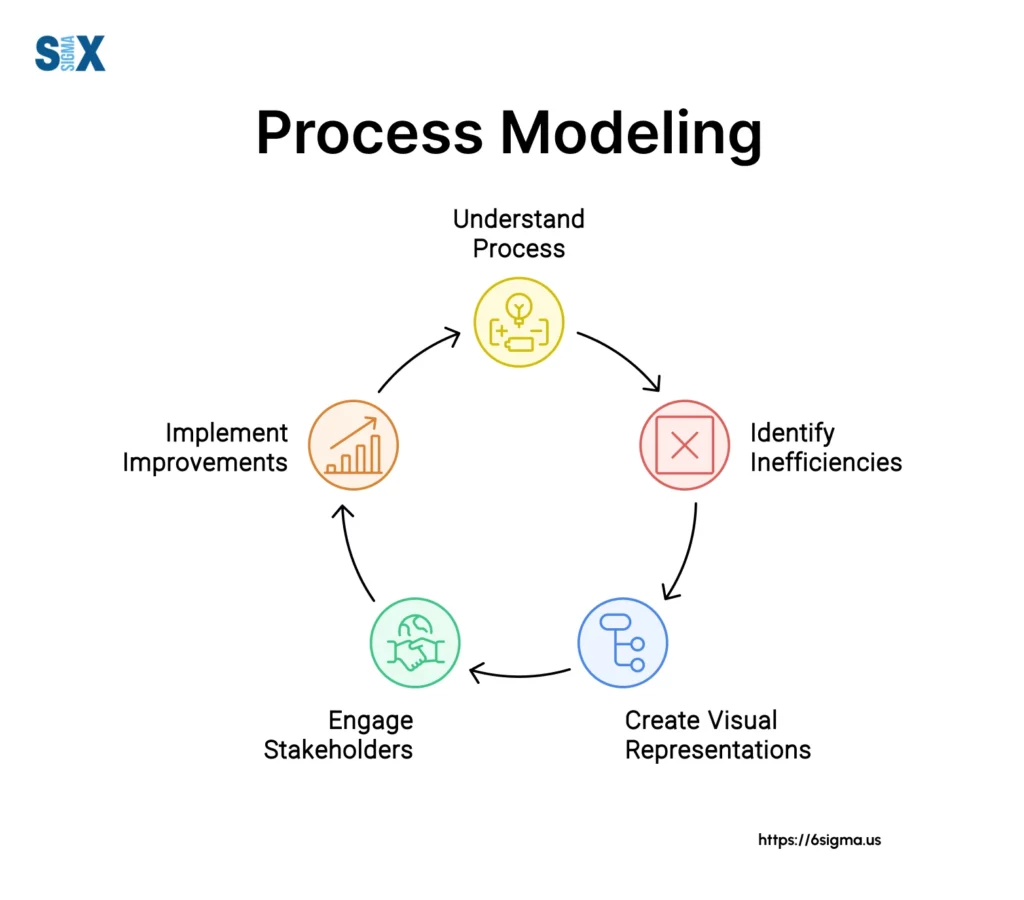
Modeling shows how tasks link together from start to finish. It helps understand, document and explain to others what work involves.
Pictures help find trouble spots and chances to streamline work. They act as blueprints to make changes, automation or tie tech together better. For those seeking to enhance their ability to identify and address these inefficiencies, enroll in our six sigma certification and training program, and equip yourselves with valuable methodologies and tools.
Different types help like BPMN maps using standard symbols or basic flowcharts.
First, decide what routine needs modeling. Then gather details from experts and records. Draw pictures mapping the process flow.
Review with others and tweak based on feedback. Finally, use maps to put changes into practice or integrate new tools.
Continually check maps align with reality. Tweak if needed since processes evolve over time.
By keeping models aligned with reality, organizations optimize to run efficiently, and fresh ideas surface for even better work customs. It helps them progress together with transforming landscapes.
For teams aiming to systematize these efforts, combining process modeling with programs like our Six Sigma certification can standardize problem-solving frameworks across departments.
Process Modeling Techniques
There are several widely used techniques and notations. The most common and standardized approach is Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN). BPMN provides a graphical notation for specifying business processes in a workflow. It uses standardized symbols and diagrams that are easy to understand for all stakeholders involved.
Another popular technique is Unified Modeling Language (UML) Activity Diagrams. UML is a general-purpose modeling language with Activity Diagrams focused specifically on defining the sequence and conditions for coordinating processes and process flows.
Other techniques include:
- Flowcharting – One of the earliest techniques using basic shapes and arrows to map out process steps and sequence.
- Value Stream Mapping – This lean technique maps the flow of processes involved in delivering a product/service to identify waste and areas for improvement. Understanding the fundamentals of Lean can enhance the ability to apply this technique effectively.
- Process mapping/workflow modeling – Creating a visual model and documentation of the sequence of tasks, activities, roles, inputs/outputs within a process.
- Swimlane diagrams – Developed for visualizing cross-functional processes by assigning roles or responsibilities to each swimlane.
The choice of process modeling technique depends on factors like the complexity of processes, purpose, stakeholder familiarity, and integrations with other process management tools. Many organizations use a combination of complementary techniques.
Process Modeling Tools and Software
Once you have chosen the appropriate technique, the next step is to select the right tool or software to create your models.
There are many tools available in the market, ranging from simple diagramming tools to comprehensive business process management (BPM) suites.
Some popular process modeling tools include:
- Lucidchart – An intuitive and user-friendly diagramming tool that supports various notations like BPMN, UML, flowcharts, etc.
- Microsoft Visio – A versatile diagramming and vector graphics application that comes with built-in templates for process modeling using BPMN, flowcharts, and more.
- Bizagi Modeler – A powerful process modeling and documentation tool that uses BPMN notation and integrates with Bizagi’s process automation suite.
- ARIS by Software AG – A comprehensive BPM suite that includes tools for process modeling, analysis, optimization, and execution using various notations like EPC, BPMN, etc.
- IBM Blueworks Live – A cloud-based process modeling and documentation tool that uses BPMN notation and supports collaboration among teams.
When selecting a process modeling tool, consider factors such as:
- Notation support (BPMN, UML, flowcharts, etc.)
- Ease of use and learning curve
- Collaboration and sharing capabilities
- Integration with other systems (e.g., BPM suites, enterprise applications)
- Simulation and analysis features
- Pricing and licensing models
Many tools offer free trials or community editions, allowing you to test them before making a purchase decision. Additionally, some open-source tools like bpmn.io and Camunda Modeler are available for those on a tight budget.
Benefits of Process Modeling
Process modeling offers numerous benefits that can help organizations streamline operations, increase efficiency, and improve overall performance. Here are some key advantages of process modeling:
- Improved Process Understanding: By creating visual representations of processes, process modeling helps everyone involved gain a better understanding of how work flows through the organization. This shared understanding facilitates communication and collaboration across teams and departments.
- Process Standardization: Modeling processes allows organizations to identify and document best practices, leading to greater standardization. This consistency helps reduce errors, improves quality, and ensures processes are executed the same way every time.
- Process Optimization: With a clear visual model, it becomes easier to analyze processes and identify areas for improvement. Bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies can be pinpointed and addressed, through programs like our root cause analysis training, resulting in optimized, streamlined processes.
- Change Management: When processes need to be modified or redesigned, process models serve as a valuable reference point. Stakeholders can evaluate the impact of proposed changes and make informed decisions before implementing them.
- Compliance and Auditing: In regulated industries, process models can help demonstrate compliance with standards, regulations, and industry best practices. They provide a clear audit trail and facilitate compliance monitoring.
- Training and Knowledge Transfer: Visual process models can be used as training materials, helping new employees quickly understand how work is performed within the organization. This aids in knowledge transfer and reduces the learning curve.
- Process Automation: By clearly defining processes, organizations can identify opportunities for automation. Process models provide a foundation for implementing workflow management systems, robotic process automation (RPA), and other automation technologies.
- Performance Measurement: With processes documented, organizations can establish performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). This enables continuous monitoring, analysis, and improvement of process performance.
- Risk Management: Process models help identify potential risks and vulnerabilities within processes. By analyzing these models, organizations can develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans.
- Competitive Advantage: Efficient, optimized processes can lead to cost savings, faster cycle times, and improved customer satisfaction, providing a competitive edge in the market.
By leveraging this, organizations can gain valuable insights, streamline operations, and position themselves for long-term success in an ever-changing business landscape.
Process Modeling Best Practices
Following best practices is crucial for effective process modeling that drives meaningful process improvement and optimization. Here are some key best practices to keep in mind:
Involve Stakeholders Early and Often
Process modeling should not happen in a silo. Engage relevant stakeholders from across the organization early in the modeling efforts.
This includes process owners, subject matter experts, process participants, and leadership. Their input is invaluable for accurately capturing the as-is state and envisioning optimized future processes.
Use an Established Methodology
Rather than an ad-hoc approach, leverage a proven process modeling methodology like Lean, Six Sigma, BPMN or others. This provides a consistent framework, notation standards (business process modeling notation), and governance for your initiatives.
Model for Understanding, Not Documentation
The goal should be developing a clear, comprehensive understanding of processes. Models simply document this understanding in a standardized way. Focus first on truly analyzing and optimizing processes rather than just documenting the current state.
Capture Process Context
Effective process models don’t exist in isolation. They should capture associated process context like inputs, outputs, roles, systems, rules, metrics, and other elements. This context is key for truly optimizing end-to-end processes.
Leverage the Right Process Modeling Tools
There are many modern process modeling software and tools that enable intuitive process visualization, collaboration, simulation, and integration with other platforms. Invest in the right tools to maximize the value of your efforts.
Integrate with Process Execution
For it to truly drive impact, the optimized process designs from modeling should integrate with process automation, monitoring, and continuous improvement efforts. This closed-loop is essential for processes to stay current and optimized over time.
Frameworks such as Six Sigma Green Belt certification emphasize cross-functional collaboration, aligning with best practices for maintaining accurate, actionable process models
Process Modeling Challenges and Solutions
While process modeling offers many benefits, there are some common challenges that organizations face when implementing it:
Challenge 1: Resistance to Change
One of the biggest hurdles is resistance from employees who are used to doing things a certain way. Introducing new processes and having to learn modeling techniques can be disruptive.
The solution is to clearly communicate its benefits and involve employees early in the process to get their buy-in.
Challenge 2: Lack of Standardization
Different departments or business units may have their own way of modeling processes, making it difficult to create an integrated, enterprise-wide view. Establishing company-wide process modeling standards and using consistent notation can help resolve this.
Challenge 3: Complex Processes
Highly complex processes with many stakeholders, decision points, and exceptions can be extremely difficult to accurately model. Breaking down processes into manageable sub-processes and prioritizing the most critical processes to model first can help.
Challenge 4: Keeping Models Updated
Business processes constantly evolve, so process models can become outdated quickly. Implementing a process modeling governance plan with regular reviews and updates is crucial.
Challenge 5: Tool Selection
There are many modeling tools on the market with varying features and capabilities. Carefully evaluating your organization’s specific needs and taking advantage of free trials can help select the right tool.
Future of Process Modeling
Process modeling is continuously evolving to keep pace with the latest technological advancements and changing business needs. Here are some of its key trends and future directions:
Integration with Emerging Technologies
- Process modeling will increasingly integrate with emerging technologies like robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- AI and ML can analyze process data to identify inefficiencies, recommend optimizations, and even automate certain tasks.
- IoT connectivity will enable real-time monitoring and analysis of processes, leading to more accurate and up-to-date process models.
Cloud-Based Process Modeling
- Cloud-based process modeling tools and software will become more prevalent, offering greater accessibility, scalability, and collaboration capabilities.
- Cloud solutions will enable remote teams to work together on these projects seamlessly, regardless of their location.
Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
- Low-code and no-code platforms will gain traction, allowing non-technical users to create and modify process models without extensive coding knowledge.
- These platforms will democratize process modeling, making it more accessible to a broader range of users within organizations.
Simulation and Predictive Analytics
- Process simulation capabilities will become more advanced, enabling organizations to test and optimize processes before implementing them.
- Predictive analytics will be integrated into these tools, helping organizations anticipate potential bottlenecks, risks, and opportunities.
Increased Focus on Process Governance
- As it becomes more widespread, there will be a greater emphasis on process governance to ensure consistency, compliance, and standardization across the organization.
- Process modeling governance frameworks and best practices will be established to maintain the integrity and quality of process models.
Process Mining and Automated Process Discovery
- Process mining techniques will be used to automatically discover and analyze real-world processes based on event log data.
- This will help organizations create accurate and up-to-date process models that reflect the actual processes being executed.
Collaborative and Social Process Modeling
- It will become more collaborative and social, with features like commenting, sharing, and real-time editing to facilitate team collaboration.
- Social process modeling will encourage user participation, feedback, and continuous improvement of process models.
As process modeling continues to evolve, organizations that embrace these trends and leverage the latest technologies and methodologies will gain a competitive advantage by optimizing their processes, increasing efficiency, and driving business growth.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






